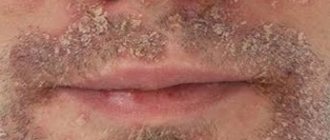
People who have flaky skin on their pubic area should understand that they can get rid of this problem very quickly by going to a dermatologist for an in-person examination. The fact is that in 70% of cases the cause lies in contact dermatitis, which can only be eliminated by eliminating the allergen. Any peeling on the pubic area brings a lot of discomfort, especially if it is accompanied by weeping and itching. Let's try to figure out what diseases can provoke this symptom and is it possible to get rid of it on your own?
The structure of the skin and its appendages
Skin is a part of the body that performs many functions:
- Protective. A function that protects the body from harmful influences - chemical, mechanical, hypothermia and overheating, etc.
- Respiratory. The surface of the skin makes 2% of the total “breathing” of the entire human body.
- Regulatory. Mineral and water balances, thermoregulation (due to sweating) are carried out by this function.
The skin consists of three components:
- Epidermis is the outer layer.
- The dermis, that is, the skin itself, is an intermediate layer (connective tissue). The dermis is the support for blood vessels, nerves and skin appendages.
- The hypodermis is the layer that lies deeper than the others.
Hair, sebaceous, sweat glands are skin appendages on the head.
Epidermis
Several layers make up the epidermis. Cells originate in the basal layer, some of them continuously move towards the stratum corneum, changing their appearance along the way and, at the final stage, losing their nucleus. By the end of the movement, these cells become keratinized, nuclear-free scales that form the stratum corneum.
These scales are constantly replaced by others that rise from the basal layer. This is how skin regeneration or renewal occurs. Melanin, which determines the color of hair and skin, is produced by cells located in the cuticle. And the immune system of the skin is macrophages.
Dermis
A set of bundles of connective tissue and elastic fibers, which is the dermis, helps maintain the shape of the skin, that is, stretch and contract without visible changes.
Here are located:
- nerves;
- hair follicles;
- vessels;
- sweat and sebaceous glands.
Sweat creates comfortable thermoregulation and removes dangerous substances from the body. The sebaceous glands have an equally important function. They produce sebum, which protects against hypothermia and drying out, and prevents the dermis from cracking.
Hypodermis
The layer that is located deeper than the others. This is where blood vessels and nerve trunks are located. The thickness of the hypodermis on the head is about 2 mm.
Possible diseases
There are also many diseases that cause redness in the groin of men. The most common of them are manifested by the following symptoms:
- Inguinal athlete's foot. A fungal infection that affects the pubis, inner thighs and sometimes the genitals. It is transmitted sexually and through household contacts through personal hygiene products (bed linen, towels, etc.). At the initial stage, it may appear as slight redness in the groin area. As the process progresses, a clear outline of the spot begins to appear, the surface of which is covered with peeling and rashes. The itching is tolerable. An exacerbation is observed during the hot period of the year. Men who are obese and lead a sedentary lifestyle are at risk. Also, this disease is often diagnosed in men of certain professions (office workers, loaders, truck drivers, taxi drivers, etc.). Treatment is long-term with frequent relapses. Compresses, rubbing ointments and taking medications orally (in advanced cases) are indicated.
- Psoriasis. Rarely found in the groin area, it can also cause redness and severe peeling. It all starts with one or more scaly plaques the size of a coin. As the process progresses, the number and size of plaques increases. There is no itching. Treatment includes taking medications to reduce symptoms. There are currently no drugs to completely cure psoriasis.
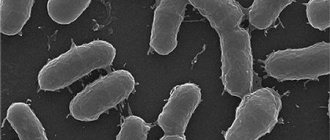
- Erythrasma. This is a bacterial disease that affects the groin area and inner thighs. Characteristic differences are redness of the skin, the formation of large spots that change color over the course of the process from light red to dark brown. The lesions do not itch or hurt. You can become infected in a bathhouse, public showers and through the personal belongings of a patient with erythrasma. Treatment is individual. After confirming the diagnosis, antibacterial drugs are selected. At the initial stage, it can be confused with epidermophytosis, so diagnosis includes glowing of the lesions under a Wood's lamp.
