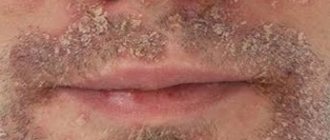
One of the most common problems related to both cosmetology and medicine is peeling skin on the nose.
Characteristic symptoms are:
- Skin hyperemia.
- Itching around the nose.
- Feeling of skin tightness and soreness.
Sometimes it’s enough just to properly care for your skin and properly protect it from drying out. If the problem remains a problem and peeling of the skin on and around the nose continues, you will need to consult a qualified specialist - a cosmetologist or dermatologist.
It is a mistake to think that peeling skin near the nose is the prerogative of those with dry skin. The skin begins to peel off due to the accelerated death of the epidermis, and the disease can be provoked by many reasons, including: vitamin deficiency, runny nose, allergies. The most unpleasant thing is that areas of flaky skin are difficult to hide even with the help of cosmetics and foundations, since they only highlight the existing problem.
Why does the skin peel around the nose?
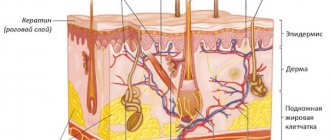
When old cells die and do not have time to exfoliate naturally, light scales appear on the skin, giving a person a sickly appearance. The main cause of dryness is considered to be a violation of the water-fat balance. The pathological process is facilitated by:
- chapping of the face;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- unsuitable cosmetic care products;
- avitaminosis;
- temperature difference;
- chronic fatigue and stress.
Around the nose there are large sebaceous glands that influence the formation of blackheads and pimples. The inflammatory process causes the skin to become red and flaky.
Respiratory diseases cause a negative reaction. Instillation of medicinal drops into the nose and discharge of mucus provoke redness and itching. The person constantly wipes his nose with a handkerchief, increasing irritation. As healing progresses, the affected areas become covered with scales, which gradually disappear.
If irritation and peeling on the nose continues for a long time, do not ignore the problem, but get examined to exclude the development of dangerous diseases. Symptoms may be heralds:
- allergic reaction. The disease manifests itself chronically with a runny nose and lacrimation. There are inflamed areas around the nose that are very itchy;
- seborrheic dermatitis. The pathology is provoked by a fungus that causes excessive oiliness, pimples and red flaky spots on the nose;
- demodicosis. A microscopic mite attacks the sebaceous glands. Swelling and inflamed purple areas form on the face;
- diabetes mellitus The disease disrupts the functioning of internal organs and systems. The imbalance is manifested by itchy skin and flaking on the nose, hands and other parts of the body;
- psoriasis. An autoimmune disease affects healthy epidermal cells. A scaly layer appears on the skin. Psoriatic plaques are located not only around the nose, but also in the scalp, behind the ears, and under the armpits.
Important! The primary task to guarantee successful treatment is to find out why the skin on your face is peeling. Having gotten ahead of the provoking factor, eliminate its harmful influence. If this is not done, you will not be able to completely get rid of the redness.
Answers on questions
Can oil-based vitamins be used to treat flaking?
Oil-based vitamins A and E have a good effect on the skin. However, you cannot apply them yourself to the affected area. Add vitamins to masks or peeling products.
Can autoimmune diseases cause redness?
Autoimmune diseases can cause redness of the skin under the nose, as well as on the cheeks. One of these pathologies is lupus. Another common autoimmune disease is psoriasis. To treat these diseases, immunostimulants are used, which can only be prescribed by a doctor after diagnosis and laboratory tests.
Can diabetes cause peeling?
Peeling skin is often present in diabetes, but is not a mandatory symptom. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to donate blood for sugar. However, along with elevated sugar levels, there may be other causes of peeling, so do not rush to conclusions. Only a doctor can prescribe the final diagnosis and treatment.
What to do to prevent skin from peeling
Peeling can be eliminated with comprehensive preventive measures. Be sure to review your diet and include dishes rich in B vitamins, tocopherol and retinol. Eat more:
- fresh carrots;
- green vegetables;
- sea fish;
- dairy products;
- nuts;
- whole grain porridge.
Advice. Avoid eating citrus fruits, chocolate, smoked meats and pickles. They are a common cause of allergic reactions that appear on the nose.
