Acne: definition - characteristic causes
Acne is a common acne skin condition.
To determine an effective treatment method, you need to contact a dermatologist. The reasons for its formation are being clarified by scientists. Inflammatory process of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. Human skin consists of 3 layers:
- epidermis;
- dermis;
- hypodermis, characterized by subcutaneous fat.
Reference: the epidermis contains several layers: the upper one is the horny layer. Contains an abundance of dead cells, organizing a protective function against negative effects.
The dermis is the key slot of the skin. Contains microelements and microorganisms that support cell vital activity. Contains nerve endings and blood vessels. Produced by fibroblasts. It contains sebaceous and sweat glands, an abundance of hair follicles.
Hypodermis - contains an abundance of connective tissue of loose consistency, fat cells. Characterized by different thicknesses - determined by location on the human body, the presence or absence of a balanced diet.
Of increased interest to patients and dermatologists are:
- sebaceous glands;
- appendages.
The sebaceous glands produce natural subcutaneous sebum. Adds shine - in the frontal area, in the area of the nose, chin. A type of gland is hormone-dependent. Production under close control:
- hypothalamus;
- pituitary;
- adrenal cortex, gonads.
Help: every hormonal imbalance is the cause of the rapid production of subcutaneous sebum by the sebaceous glands.
Seborrhea is a type of skin with increased activity of the sebaceous glands. Clinical manifestations boil down to rapid expansion of the pores and an increased level of blockage of comedones. Additionally: oily, dry exfoliation of damaged cells, increased greasiness of the scalp.
Inflammation makes changes in composition. Clinical trials reveal excess androgens and decreased estrogen levels. The structure of subcutaneous sebum reduces the production of linolenic acid. An increase in the alkaline level of the subcutaneous layer, failure of protective reactions, rapid proliferation of harmful microorganisms.
Acne: definition - characteristic causes
Causes of acne
Acne affects all age groups, affecting 85% of adolescents and 12% of adult women.
The leading role in pathogenesis is played by:
- hyperkeratinization of the hair follicle (the duct becomes clogged with excess skin cells exfoliated);
- microbial colonization of Cutibacterium (Propionobacteria) acne (normal microflora of human skin);
- excess production of sebum (sebum);
- complex of inflammatory mechanisms.
Neuroendocrine factors (hormonal) and genetic predisposition also play a role in the development of acne.
Acne development
Changes in microflora are common causes of the development of the inflammatory process of acne. Clinical studies indicate an increased volume of anaerobic lipophilic bacteria, micrococci, and gram-positive rods. Inflammation involving several microorganisms:
- corynobacteria;
- cocci;
- lipophilic fungi.
The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes play a role in the development of the inflammatory process, the rapid spread of acne, and the formation of lipase. The enzyme damages the structure of the follicle walls from the inside. The immune system is not excluded. A decrease in functions is the formation of a favorable atmosphere for the proliferation of harmful microorganisms. The patient's hormonal status is the cause of acne. Hyperandrogenism is an increase in the volume of male sex hormones.
The sebaceous glands have receptors with increased sensitivity to androgens. With an increased volume of hormone production, the organ actively begins to develop subcutaneous fat. Hereditary factor is an additional reason for the rapid development of acne.
Other development factors
Etiological factors are common endogenous causes of pathology formation, with internal natural penetration. The exogenous basis for development is considered to be prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. The active stage of insolation of the immune system of the skin is reduced - the formation of a favorable atmosphere for the proliferation of harmful bacteria.
Active participation in fitness and gyms is one of the common reasons. Bodybuilders are a vulnerable group. Eating high-calorie foods while taking anabolic agents that produce testosterone increases the risk of developing acne. Use as prescribed by treating specialists - dermatologists, cosmetologists. Increased activity of the sebaceous glands among men and women leads to the rapid development of pathology.
There are different forms of development of chronic disease - from severe acne to conglobate forms. Among women - deterioration in the functioning of the vocal apparatus, in men - male-type hair growth, decreased menstruation. Laboratory studies indicate a decrease in the concentration of sperm in the seminal fluid. Comprehensive medical treatment - refusal of testosterone, anabolic steroids.