- Candidiasis. Also has a fungal breed. It affects mainly large folds, in isolated cases it spreads to the legs. Characteristic differences are a white coating, a sour smell and redness in the groin. The course is long, with periodic exacerbations after overheating (the process can be activated by going to a sauna, hot bath, etc.). During the hot season, the most pronounced symptoms are observed, since increased sweating creates a favorable environment for this fungal culture. Mostly obese men suffer. People with diabetes are also at risk. Long-term treatment with the use of antifungal ointments and tablets.
- Pityriasis rosea. Infrequently found in the groin area, it can also cause redness of the skin. At the initial stage, small plaques the size of a small coin are formed. The color is bright pink. As the process progresses, the spots may merge, forming one large lesion. The color is dark red. The itching is tolerable. No pain or swelling is observed. The routes of infection and the causes of this disease are not fully understood, so it is impossible to say for sure that it is sexually transmitted. Antifungal ointments can be used as treatment.
- Rubrophytia. Another fungal disease that affects the groin area. It begins with slight redness of the skin, smoothly flowing into large spots covered with a rash. There is peeling and slight itching. Contagiousness is very high. You can become infected in public showers, saunas and other places where there is high humidity and high temperatures. It is treated only after confirmation of the diagnosis, which includes collecting scales from the lesions to determine the culture of the fungus. After this, drugs are selected to destroy the fungus. Special care of the affected areas is also indicated - avoid moisture and avoid sweating.
From everything written above, we can conclude that redness in the groin in men is harmless only if it is not accompanied by accompanying symptoms.
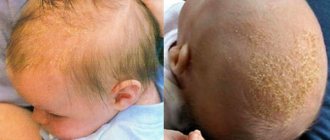
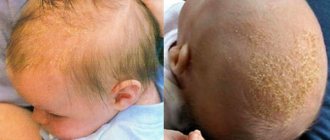
Dandruff symptoms
Since dandruff is one of the manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis, it is the main symptom of the disease. Signs of dandruff include the following:
- peeling of the scalp;
- greasy hair;
- itching sensations and hypersensitivity of the dermis;
- excessive hair loss, appearance of white scales;
- redness of the scalp as the condition worsens.
Scales are noticeable on the hair. Usually they are very thin, almost transparent, and with normal sebum separation they are whitish or whitish-grayish in color. They can accumulate on any part of the scalp.
Itching is often observed and reddish, ill-defined spots are noticeable on the skin; they are covered with thin flakes of dandruff. The process can extend beyond the hair, onto the forehead, neck, and behind the ears.
Diagnostics
The answer to the question of how to treat peeling and with what depends on the reasons that led to the appearance of unpleasant sensations. To clarify them, the following diagnostic procedures are performed:
- you will have to donate blood and urine for general and biochemical analysis to the laboratory;
- the doctor will take a smear of flora from the urethra or vagina;
- They practice collecting scrapings from the affected area for further diagnostic procedures.
The doctor may recommend taking blood tests for HIV, syphilis, and other serious and dangerous sexually transmitted diseases, even if there are no other accompanying symptoms.
If such a problem occurs, you should contact the following specialists:
- A dermatologist will help in the diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases; he will rule out fungal infections, bacterial damage to the epidermis, and select appropriate medications.
- If there are signs of a hypersensitivity reaction, an allergist will help. The doctor will take samples, identify the allergen and prescribe medications to relieve itching, burning and swelling of the skin.
- A gynecologist, urologist or venereologist - one of these doctors will have to be visited. This will help rule out the presence of genital diseases.
Doctors may recommend that the patient undergo other examinations to clarify the diagnosis if certain problems arise with this. More often they are sent for an ultrasound of internal organs, and secretions or skin flakes are collected for further examination in a laboratory.
Causes of dandruff
Experts clearly consider dandruff or seborrhea to be a disease.
They identify three main causes of dandruff:
- The sebaceous glands begin to malfunction. This can be caused by a metabolism that is somehow disrupted, a weakened immune system, or unhealthy food.
- A fungus that affects the skin, usually lives quietly on the head, but at a certain moment becomes activated for some reason. Epidermal cells begin to be produced at an accelerated rate, which dramatically shortens the period when the cells are exfoliated. Of course, a large number of scales appear, which can be called superfluous.
- The body's predisposition to dandruff. There may be some differences from the norm in the structure of the scalp and its secretion; heredity is possible. Also, the appearance of dandruff can be caused by certain diseases, including neurological ones.
Obviously, the causes are so varied that the treatment of dandruff must be selected exclusively individually.