Drink at least 2 liters of clean water daily to prevent lack of moisture in your cells. During the off-season, take vitamin complexes to increase the body's defenses.
A red, scaly nose does not tolerate hot or ice water. To wash your face, use mineral water at room temperature. Avoid alkaline soap. Cleanse with cosmetic milk or oatmeal.
- Grind the flakes with a coffee grinder and place in a plastic container.
- Before washing, pour a little powder into your palm and dilute with warm water until it becomes sour cream. Apply to face, massage the sides of the nose and rinse.
- Do not rub your skin with a towel. Gently blot the moisture with a napkin, wipe the dermis with tonic and apply moisturizer.
Do not use alcohol-based products for daily care. They dry out and increase flaking. When going outside in the summer, protect your face from ultraviolet radiation with special means. In winter, use a thick foundation that protects from frost and wind.
If the area around your nose is covered with white scales, under which red spots have formed, do not rush to clean them with your fingers. First, soak the peeling with water and lubricate with Vaseline. Take a piece of gauze, folded several times, and rub the affected areas, removing the scales. After completing the manipulation, rinse the epidermis with chamomile infusion, dry and lubricate with cream.
What to remember
- If there is peeling under the nose, avoid using any cosmetics or medications that irritate the skin.
- Eliminate contact with potential allergens.
- If you suspect a disease of the internal organs, go to see a doctor and do not take any measures until laboratory tests are performed and a diagnosis is made.
- In cold and dry weather, use rich creams to protect your skin.
- Use folk remedies to moisturize and relieve inflammation.
Recommendations from cosmetologists
Experts advise getting tested and, if peeling is a consequence of pathological processes in the body, undergoing appropriate therapy. To exclude a fungal infection, a scraping is taken from the reddened area. The doctor examines the scales and determines the presence of pathogenic flora.
Cosmetologists recommend a combination treatment, including:
- proper nutrition;
- salon treatments;
- medicinal ointments and creams;
- traditional methods.
Flaky skin near the nose ceases to bother you after a course of moisturizing professional masks. The doctor selects ingredients that match the type of epidermis. Good results are provided by collagen, hyaluronic acid, emollient oils, herbs, and seaweed.
Mesotherapy eliminates red spots and peeling on the nose. The procedure involves the injection of various drugs under the skin. To treat acne and relieve inflammation, absorbent and antibacterial agents are used, and moisturizing components are used to soften.
This is interesting! Biorevitalization helps against severe dehydration. During the session, hyaluronic acid is injected into the deep layers of the skin. The procedure triggers cell regeneration, restores metabolic processes, and eliminates dryness and sagging.
When the wings of the nose peel off, cosmetologists offer salon peeling, hardware massage, and paraffin therapy. One of these procedures is shown in the video:
Causes and etiology
Redness around the nose: the causes usually correspond to dermatological diseases of the skin. In medical practice, women most often suffer from changes in skin color in this part of the face. At risk are teenagers during puberty and women who abuse the use of cosmetics.
Pathological condition of the epidermis: peeling in the nasolabial part of the face, redness caused by a number of negative factors. It is necessary to analyze each possible case in more detail.
The best remedies for flaking around the nose
It is easier to achieve the best results by combining the use of pharmaceutical drugs and traditional methods. If the skin on your nose is peeling, carry out the procedures regularly and coordinate the actions with a cosmetologist. This will help prevent adverse reactions and worsening of the condition.
Pharmacy drugs
Pharmacies sell ointments and creams that eliminate the inflammatory process and remove peeling.
- Bepanten provides quick results. The ointment contains dexpanthenol, which, penetrating deep into the skin, is converted into vitamin B5. The substance activates metabolic processes, heals damage and rashes. Bepanten is applied to the cleansed dermis 1-2 times a day and rubbed in thoroughly.
- Pantoderm ointment is useful, which forms a protective film that protects from the harmful influences of the environment and accelerates healing. The ointment quickly soothes itching and removes peeling of the skin.
- It is useful to lubricate rough areas around the nose with baby cream with the addition of vitamins A and E, cosmetic Vaseline, including mink oil, and warm sea buckthorn oil.