Newborn acne
Research indicates that 25% of newborns suffer from acne. In infants, inflammation is characterized by the formation of papules on the cheeks, closed types of comedones. The occurrence is explained by a hormonal crisis, an excessive amount of testosterone secretion. The crisis with a decrease in esterol in the blood is the first week of life.
The disease occurs when glucocorticosteroids are used in the last trimester of pregnancy. There is no complex treatment - it goes away naturally in 2 weeks. No scar formation is observed. Manifestation of symptoms with consultation of a doctor.
ACNE: pathogenesis and modern treatment methods
Acne is one of the most common skin diseases in the practice of a dermatologist. The onset of the disease usually manifests itself in girls aged 12 to 14 years, in boys - at 14–15 years. At this age, two variants of the course of the disease are possible - “physiological” acne and “clinical” acne, observed in 15% of patients who require treatment. 7% of patients may develop late acne, occurring after 40 years [1, 3, 5].
Acne is often one of the complications of oily or mixed forms of seborrhea. In a significant proportion of patients, acne is prone to a chronic course, frequent relapses, and is often resistant to therapy.
Pathomorphologically, acne vulgaris is a purulent inflammation of the sebaceous gland and periglandular tissue. It is customary to distinguish several clinical varieties of this disease. Milder and relatively favorable forms include vulgar or juvenile, papular and pustular acne. They are easier to treat and usually do not leave behind gross scar changes on the skin. On the contrary, indurative, confluent, phlegmonous and conglobate acne, due to resistance to therapy, frequent relapses and the occurrence of gross cosmetic defects in these forms, pose a complex medical and socio-psychological problem for the doctor and the patient [3].
Psychoemotional disorders are detected in 40–50% of patients with acne, the leading one being nosogenic depression of a neurotic level, most often occurring in astheno-anxious and anxious types. The highest frequency of psycho-emotional disorders is observed in acne severity levels II–III, and there is an inverse relationship between the severity of psycho-emotional disorders and the severity and duration of the disease [2].
Therefore, it is important for a practicing physician to have early diagnosis, correct clinical assessment, and timely prescription of effective and safe drugs depending on the clinical form of the disease, which allows one to avoid dysmorphophobia, treatment failures, and improve the quality of life of patients.
The pathogenesis of acne is multifactorial. Today, there are four leading factors in the etiology of the disease: follicular hyperkeratosis, an increase in the number of Propionibacterium acnes, changes in sebum production and inflammation.
The initial stage of the formation of the disease is the appearance of microcomedones, which are subsequently colonized by Propionibacterium acnes. Microcomedones are the result of the development of two processes - hyperproliferation of keratinocytes of the acrocrone of the hair follicle and excess production of sebum, which in combination leads to blockage of the follicle and the formation of open and closed comedones. Keratinocytes are characterized by an increase in tonofilaments and desmosomes, an increased amount of keratins K6 and K16 [9].
Propionibacterium acnes are anaerobic resident representatives of the microflora of human skin, capable of exhibiting their pathogenic properties only under certain conditions. Propionibacterium acnes is involved in the development of inflammation at the site of the disease, promoting the release of chemotactic factors and cytokines, as well as the conversion of sebum triglycerides into free fatty acids.
In the mechanism of acne development, the following components of pathogenesis are important - the relative lack of linoleic acid, the action of androgens and free fatty acids. The production of sebum is greatly influenced by androgens, which begin to enter the skin in large quantities during puberty; growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor and substances that activate the formation of peroxisomes are of particular importance [8].
The targets of sex hormones in the skin are the epidermis, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and fibroblasts. The production of sebum is influenced by hormones of testicular or ovarian (free testosterone) and adrenal (dehydroepiandrosterone, androstenedione) origin. A similar effect is exerted by the precursor of testosterone, estrogens and adrenocorticosteroids - progesterone, which has androgenic and antiestrogenic effects on the secretion of the sebaceous glands. This explains the increase in sebum secretion and increased acne formation during the premenstrual period.
It is important not only to increase the level of androgens, but also to increase the sensitivity of target cells, in particular sebaceous gland cells, to androgens circulating in the blood.
In the pathogenesis of acne, an important role is played by zinc deficiency, which is registered in 80% of patients. Against the background of a zinc deficiency state, the rate of sebum excretion increases, and the severity of the disease correlates with the degree of zinc reduction in the patient’s body. Zinc reduces the activity of 5a-reductase, which helps normalize the ratio of hormones and leads to a decrease in sebum secretion.
