This article uses excerpts from the chapter of the same name in the Face Anatomy atlas. It is of particular importance for specialists involved in the correction of age-related changes and contouring using fillers. The title “Dangerous triangle of the face” was not chosen by chance; it is in this zone that there are prerequisites of an anatomical and functional nature that can interfere with medical manipulation and cause side effects, including severe ones. Let's look at the topography of this triangle and the reasons for its danger.
Introduction
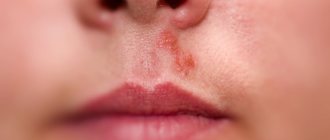
So, a dangerous triangle of the face. We can describe this zone in this way: the apex of the triangle is located in the glabella area, its legs enclose the nasolabial folds and reach the base, which is located under the lower lip [Fig. 1].
Rice. 1. Dangerous triangle of the face.
The area within this zone is often corrected with filler: just think about glabellar lines, nasal hump correction, nasolabial folds and lip remodeling. The anatomical feature, or originality of this zone, which makes it so “insidious”, lies in its blood supply and especially in the topography of the arteries.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the specific pathological process. Let's look at the problems in order with possible solutions:
- Heart defects. The operation is indicated. Plastic or prosthetics. For example, replacing a valve with an artificial one. There are no other options.
- Myocardial inflammation. Antibiotics and beta blockers are prescribed to relieve rhythm disturbances. If necessary, use cardioprotectors (for example, Mildronate).
- Functional deviations from cardiac structures. Protective agents (Riboxin and analogues), antiarrhythmics, and beta blockers are indicated as support measures.
- Coronary insufficiency. The same drugs are used. Plus, you need to find the root cause and eliminate it.
- Heart attack. The list is the same. Additionally, organic nitrates (not always), vitamins are used, and intravenous infusions of solutions are performed.
- Asthma. Bronchodilators (Berodual and similar), inhaled corticosteroids, oral hormones (Prednisolone and others), first and third generation antihistamines (Cetrin, Suprastin, Tavegil).
- Inflammation of the respiratory tract. Antibiotics, antivirals, hormonal drugs and similar.
- Respiratory failure. Glucocorticoids, bronchodilators. They look for the primary cause and carry out correction. In extreme cases, the patient is connected to a ventilator.
- Anemia. Iron supplements, B vitamins, also need to eliminate the cause of insufficient absorption of nutrients.
- Poisoning. Detoxification measures, introduction of antidotes. The correction is carried out in the hospital.
- Atherosclerosis. Statins, fibrates, nicotinic acid, special diet, giving up bad habits.
- Thrombosis. Antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, also thrombolytics.
- Drug addiction and alcoholism. Detoxification measures, coding, rehabilitation.
- Infections. Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, antipyretics, as well as antiviral and immunomodulators are prescribed.
There are a lot of options. The strategy needs to be developed individually.
Triangle and arteries
One of the main arteries in this area is the facial artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. The facial artery, immediately after its origin, goes upward and passes to the face in front of the masticatory muscle, where its pulsation can be determined by palpation. Next, it is directed medially and towards the lips, giving off branches - the superior and inferior labial arteries, then passes under the muscle that lifts the upper lip, and reaches the wing of the nose, where its course becomes superficial and ends with two terminal branches - the arteries of the wing of the nose and the angular . Up to this point, everything is clear and clear, but in reality this is not always the case [Fig. 2].
Rice. 2. Facial artery - angular artery.
I will explain more clearly: there are many works with cadavers that emphasize the fact of the existence of frequently encountered anatomical variations and the place of origin of the facial artery, the course of this vessel and its branches. Often such variations are more the norm than the exception. Therefore, it can be argued that even with in-depth knowledge of anatomy, there is a possibility of complications due to the abnormal arrangement of blood vessels. Therefore, it is necessary to use techniques that help to avoid possible side effects as much as possible.
Historical reference
To many, it seems far from them (or even a medical exaggeration) the situation when you can die due to damage in the area of the nasolabial triangle. In fact, history knows many examples when people died almost instantly. For example, the composer Scriabin . He was in England on tour when he developed a boil on his upper lip. Its appearance was accompanied by fever, headache and intoxication. Measures in the form of bandages with a special ointment seemed to have yielded results.
But almost a year later, when the composer had a small boil again, he simply tore it off with his hands. And after a while he felt bad. An ordinary pimple led to swelling, an increase in temperature to 40 degrees, and the development of infiltration. The composer developed a carbuncle. With such a pathology, fatal blood poisoning often developed. The composer's condition rapidly deteriorated, and pleurisy began. As a result, 7 days after he felt unwell, and a little less than two weeks after he accidentally popped a pimple on his face, Scriabin died.
There are many other examples of how intervention in such a controversial and sensitive area has caused serious health problems and deaths.