If the skin around your nose is peeling due to allergies or a fungal infection, powerful medications are needed. Hydrocortisone ointment is highly effective. The product is distributed in a thin layer onto the areas of redness 1-2 times a day. The course of therapy is no longer than 2 weeks. You can buy Griseofulvin ointment, Mycocid lotion, Dermazol.
For seborrheic dermatitis the following are in demand:
- Nystatin ointment;
- Ketoconazole;
- zinc paste;
- Sulfuric ointment.
Redness caused by a runny nose is eliminated with oxolinic ointment or Viferon.
A persistent infection that causes redness between the sinuses is treated with antibiotics. Effective ointments: Gentamicin, Tetracycline, Erythromycin.
Attention! Use hormonal external agents and antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor. They are fast-acting, but have many contraindications, so self-medication is unacceptable.
Traditional methods
Using unconventional methods, you can solve the problem caused by excessive dryness, chapping, and inappropriate cosmetic care. In other cases, traditional medicine recipes are used as auxiliaries that complement the main treatment.
Masks
Mix a spoonful of natural honey with mineral water in equal proportions. Apply to inflamed areas with a cotton pad, massage with your fingers, leave for 5 minutes and wash.
- A simple mask quickly copes with flaky skin on the nose. Pour a spoonful of oatmeal with a small amount of boiling milk. After 10 minutes, strain off excess liquid. Add a teaspoon of olive oil and May honey to the warm porridge. Apply the mixture to your nose. After 20 minutes, wash off the composition.
- Mash a large spoonful of homemade cottage cheese with a fork, after adding a spoonful of olive oil. Wash the parsley sprigs and chop. Take a spoon and mix with cottage cheese. Distribute over problem areas and do not rinse for 20 minutes.
- Pour a tablespoon of linden blossom into a glass of boiling water. After half an hour, filter. Place a spoonful of oatmeal and olive oil in a ceramic bowl and pour in the linden infusion a little at a time, stirring constantly. The composition should acquire the consistency of liquid sour cream. Lubricate the epidermis around the nose and face along the massage lines. After 15 minutes, clean the skin with a cotton pad soaked in linden infusion.
And this simple and affordable remedy will allow you to get rid of peeling after 2-3 applications:
Apply anti-flaking masks daily for a week. If the problem does not disappear during this time, consult a cosmetologist.
Rhinitis is inflammation of the nasal mucosa.
The main risk factors for the development of AR are: 1. Family history - hereditary factors, allergic diseases in the family. 2. Allergic sensitization. Year-round AR is characterized by exposure to allergens characteristic of enclosed spaces (household allergens, house dust mite allergens, fungal allergens, pet allergens) 3. Contributing factors (smoking, quality of inhaled air in the home, air pollution, climatic factors). 4. “Lifestyle” factors. 5. Relatively high socio-economic status.
Distinguishes the following main stages of AR: 1. Vasotonic stage
.
It is characterized by a constant change in vascular tone and is clinically manifested by variable nasal congestion. 2. Stage of vasodilation.
Nasal congestion is constant due to dilation of the mucous vessels.
3. Stage of chronic edema.
The nasal mucosa changes from pale marble to bluish, and nasal congestion is almost constant.
4. Stage of hyperplasia.
The nasal mucosa grows, polyps form, the paranasal sinuses are often involved in the process, secondary otitis develops, and a secondary infection is almost always associated.
These stages of development of a single pathological process are realized due to markers of inflammation in the territory of the nasal mucosa.
Biological markers of inflammation in allergic rhinitis
1. Cytokines: - Monokines (GM-CSF, TNF, IL1, IL5, IL6, IL8, IL12, IL15) - Lymphokines (IL2, IL4, IL13, gamma-IFN) 2. Leukotrienes: - Cysteine (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4 ) - Non-cysteine (LTB4) 3. Granular proteins: - Eosinophil (cationic protein, peroxidase, protein X, neurotoxin) - Mast cell tryptase 4. Adhesion molecules: - Endothelial adhesion molecule - ELAM-1 - Vascular adhesion molecule - VCAM-1 - Intercellular adhesion molecule - ICAM-1
Clinical forms of allergic rhinitis:
The definition of
“mild”
means that the patient has only minor clinical signs of the disease that do not interfere with daytime activities and/or sleep.