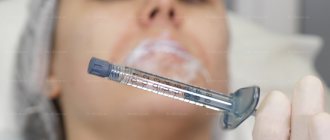
External therapy is the first line of treatment for acne in newborns, children, at the onset of acne and juvenile acne. Prescription of only external therapy is indicated for mild inflammatory and non-inflammatory forms of acne, and non-inflammatory forms of moderate acne. In all other cases, combination therapy with systemic drugs is prescribed.
Drugs for external therapy are prescribed for a long time, the minimum course of treatment is 3 months, after completion of the course it is necessary to prescribe medications for prophylactic purposes to prevent exacerbation of the disease.
In 2002, recommendations and an algorithm for the pathogenetic treatment of various forms of acne were developed (XX World Congress of Dermatology, Paris, 2002), in which topical retinoids . Topical retinoids affect the processes of keratinization (keratinization and desquamation), reduce sebum secretion, increase the proliferation of skin epithelial cells and have a certain anti-inflammatory effect. The most promising is adapalene (Differin), which is well tolerated, has no photosensitizing effect, and is highly effective for comedonal and papulopustular acne [6]. Adapalene is used after cleansing the skin once a day at night, persistent clinical improvement is observed after 3 months, in a maintenance mode the drug is applied 2-3 times a week.
Benzoyl peroxide (Baziron AC, oxy-5, oxy-10) after application to the skin leads to the release of reactive oxygen species, a decrease in the synthesis of free fatty acids and the formation of microcomedones. The drug has a pronounced effect on P. acnes, St. epidermidis, Malassezia furfur and reduces the risk of developing resistance when combined with antibiotics. Benzoyl peroxide is available in the form of a 2.5–10% gel and 5–10% lotion. Benzoyl peroxide is applied to the skin 2-3 times a day for 1-3 months. Side effects of the drug are irritation, especially when using high concentrations, as well as increased photosensitivity due to thinning of the stratum corneum. The drug can bleach hair, so its use is recommended for a combination of acne and hypertrichosis. Contraindication is hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Azelaic acid (skinoren), which has the ability to normalize the processes of follicle keratinization, has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, and can reduce skin pigmentation, is widely used for external treatment The drug is produced in the form of 20% cream and 15% gel. Apply it to the entire surface of the face or other affected areas of the skin in the morning and evening, treatment is continued until a therapeutic effect is achieved. There are no specific contraindications to the drug.
Topical antibiotics. Prescription is indicated for papulopustular acne of mild to moderate severity in combination with topical retinoids or benzoyl peroxide. Among antibiotics for external use, erythromycin, clindamycin, and fusidic acid come first. Monotherapy with local antibiotics will not give the desired effect, since it does not have a sufficient effect on the main pathogenetic factors, except for colonization by P. acnes.
Erythromycin is available in combination with a zinc preparation (Zinerit). The lotion is applied to the skin 2 times a day for 12 weeks. Side effects: dryness, burning, dermatitis.
Clindamycin is available as a 1% gel or lotion, which, when applied to the skin, hydrolyzes in the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands. Despite minimal absorption, the drug can cause gastrointestinal disorders and allergic reactions. Apply the drug 1-2 times a day for 3 months.
Fusidic acid is available for external use in the form of a 2% cream (fucidin), has the ability to penetrate well through intact skin and has a pronounced bactericidal effect [7]. The cream is used 2 times a day for 7 days. There was no systemic effect of the drug and no individual intolerance.
Topical antibiotics are usually well tolerated, and allergic contact dermatitis is rare. Long-term external use of antibiotics can lead to the development of bacterial resistance in P. acnes.
α- hydroxy acids (AHA) - malic, tartaric, citrus, lactic, glycolic - have comedolytic properties. With an ANA concentration of 30–70% (glycolic peeling), treatment is carried out in the morning once a day, and retinoids are prescribed in the evening. Preparations with an acid concentration of 10–15% (exfoliac, cream 10; exfoliac, cream 15) are prescribed to patients with acne daily for 8 weeks. At low concentrations of ANA, drugs are prescribed during the inter-relapse period and for the prevention of acne complications (scarring and pigmentation).
