Causes of the disease
The causes of urticaria in children are:
- sensitivity to allergens;
- consumption of allergens in food, their inhalation;
- taking certain medications;
- bites of some insects;
- tactile contact with the allergen (urticaria in a child may appear after sleep due to a reaction to the dye in the bedding fabric or washing powder). Source: L.V. Luss Causes and treatment of urticaria in children, swelling in children // Medical Council, 2015, No. 14
Upon contact with an allergen, inflammation occurs, fluid accumulates in the body tissues, and a rash and swelling appear. This reaction of the body is an attempt to reduce the amount of harmful substances.
Chronic urticaria, which can appear as early as one year of age, occurs due to:
- chronic or long-term gastrointestinal diseases;
- chronic inflammation;
- viral infections;
- parasite infestation;
- fungal diseases;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system;
- hereditary predisposition.
The disease can be provoked by overheating or hypothermia of the skin, exposure to UV or water, when combing or injury by elements of clothing, due to severe stress. With such urticaria (it is called “cholinergic”), children do not have an elevated body temperature, and external manifestations quickly disappear (in a few minutes, maximum half an hour). Source: I.I. Balabolkin. Urticaria in children: clinical and pathogenetic variants, diagnosis and treatment // Russian Pediatric Journal, 2022, 20(2)
Types of allergic urticaria
Hives can be acute or chronic.
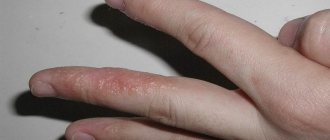
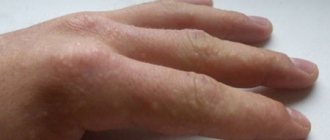
Acute allergy with urticaria is the most common type. Symptoms last less than 6 weeks and usually occur in allergic urticaria on the face and neck, fingers and toes. In the acute type, the allergen is usually immediately clear.
Chronic urticaria in adults lasts more than 6 weeks. Most often, it is an idiopathic form of urticaria of unknown origin that can last for months or years. On the skin, allergies with this type of urticaria occur in completely different places.
Diagnostic methods
When this disease develops, the patient or his parents are interviewed and the symptoms are analyzed.
The doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis after examining the child’s skin. A rash with urticaria is difficult to confuse with another. However, to exclude errors and establish the cause, tests are prescribed:
- stool analysis, which will help identify parasites - they can be pathogens;
- general blood test - identifies or excludes inflammatory and immune processes;
- allergy tests - skin tests to identify the pathogen;
- liver tests - to determine liver function and exclude its pathologies.
Thyroid function may be tested because the disease can be caused by hypo- or hyperthyroidism.
How to treat other forms of pemphigus?
The treatment process for pemphigus is quite complicated. Therefore, self-medication of this type of disease is under no circumstances acceptable. The disease progresses rapidly, affecting large areas of the skin, which leads to disruption of the internal organs.
Treatment of pemphigus is mandatory in a dermatological hospital. First of all, corticosteroid drugs, cytostatics and other drugs are prescribed to alleviate the course of the disease and the life expectancy of patients.
The drugs must first be taken in large doses. At the same time, pay attention to blood and urine sugar levels, monitor blood pressure and observe personal hygiene rules. With frequent changes of bed linen and underwear, secondary infection is prevented.
Types of disease
In medicine, there are five main forms of this disease:
- chronic with periodic exacerbations;
- acute, arising and spreading rapidly;
- allergic (affects 70% of children);
- pseudo-allergic (provoked by disturbances in the functioning of the liver and digestive organs);
- hereditary non-allergic (accompanied by Quincke's edema, similar to allergic). Source: L.P. Sizyakina, A.A. Lebedenko, C.B. Maltsev, A.N. Posevina, L.A. Averkina Urticaria in children: a modern view of the problem // Medical Bulletin of the South of Russia, Reviews, 2015
Let's take a closer look at the types of urticaria, depending on the triggering factor:
- Medicinal. A type of drug allergy is a reaction to certain drugs. The most common provocateurs are iodides, streptomycin, sedatives, NSAIDs, and drugs containing gold. The rash may be accompanied by a runny nose, conjunctivitis and bronchial asthma. To cure this form of urticaria, you need to eliminate the allergen, adjust the diet, removing the brightest allergens from it - citrus fruits, red vegetables and fruits, nuts, cow's milk, fish.
- Mechanical – appears when pressure is applied to the skin. Its causes have not been reliably studied, but the disease is associated with skin sensitivity, heredity and the condition of the blood vessels. Divided into several subspecies:
- dermographic – develops quickly due to friction or pressure, often caused by wearing tight clothing;
- cold - a reaction to contact with something cold, drinks or foods;
- heat – the rash appears when the environment is hot;
- solar - occurs during prolonged exposure to the sun, manifested by swelling and red spots on the skin;
- aquagenic - rare, but very dangerous, appears upon any contact with water;
- papular - the result of an insect bite;
- cholinergic - a rash appears when the child is nervous and sweats a lot.