The patient is aware of the presence of manifestations of the disease and may be ready to be treated, but here everything depends on his personal desire. The definition of “moderate”
means that the symptoms disturb the patient’s sleep, interfere with work, study, and sports.
The quality of life deteriorates significantly. The term "severe"
means that the symptoms are so severe that the patient is unable to work, study, play sports or leisure activities during the day, or sleep at night unless treated.
The term “episodic (or intermittent)”
means that the manifestations of AR bother the patient less than 4 days a week or less than 4 weeks a year.
The term “frequent (persistent) presence of symptoms”
means that the patient reports symptoms of the disease more than 4 days a week or more than 4 weeks a year.
Perennial allergic rhinitis (PAR) (persistent)
caused by the following allergens:
- House Dust Mites
House dust mites are microscopic arachnids (Arachnids) found in indoor dust, especially in bedrooms, upholstered furniture, carpets, curtains, etc. The sizes of the most common species, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and Dermatophagoides farinae, do not exceed 0.4 mm. At all stages of their development, these mites are keratinophages, i.e. they feed on desquamated epidermis (dead flakes of the upper layers of human or animal skin, which sometimes make up up to half the volume of house dust). Under conditions of optimal humidity (relative humidity 70-80%) and temperature (20-300C), the life cycle of ticks is approximately one month and includes the following stages: egg, larva, protonymph, tritonymph and adult. During her life, a female tick lays 70-100 eggs. o Under favorable living conditions, the mite population can grow very quickly, and tens of thousands of individuals can be found in 1 g of dust.
- Microscopic fungi are distributed almost everywhere. Fungal spores were found even at an altitude of more than 2000 m. The concentration of fungal spores in the air, even during the period of intense flowering of plants, is a thousand times (1000!) higher than the concentration of pollen grains. Molds consist of a system of small threads - mycelium - and reproduce by spores. The spores are small enough to enter the lower respiratory tract and even reach the alveoli. Yeasts are single-celled fungi that do not form filaments. In reality, a person comes into contact with 100 species of mushrooms. The species composition of mushrooms differs indoors and outdoors. In the air of cities in warm weather there is an average of 3100 spores/m3 of air. In the open air, Cladosporium and Alternaria predominate, in smaller quantities - Penicillium and others. These fungi are characterized by great seasonal variability with a maximum in summer and a minimum in winter. But, since the concentration of their spores is increased throughout the warm period, the flowering and spore formation calendar does not help diagnose allergies. In house dust and indoor air, the fungi Aspergillus and Penicillium are more often released, in smaller quantities - Cladosporium, Alternaria, Mucor, Candida, etc. Aspergillus and Penicillium reproduce all year round. Indoors, higher levels are observed in autumn and winter. They are called storage fungi and cause rotting of stored grains, fruits and vegetables. Penicillium can often be seen on items stored in basements as patches of green mold. There are no clear standards for the content of fungi in the air, only a conditional standard - no more than 500 spores/m3, but during research it turned out that in more than 80% of rooms it was exceeded, and in some the concentration of spores in the air reached tens and hundreds of thousands per m3. For Cladosporium and Alternaria, the content norm is 102 and 3 x 103/m3. The highest concentrations of fungi were found in old houses, on the first floors of buildings and in rooms with various leaks. Mold loves damp and warm places, bathroom walls, shower stalls, trash cans, refrigerators. The source of mold can be moldy products, old paper wallpaper, linoleum. Fungi can colonize household appliances such as humidifiers or air conditioners. Flower pots are often the source of Cladosporium and Alternaria, which live on rotting parts of plants, but the connection between indoor flowers and the number of fungi is not as great as thought. Yeasts can also live in the soil.
- In the dwellings of central Russia, there are mainly three species of cockroaches, the allergens of which are the cause of the development of allergic diseases in humans: Blatta orientalis, Blattella germanica and Periplaneta Americana. The high antigenic activity of insect body particles is mainly associated with anthropodin (a water-soluble protein that makes up 15% to 50% of the cuticle). Sensitization to cockroaches can develop through bites, direct contact with insect bodies and cockroach metabolites. House dust from infected apartments contains cockroach allergens: saliva, feces, insect body tissue. The most pronounced allergenic properties are found in fragments of the head, cuticles and excrement.