β-hydroxy acids - salicylic acid, resorcinol - affect follicular hyperkeratosis, as they are weak keratolytics and have anti-inflammatory properties. They are used in various dosage forms, most often in solutions (salicylic acid 0.5%–5%, resorcinol 1–3%).
Hyaluronic acid in combination with zinc (curiosin, gel) is used as a prophylactic agent after the resolution of clinical manifestations of acne. Hyaluronic acid promotes the formation of cosmetic scars. The drug is applied 2 times a day until a clinical effect is achieved. Adverse reactions include burning, a feeling of skin tightness, and mild hyperemia, which disappear on their own with continued therapy.
Systemic acne therapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe acne, especially in cases of scarring, dyschromia, or significant psychosocial impairment. Systemic therapy may be necessary if local treatment is intolerant or ineffective.
The most effective drug for the treatment of moderate and severe acne is isotretinoin (Roaccutane) , which, when used systemically, causes long-term remissions or cure in most patients. The drug is a retinoid recommended for systemic use; it affects the processes of differentiation and keratinization of epidermal cells, including the sebaceous glands, and has a pronounced sebostatic and anti-inflammatory effect. The optimal daily dose of isotretinoin is 0.5–1.0 mg per 1 kg of patient body weight. The standard initial therapeutic dose is 0.5 mg/kg. The usual treatment time is 4–8 months. After achieving a pronounced therapeutic effect (usually by the end of the 2nd month), the initial daily dose is reduced (from 1.0 to 0.5 mg/kg; from 0.5 to 0.2–0.3 mg/kg) and used until healing the patient. For phlegmonous and conglobate acne, it is advisable to reduce the daily dose at a later date (3–4 months after the start of treatment) [3].
Roaccutane has a teratogenic effect, which limits its use for women of childbearing age. Before starting treatment, pregnancy must be excluded; patients must use effective contraceptives 1 month before the start of treatment, the entire period of treatment and for 1 month after its cessation.
Adverse reactions when taking roaccutane are diverse and affect various organs and systems (dry skin and mucous membranes, cheilitis, conjunctivitis, nosebleeds, retinoid dermatitis, photosensitivity of the skin, muscle stiffness, hyperostosis, increased activity of transaminases, blood lipids, etc.), in addition to the teratogenic effect other adverse reactions are dose-dependent. Before and during treatment, careful monitoring of the patient's condition is necessary. Patients with renal and liver failure, diabetes mellitus, and a tendency to metabolic disorders (hyperlipidemia) should not receive treatment with this drug.
Systemic antibiotics. The most commonly used are erythromycin and tetracycline. Treatment with antibiotics is carried out for a long time, 6–8 weeks or longer. Doses of 1 g per day are prescribed in cycles of 5–10 days without breaks, but with a decrease in the daily dose in each subsequent cycle by 0.1–0.2 g, gradually bringing the daily dose to 0.1–0.2 g [3 ]. Along with antibiotics, it is necessary to prescribe antifungal drugs for the prevention of candidiasis and zinc preparations (zinc sulfate or oxide 0.02-0.05 - 2-3 times a day after meals). Contraindications for prescribing systemic antibiotics are individual intolerance, pregnancy and breastfeeding, the presence of concomitant fungal infections of the skin and mucous membranes, severe liver and kidney diseases, and leukopenia.
Oral contraceptives (Diane-35) have a pharmacological effect associated with blocking androgen receptors and reducing their endogenous synthesis. As a result, the secretion of the sebaceous glands is inhibited. Diane-35 contains 2 mg of cyproterone acetate and 35 mcg of ethinyl estradiol. The drug is prescribed only to women, from the 5th day of the menstrual cycle, 1 tablet daily for 21 days, then a 7-day break. Contraindications for prescribing the drug are pregnancy and lactation, severe liver diseases, thromboembolic processes, diabetes mellitus, lipid metabolism disorders, hypertension.
According to the degree of influence on the main factors of pathogenesis, the effect of the drugs is manifested in such a way that retinoids are the most effective means for controlling hyperkeratinization of the follicle and preventing the development of microcomedones. To a lesser extent, this process is affected by benzoyl peroxide, azelaic and salicylic acid. In terms of their effect on P. acnes, benzoyl peroxide ranks first, followed by antibiotics and azelaic acid, and to a lesser extent isotretinoin. Retinoids and hormonal drugs help reduce sebum secretion. Modern medications have the least effect on the process of inflammation in the area of acne [8].