Possible side effects
Basically, complications arise not so much due to rupture of a venous vessel, but due to interruption of arterial blood flow due to compression or when the drug is administered into the lumen of the vessel with subsequent embolization of the terminal branches with small fragments [Fig. 3].
Rice. 3. Reasons for the development of skin necrosis. Intravasal injection (top), vessel compression (bottom).
What could happen next? Stopping arterial flow leads to necrosis and tissue death in the blood supply zone of a given vessel. Cases of necrosis of the skin of the wing and tip of the nose, lip tissue and glabella area have been described [Fig. 4–5].
Rice. 4. Necrosis of the tip or wing of the nose.
Rice. 5. Zones of necrosis.
An even more serious risk factor is associated with the fact that the facial artery represents the communication between the external and internal carotid arteries. Its terminal branch, the angular artery, anastomoses with the ophthalmic artery, a branch of the internal carotid artery. It is this connection between the vessels that can lead to embolization of the ophthalmic artery with small fragments of filler and further penetration into the central retinal artery with a possible decrease in vision up to blindness [Fig. 6–7].
Rice. 6. Iatrogenic retinal artery occlusion caused by the injection of fillers.
Rice. 7. Microembolism of the ophthalmic artery: etiopathogenesis.
Development mechanism
The pathogenesis of the pathological process is based on a group of factors. If we talk about them in a generalized format:
Breathing problems
They are especially common. In this case, the oxygen concentration itself decreases. During biochemical processes, carbon dioxide is released into the riverbed. This is a harmful, waste product. It needs to be brought out faster.
And this is where the problem arises. Not only are the lungs unable to deliver enough oxygen, but they are also unable to eliminate harmful gases that are toxic to the body.
The concentration grows, poisoning of all tissues and systems of the body begins. Need urgent medical attention.
Cardiovascular disorders
Another common factor in the development of the pathological process. There are a lot of diseases that cause cyanosis. Often we are talking about heart defects and functional disorders.
It makes sense to check this part with a cardiologist. The mechanism is based on a violation of blood transfer, its stagnation in the large and small circles.
Hence dysfunctional disorders. The heavier they are, the worse the situation is overall.
Blood abnormalities
In some cases, red blood cells themselves are not able to combine normally with oxygen and form full-fledged hemoglobin. This leads to the accumulation of carbon dioxide, which begins to poison the patient's entire body.
As a rule, the problem is acquired, but there are congenital types of the disorder.
It is necessary to approach the diagnosis carefully. A hematologist works with patients of this profile.
Endocrine disorders
Deviations from hormonal levels. They are extremely common. In this case, the tissues themselves are unable to normally receive and absorb oxygen. They produce carbon dioxide as usual.
The concentration of carboxyhemoglobin increases several times. Cyanosis is pronounced and clearly visible. Treatment is very difficult.
Intoxication processes
In case of poisoning with salts of heavy metals, vapors of acids and volatile compounds, cellular respiration is disrupted. Rapid ischemic processes occur that pose a danger to life and health. Urgent inpatient correction is needed.
These are the basic mechanisms of the problem. Typically they occur individually and not as a system. There are exceptions to what has been said.
Therapeutic strategies to prevent and manage complications
It is obvious that it is necessary to use techniques that minimize the risk of developing these dangerous complications. The text of the atlas describes, area by area, all the precautions and manipulations that must be taken to reduce this risk: the use of a cannula, the depth of injection, the quantity and quality of filler injected, and so on. Pallor of the skin and patient complaints of sudden pain in the injection area are signs that blood flow has stopped in this area. We must be able to control this situation.
All measures are aimed at restoring blood flow: urgent dissolution of the filler (if hyaluronic acid was used), warm compresses, massage, etc. Then there are prescriptions that need to be followed at home: antibiotic therapy to prevent bacterial superinfection, antiplatelet agents, topical medications.
In the introduction to the atlas I placed the inscription
“Only non-practitioners do not make mistakes; only through practice does it become possible to reduce the risk of error.”
If all measures are carried out on time and correctly, the spread of the necrosis zone will be minimal, a large area of skin will be preserved and, therefore, the chance of restitutio ad integrum will be higher.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out under the supervision of cardiologists, pulmonologists and therapists. Subspecialty doctors are hired as needed.
A sample list of events would be:
- Questioning the patient about complaints and symptoms of the pathological process.
- Taking a history to better understand the origin of the disorder.
- ECG, ECHO-Kg. In order to investigate the condition of the heart. Anatomical (structural) and functional, detect defects and other disorders.
- Spirometry. Function of external respiration. To assess the condition of the pulmonary structures.
- General blood tests, biochemical, hormone tests. An expanded picture of lipids (lipid profile) is also needed.
- Allergy tests.
- Serological studies, bacteriological cultures, PCR, ELISA and other methods.
The question is put to rest by a specialized specialist or a group of doctors.