- The main allergen in cats is Fel d1 (1-10 µm, average 3.5 µm). The main source of Fel d1 is animal saliva; it is also found in the sebaceous glands of the skin. In cats, but not in cats, Fel d1 is also excreted in urine. In general, cats produce significantly more allergens than cats. After removing the cat from the premises and/or carrying out elimination measures against the cat allergen, a decrease in the level of allergens and the symptoms they cause is usually observed no earlier than 6 months. Because Fel d1 is very resistant to the environment. Do you like to visit prostitutes? And even at an age? There are mature prostitutes from Tyumen here: https://sex-tumen.prostitutki72.com/zrelye Intimacy for the evening is guaranteed. Dog allergens are found in animal dander, saliva, urine and serum. The main dog allergen is Can f1. Different breeds of dogs emit allergens that vary in spectrum and quantity.
| Profession | Allergen |
| Baker | Flour |
| Laboratory worker | Laboratory animals |
| Painter painting with spray gun | Isocyanates |
| Workers exposed to plastics and resins | Anhydrides |
| Carpenter | Western Red Cedar Wood |
| Medical workers | Latex |
Food products as etiological factors of food allergies, according to the degree of allergenic activity (without taking into account individual characteristics)
| Activity level | Products |
| High | Cow's milk, fish, crustaceans, eggs, chicken meat, strawberries, raspberries, wild strawberries, blackcurrants, blackberries, grapes, pineapples, melons, persimmons, pomegranates, citrus fruits, chocolate, coffee, cocoa, nuts, honey, mushrooms, mustard, tomatoes , carrots, beets, celery, wheat, rye |
| Average | Pork, turkey, rabbit, potatoes, peas, peaches, apricots, red currants, bananas, green peppers, corn, buckwheat, cranberries, rice |
| Weak | Horse meat, lamb (low-fat varieties), zucchini, squash, turnips, pumpkin (light colors), green and yellow apples, white currants, gooseberries, plums, watermelon, almonds, green cucumbers |
In addition to antigens, clinical manifestations of AR
can be provoked by such trigger factors as infection, nonspecific irritants, tobacco smoke, pollutants, cold air, drafts, which indicates the formation of nonspecific hyperreactivity of the nasal mucosa.
Diagnostic measures for CAP:
1. Taking an anamnesis. 2. General blood test. 3. Examination by an allergist-immunologist, ENT doctor. 4. Skin testing with a set of mixed allergens followed by additional examination with the corresponding group of allergens. Determination of total serum IgE and specific IgE to specific allergens. 5. Conducting provocative nasal tests 6. Cytological examination of a smear-imprint from the nasal mucosa, washings for bacteriological examination. 7. Determination of the function of the ciliated epithelium of the nasal mucosa. 8. X-ray examination of the nose and/or paranasal sinuses.
Preventive and therapeutic measures for CAP:
1. Elimination of causally significant allergens.
(detailed information is presented 2. SIT 3. Antihistamine therapy, taking into account the need for long-term use of antihistamines (it is advisable to prescribe 3rd generation drugs, since they have minimal side effects and can be used for a long time) 4. Prescription of cromones (for example, cromohexal in the form of a nasal spray, practically has no side effects) . Immunology and allergology. Algorithms for diagnosis and treatment. - M.: Geotar-Med, 2003. 2. Pukhlik B. M. Elementary allergology. - Vinnitsa, 2002. 3. Gushchin I.S., Ilyina N.I., Polner S.A. Allergic rhinitis. - M., 2002. 4. Stanley M. Nagua, M. Eric Gershwin. Secrets of allergology and immunology. M.: Binom, 2004. 5. Khaitov R.M. Clinical allergology. - M.: "MEDpress-inform", 2002. 6. Roy Patterson, Leslie K. Gremmer. Allergic diseases. - M., Geotar Medicine., 2000.
Cuperosis
This is a serious disease of vascular-cutaneous pathology. As a result of the pathological process, the vascular walls become less elastic and thin. Spider veins appear on the nose of patients.
Cuperosis is not a cosmetic problem, but a serious illness. When the capillary walls are weakened, paralysis of muscle fibers occurs.