None of the modern acne treatment methods can guarantee the absence of relapses of the disease in the future. Therefore, upon achieving clinical recovery, each patient should be recommended a set of therapeutic and preventive measures, which can be divided into recommendations for skin care and general ones.
Among the general recommendations, the most important are the sanitation of foci of chronic infection, examination of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system, and general hardening of the body.
A diet limiting chocolate, coffee, carbohydrates, and alcohol should be recommended in cases where eating these foods leads to increased oiliness of the facial skin and exacerbation of the disease.
The development of acne is not associated with insufficient facial skin care, as patients often believe, starting treatment for the disease with a visit to a cosmetologist. At the same time, daily cleansing procedures of a cosmetic nature are indicated for any severity of the disease. It is recommended to cleanse the skin daily using a variety of cleansers that maintain a neutral or acidic pH of the skin and have an antibacterial effect. The patient should be aware of the need to exclude cosmetics that cause blockage of the sebaceous gland ducts (ointments, fatty creams) and scrubs.
Thus, having a wide selection of products for the treatment of acne and cosmetic products for the care of acne-prone skin, the doctor in the treatment process can move from targeting some mechanisms of pathogenesis to drugs that affect its other components. In this case, the most important thing is regular correction of the prescribed treatment and long-term dynamic follow-up monitoring of the patient, even after achieving clinical remission.
Literature
- Adaskevich V.P. Acne vulgar and pink. - M.: Medical book; N. Novgorod: Publishing house NGMA, 2003. - 160 p.
- Ivanov O. L., Samgin M. A., Monakhov S. A., Lvov A. N. Characteristics and correction of psycho-emotional disorders (PED) in patients with acne // Abstracts of scientific works of the IX All-Russian Congress of Dermatovenerologists. - M., 2005. - T. 1. - P. 90.
- Krivosheev B. N., Ermakov M. N., Krinitsyna Yu. M. Modern methods of treating acne: Method. recommendations. - Novosibirsk, 1997. - 16 p.
- Kungurov N.V., Kokhan M.M. Experience of using azelaic acid 20% (Skinoren) in the treatment of acne // Clinical dermatology and venereology. - 2002. - No. 2. - P. 31-35.
- Masyukova S. A., Akhtyamov S. N. Acne: problem and solution // Consilium medicum. - 2002. - T. 4. - No. 5. - P. 217-223.
- Masyukova S. A., Gladko V. V., Bekmagomaeva Z. A. Experience of using a new topical retinoid - adapalene in the treatment of acne // Clinical dermatology and venereology. - 2002. - No. 2. - P. 36-39.
- Sergeeva I. G., Krinitsyna Yu. M. Experience in the use of fusidic acid preparations in dermatology // I Russian Congress of Dermatologists. - 2003. - T. 1. - P. 112.
- Thiboutot D. Pathogenesis and treatment of acne // 10th Congress EADV. Munich, 2001; 91.
- Wolf JE Increasing the role of retinoids in acne treatment // 10th Congress EADV. - Munich, 2001; 91.
I. G. Sergeeva, Candidate of Medical Sciences Yu. M. Krinitsyna, Doctor of Medical Sciences
Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk
Symptoms
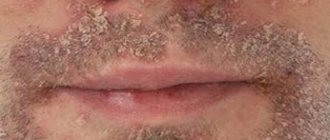
Pathology forms in problem areas where there is an increased volume of sebaceous glands. Visually manifests itself in the form of comedones and milia. Signs of acne:
- increased fat content of hair;
- Friday;
- scar formation;
- spread of painful nodes.
Pathology education:
- Formation of hypersecretion of sebum.
- Rapid increase in sebum.
- Formation of follicular hyperkeratosis. Rapid spread of horny epithelium in the structure of hair follicles. The appearance of blackheads all over the body.
- The active stage of the inflammatory process, characterized by the proliferation of bacteria. The microorganism is a lipophilic anaerobe; clogged areas of hair imply a favorable microclimate for the rapid spread of infection.
Inflammatory process. During the period of active reproduction, the infection actively releases harmful components characterized by reproduction. Inflammation manifests itself in all areas.