- Generalized. It differs in that the rash spreads throughout the body, including the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, which makes breathing difficult. Quincke's edema may develop. Such urticaria appears in children with atopic diseases and can be caused by antibiotics and NSAIDs. Rarely are food products allergens.
- Idiopathic. The cause is unknown, but itchy blisters appear regularly over a period of 6 weeks at varying intervals. The process is considered chronic. Spontaneous occurrence and the lack of diagnostic methods make it difficult to control the course of the disease, treatment and prevention.
Symptoms
Considering that experts have identified several different types of this pathology, the symptoms of each of them will be very specific. Of course, there are a number of general trends and signs inherent in all types of the disease. This may include, for example, the wave-like course of the pathological process.
Periods of exacerbation alternate with the transition of pemphigus to a calmer stage, when the main symptoms subside or completely disappear. An important factor for the patient will be the fact that in the absence of timely diagnosis and prescription of an effective course of treatment, there is a high risk of developing severe conditions aggravated by concomitant diseases.
- The presence of crusts, ranging from pale pink soft to red dense, reminiscent of lichen;
- There is a deterioration in the general condition;
- Decreased immune response of the body;
- Formation of bubbles of varying densities;
- Also, in severe cases, separation of the layers of the epidermis is noted, and it can occur both in the lesion and away from it.
- Damage and ulcers of the mucous membrane of the mouth, nasopharynx or genitals;
- Pain when performing the act of swallowing or when eating;
- Bad breath, indicating damage to the mucous membranes;
- Hypersalivation or, in other words, increased salivation;
- In the seborrheic form, characteristic yellowish or brown-brown crusts appear on the scalp.
- Bubbles vary in appearance, ranging from flat to thin-walled, which burst with a slight touch. In their place, erosions and, subsequently, crusts form.
- In severe cases, an eroded surface of the skin may form in place of the blisters. Their feature is a tendency towards peripheral growth. Over time, such erosions occupy a large surface of the skin, causing pain and inconvenience to the patient.
- In children, manifestations of pemphigus are localized over the entire surface of the skin, including the limbs.
Experts say that with this disease, both a pure form of the pathological process and mixed forms that smoothly transform into one another can be observed. Therefore, the symptoms and signs of pemphigus in a given person may vary and indicate the presence of several types of disease.
Treatment methods for urticaria in children
This disease should be treated depending on its form. The pseudoallergic variety requires examination for the underlying disease. Allergic – allergen exclusion and immunotherapy.
In the acute period:
- eliminate contact with the allergen;
- the child is prescribed a hypoallergenic diet for several days;
- remove the allergen from the body, prescribe plenty of fluids;
- use sorbents and antihistamines (types and dosage regimen are determined only with a doctor);
- for severe swelling, a specialist may prescribe a diuretic;
- Prescribe antipruritic ointments for the arms, legs, or other areas of the child’s body that are prone to hives.
Parents should carefully monitor the cleanliness of the house and promptly wash clothes and bedding with hypoallergenic products.
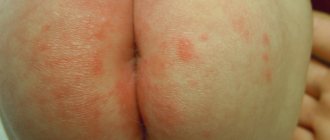
What do allergic rashes look like?
There are a large number of types of allergy rashes in children, it all depends on the irritant that caused it. In many cases, exanthemas appear on the child’s body (this is the name given to various manifestations of allergic rashes):
- pustules (filled with pus);
- plaques;
- spots;
- vesicles (filled with liquid);
- blisters (large vesicles larger than 0.5 cm).
With food allergies in children, the rash can be found primarily on the cheeks and near the mouth. With a contact allergy, a rash or irritation will appear in the area where the allergen touched. If the child’s body reacts negatively to medications, inflammation will appear in the area of the lymph nodes.
Are there any complications?
Acute urticaria in children can have a dangerous complication - Quincke's edema (giant urticaria, angioedema). It consists of swelling of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. The child has coughing attacks and has difficulty breathing. Very young children may experience swelling of the gastrointestinal mucosa (the reaction to this is vomiting). In severe cases, the membranes of the brain and nervous system are affected. Any of these conditions is very dangerous and can be fatal. Therefore, it is very important not to delay visiting a doctor if there are signs of illness.
Important! Many parents do not know what to do with Quincke's edema. You should immediately give your child an antihistamine (any one from your home medicine cabinet) and call emergency medical help.
Treatment of streptoderma
Even if the initial examination was carried out by a pediatrician, a dermatologist should prescribe treatment for streptoderma in children.
A specialist in this profile is aware of narrow-spectrum drugs that will help to quickly cope with the disease. The first step is to transfer the child to a therapeutic diet with restrictions on sweets, fatty and salty foods. The course of therapy involves avoiding bathing: water procedures contribute to the spread of the disease. It is recommended to wash healthy areas with chamomile decoction, and never touch inflamed areas.
It is important to choose the right clothes for a sick child. Synthetic and wool items should be excluded from your wardrobe. These tissues cause discomfort and contribute to the spread of the disease.