Classification
Classification by age category is the optimal solution. Proposed by scientists at an international conference.
| Age | Manifestation |
| Youth | Comedones, papulopustular formations, painful nodes, acne |
| Children | Small tumors, acne, pimples |
| Age category | Late, inverse pathologies, neoplasms, bodybuilding acne |
Acne is a disease caused by exogenous, mechanical factors. Acneform formations:
- comedones;
- papulopustular acne;
- conglobate formations.
Comedonal type formations are signs of the papulopustular stage. The age group of patients is 8+. Increased level of sebaceous glands, oily hair. Formations of microcomedones developing into closed forms. It is characterized by the appearance of white and flesh-colored tubercles. The internal fluid does not cut through.
Papulopustular pathology with increased rates of spread of acne, Fridays. The neglected condition forms the process of scarring in areas of inflammation. Localization is observed on the face, back, and neckline visibility area.
Conglobate manifestations of acne pathology are a complex stage of the disease. Clinical symptoms: the formation of painful neoplasms that rise significantly above the skin level. A common location is the back. When opened, ulcers develop that do not go away for a long time. The rehabilitation period is 2 months, cell regeneration is slow.
Degrees of pathology
Classification of skin abnormalities:
- initial – formation of comedones, small papulopustules;
- medium – painful nodes, papulopustules develop throughout the body;
- complex – the formation of nodular pathologies.
Ignoring complex drug treatment of abnormalities:
- significant expansion of pores;
- development of post-inflammatory pigment spots;
- scarring of damaged areas;
- formation of atheromas;
- manifestation of erythema spots.
Pronounced enlargement of pores is the active stage of production of subcutaneous sebum by the sebaceous glands. Sebum accumulation, significant stretching, wall hypertrophy.
Pigment spots are a violation of the process of pigment formation. Active process of insolation during the inflammatory process. With self-squeezing, causing open injuries on the skin.
Formation of erythema spots. Localization – damaged areas with pimples. Manifestation due to failures of the microcirculation process during inflammatory processes.
Milia. Formation of round capsules with increased sebaceous content. Localization – superficial, under the epidermal film. Often - on the eyelids, near the eyes, temporal region, lower part of the face. There is no inflammatory process. Formation of keratinization problems. The stratum corneum quickly thickens, the sebaceous fluid cannot quickly be released to the surface.
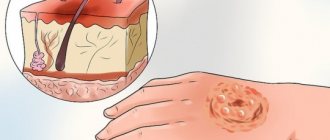
Scar formations are a complex form of deviation. Existing damage to the dermis lobe. Clinical observations: atrophic and keloid scars, severe redness.
Atheromas are a rare side effect with pain. Localization – pronounced subcutaneous tubercle up to 2 centimeters. Black dots in the center of the formation. The destruction of comedones is an opportunity to remove the fluid content. There is no color, there is an unpleasant smell. Development of the inflammatory process with infection of other areas.
Acne: definition - characteristic causes
When to see a doctor
An appointment with a dermatologist is required when primary signs of pathology appear. If there is pain, there is a risk of spreading infection and harmful bacteria.
A comprehensive diagnosis by doctors at a specialized medical clinic determines:
- total number of elements;
- nature of neoplasms;
- location;
- speed of spread;
- duration of the inflammatory process.
Making a diagnosis is a quick way to determine complex drug therapy. A mild form of the disease is the use of medications, vitamin complexes, mechanical facial cleansing, peeling of damaged skin areas.
Peeling – with salicylic and pyruvic acid. Accompanied by mechanical cleaning - at the beginning of treatment the intensity is high. In addition, a set of procedures includes cosmetics and products with active ingredients from well-known manufacturers.
Acne with moderate inflammation – complex systemic clinical therapy. Purpose of laboratory tests: general urine analysis, according to Nechiporenko, blood biochemistry, study of the patient’s hormonal background. As prescribed by a specialist: general and local antibiotics, oral contraceptives with an antiandrogenic effect.
Complications – the doctor of a specialized clinic prescribes medications with active ingredients based on isotretinoin. There are contraindications - women planning pregnancy. Should be used with contraceptive medications.
Diagnosis of papulopustular acne
Only a dermatologist determines the type of acne by making a differential comparison with other types of acne. Also, this type of rash has common symptoms with inflammation of streptococcal and staphylococcal etiology. In addition, hyperpigmentation after the inflammatory process remains not only after a purulent rash, but is also a sign of dermatitis. Post-acne scars must be distinguished from vitiligo.
When diagnosing, the stage of development of the disease is determined:
- mild form, having comedones and up to a dozen papulopustular acne;
- medium - up to 40 eels;
- the severe stage is characterized by a large number of rashes. The disease is complicated by phlegmonous, conglobate or indurative acne. Depending on the form of the disease, a therapeutic course is prescribed.
Proper care
Effective rejuvenation and normalization of water balance. Comprehensive cleaning:
- quickly removes visual scales from the surface, reduces the volume of subcutaneous fat;
- effective exfoliation of dead cells;
- comprehensive disinfection, maximum protection against overdrying and negative effects of external factors.
Cleaning is carried out using medicinal emulsions, solutions, and cosmetic soaps. Intended purpose: for skin characterized by a tendency to form pimples and blackheads. Mandatory absence of alcohol. Ignoring it will quickly damage the pH level and normal microflora inside the body.
The moisturizing effect normalizes water balance and removes excesses from the surface. Application of products based on hydrogel, liquid cream, emulsions. Anti-inflammatory medications and creams will help reduce the total number of comedones and the pronounced inflammatory process.
Treatment of papulopustular acne
First of all, medical prescriptions are aimed at:
- Reducing sebum production;
- Normalization of keratin deposition in epidermal cells;
- Stabilization of microflora;
- Removing the inflammatory process.
At the initial stage of the disease, drugs are prescribed that reduce the hyperkeratotic process, relieve inflammation and have an antibacterial effect:
- Benzoyl peroxide;
- Tretinoin;
- Resorcinol;
- Azelloic acid;
- Clindamycin;
- Salicylic acid;
- Erythromycin, etc.
- The treatment course may include cryotherapy, cryomassage, mesotherapy, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment of papulopustular acne in the moderate and severe stages of development involves general therapy, including:
- Antibiotics. Their selection is made only after bacterial inoculation;
- Synthetic derivatives of vitamin A, which effectively neutralizes the bacterial process. However, these medications can negatively affect the liver, so they should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. In addition, synthetic derivatives are prohibited for use by expectant mothers, due to the ability of the drugs to penetrate the placental barrier;
- Medicines that enhance immunity;
- Antiandrogens that reduce sebum production. They are prescribed only after a hormonal examination.
The full treatment course usually lasts more than one month.
In cases of post-acne scar formation, patients are recommended cosmetic procedures, including laser resurfacing, mechanical peeling, etc.
Recommended Diet
The effectiveness of using a balanced diet is not a scientifically proven phenomenon. Dermatologists and cosmetologists recommend that patients with acne-prone skin:
- completely eliminate whole fat milk and easily digestible carbohydrates;
- limit the intake of sausages as much as possible: boiled, smoked, dry-cured sausage, frankfurters;
- consumption of canned food is prohibited;
- ban on mineral water with high sugar content and food coloring;
- limited consumption of sweets, pastries, cakes;
- Avoid fermented milk products as much as possible: cottage cheese, cheese;
- ban on mayonnaise;
- limited consumption of coffee and strong tea.
Personal balanced nutrition is formed in the presence of problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Prevention of papulopustular acne
In order to prevent the appearance of acne and prevent the development of relapse, it is necessary to include preventive measures in your daily exercise:
- After washing, it is recommended to use special lotions that remove excess oil;
- Protect your facial skin from exposure to aggressive environments by using special creams;
- Stick to a balanced diet. Carbohydrates are known to promote sebum production and promote acne formation.
By following these basic rules, the risk of skin rashes will be minimal.
Acne and tan
Illiterate dermatologists and cosmetologists point to the positive effects of direct sunlight on skin prone to chronic pathology. In practice, this is a misconception. An increased dose of ultraviolet radiation reduces the functioning of the immune system and creates side effects of post-acne. Regular visits to the solarium - the development of the inflammatory process, rapid aging of cells. Risks of detecting malignant tumors.
Regular use of isotretinoin-based medications increases the level of sensitivity to direct sunlight and ultraviolet radiation. Local and general antibiotics have a pronounced phototoxic effect - an inflammatory reaction that entails a number of side effects.