Doctors recommend opening the blisters that form on the skin with a sterile needle, then treating the opening erosions with brilliant green 2 times a day. Areas of skin not infected with bacteria are wiped with a boron solution. Weeping erosions are lubricated with silver nitrate or resorcinol.
If crusts form on the skin, they are treated with antibacterial gels or ointments.
In severe cases, a number of other oral medications are prescribed:
- antibiotics of the tetracycline or chloramphenicol series;
- anti-allergy medications;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamin complexes;
- antipyretic drugs.
The list of medications must be agreed upon with your doctor. Only a specialist knows how to treat streptoderma in children correctly. Self-medication can provoke the pathology to become chronic. With an adequate course of therapy, the symptoms disappear after 7 days, but after curing the deep form of the pathology, scars remain on the skin. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor as early as possible.
Disease prevention methods
There are no special preventive measures. However, you can minimize the risk of developing the disease by following these recommendations:
- control the child’s diet;
- exclude contacts with potential allergens - food, volatile, contact;
- have an antihistamine in your home medicine cabinet;
- buy your child loose clothes made from natural fabrics;
- do not provoke stress in the child;
- do not trigger chronic diseases.
Sources:
L.V. Luss. Causes and treatment of urticaria in children // Medical Council, 2015, No. 14
I.I. Balabolkin. Urticaria in children: clinical and pathogenetic variants, diagnosis and treatment // Russian Pediatric Journal, 2022, 20(2)
L.P. Sizyakina, A.A. Lebedenko, C.B. Maltsev, A.N. Posevina, L.A. Averkin. Urticaria in children: a modern view of the problem // Medical Bulletin of the South of Russia, Reviews, 2015
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Watery formations on the skin
Watery pimples are scientifically called vesicles. This is when a pimple appears on the skin with clear liquid inside. There can be one or many pimples. Pimples can merge into groups or be at a distance from each other. The location can be any: on the skin of the whole body and on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, on the scalp, only on the lips, or only in the form of an isolated lesion of a segment on the skin like a twig, strewn with such pimples. The pimple itself, with clear liquid inside, may or may not have a light red rim on the skin at the base of the watery vesicle. There may also be a slight depression in the center of the watery pimple or none at all. Doctors call this an umbilical indentation.
The size of a watery pimple can vary from small to large. After the appearance of a pimple, its further development occurs. The watery blister may burst instantly and become crusty or wet. It can also have dense walls and not open for a long time. And sometimes the transparent contents are replaced by cloudy and purulent ones.
Pimples can cause severe pain at the site of the rash, a feeling of fullness and itching. There may also be changes in body temperature, runny nose, sore throat and general malaise. Or maybe none of this will happen.
So what do these many-sided watery pimples mean? What will a pediatrician, dermatologist or therapist say with each variant of the appearance of a pimple with watery contents and with its subsequent transformations? What causes such diverse types of pimples filled with clear liquid?
This can occur with allergies, with purulent skin infections, with herpes infections in the form of herpes types 1 and 2, and with herpes called varicella zoster.
All these reasons have different clinical manifestations. And only on the basis of the totality of clinical manifestations will a dermatologist or pediatrician make a diagnosis. But to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will suggest taking tests. This may be a study of the contents of the bladder in the form of PCR for viruses or culture for flora, a blood test for the presence of antibodies for viruses or infectious diseases.
And, of course, treatment directly depends on the diagnosis and tests.
If the diagnosis is “herpes simplex”, or “genital herpes”, or “shingles”, then the doctor has many effective antiherpetic drugs in his arsenal. These include ointments, tablets, syrups, and solutions for administration both intravenously and intramuscularly. The doctor may prescribe medications to correct the immune system. Your doctor may also recommend vaccines for herpes simplex and chickenpox. The fact is that the chickenpox and shingles viruses have the same origin and name, varicella zoster. And those who have suffered from live varicella zoster virus, have had chickenpox, remain carriers of the varicella zoster virus in the nervous ganglia for life. Only it is dormant and, under adverse influences, can be activated and cause an unpleasant disease in the form of shingles.
Well, what if the diagnosis is “chickenpox”? For chickenpox herpes, the doctor will prescribe treatment for pimples and isolate the patient for 11 days from the moment of the rash. By the way, it is better for contact people to receive the chickenpox vaccine within 72 hours after contact with chickenpox to avoid getting sick.
What if it's a skin infection? Doctors call this skin infection pyoderma. In the case of a purulent lesion, the doctor will prescribe local ointments and solutions and decide on the need for antibiotic therapy depending on the situation.
Well, what if it’s an allergy that manifests itself this way? For allergies in the form of eczema or other manifestations, local treatment with ointments and solutions with antiallergic properties is indicated. Everything necessary will be prescribed by the doctor based on the individual characteristics of the disease. The doctor will also prescribe a diet and medications that cleanse the body of allergens and toxic substances and prevent the development of allergies.
The main thing is not to let the situation get worse and consult a doctor in time (at the earliest manifestations of the disease).
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an allergist-immunologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) - maintenance course (excluding the cost of the drug) | 8100 rub. |