What is dandruff
Dandruff or seborrhea are yellowish or white scales. They are dead cells that for some reason begin to be intensively produced. The main reasons for this have been discussed above.
When the sebaceous glands malfunction, oily seborrhea occurs. It can be thick or liquid:
- Thick seborrhea is coarse, coarse hair under which blackheads may appear.
- Liquid seborrhea is oily, untidy-looking hair on which scales appear, and pustules may appear under the hair.
An activated fungus causes dry seborrhea. Brittle, thin and dry hair is a sign of such seborrhea.
Signs
Dandruff can be easily noticed with the naked eye. These white scales appear in large numbers on the hair and fall off onto the shoulders. They are most noticeable on dark hair and clothes; those with light hair are a little more lucky in this case, because they are not so visible against a light background. In addition to flaking scales, people may complain of the following symptoms:
- itching of the scalp;
- redness;
- dry skin.
There is an opinion that men suffer from this problem more often than women, but in reality this is not the case. It is equally relevant for both sexes. It’s just that representatives of the stronger half of humanity usually have short haircuts, on which the white parts are more noticeable. Ladies often manage to hide the defect under voluminous styling.
The following features are noted:
- In children, this phenomenon occurs extremely rarely; troubles, as a rule, begin during adolescence;
- In 20-40 year old men and women, dandruff occurs equally often;
- after 50 years the problem practically disappears.
Are you experiencing dandruff symptoms?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Complications of dandruff
There is the development of itching of the scalp, as well as baldness (seborrheic alopecia). Complications in such a situation are pustular skin pathologies, but they are more pronounced and more severe. For example:
- furunculosis - numerous boils;
- impetigo - damage to the hair roots with the formation of ulcers in their place.
When the suppuration opens, it transforms into dense crusts the color of honey. After they fall off, pigmentation can be observed in their place.
Etiology
The groin area and the area between the legs are exposed to high humidity, so the skin in this part of the body is a favorable environment for the activity of bacteria and fungi. The following factors can provoke detachment of the upper layers of the epidermis:
- increased work of sweat glands;
- being overweight;
- non-compliance with the rules of cleansing the skin of the intimate area;
- promiscuous unprotected sexual intercourse;
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalances;
- a sharp decrease in immune defense.
If the skin between the legs itches and peels, the following internal pathologies can develop in the body:
- Inguinal athlete's foot. The inner surface of the thighs can be affected by inguinal fungus. A characteristic symptom of the pathogenesis of the disease is a long-term recurrent course with the formation of flaky spots, which, as the disease worsens, tend to merge into one local lesion. The skin in places where fungi are localized becomes rough and swollen, covered with whitish scales and blisters, peeling appears on the pubis, and there is noticeable itching with progressive intensity. Spots the size of a coin appear on the inside of the thighs; as the process progresses, they can increase to the diameter of a saucer. The risk of infection with groin fungus is very high in places with high humidity, where the requirements and standards for disinfection of surfaces are not met (baths, saunas, swimming pools, showers, hot shops, etc.).
- Contact allergic dermatitis. Allergens, under the influence of which the skin between the legs of women peels off, most often are synthetic fabrics of clothing and bed linen, detergents, cleansing and caring cosmetics, condom lubricants, lubricants, personal hygiene products (tampons, pads, etc.), some medications. Under the influence of aggressive environmental factors, irritation, redness and dryness of the skin are observed. Allergic reactions are also characterized by the appearance of small red blisters and itching in the affected area. Such manifestations, if they are not expressed in an acute form, disappear 2-3 hours after eliminating the allergen. In severe cases, large red spots appear in the groin, which are accompanied by unbearable itching.
- Erythrasma. The clinical picture of this common form of pseudomycosis is characterized by the appearance of small brown spots with a smooth surface in the inguinal-femoral area. In the absence of proper treatment, the disease is complicated by the fusion of lesions and the detachment of white scales of the affected layer of the epidermis. In severe cases, painful rashes may appear in the groin area.
- Rubrophytia. A fungal infection that develops in the area of large inguinal-femoral folds provokes the formation of large red or dark spots on the skin, the surface of which is covered with small keratinized scales. There is also swelling and redness of the tissues, and noticeable itching. Not only the skin, but also vellus hair is susceptible to fungal invasion. You can become infected with inguinal fungus through bodily contact with the carrier or his personal hygiene items.
- Psoriasis. With psoriasis that develops on the inner thighs, there is a characteristic painless peeling, the shape and size of the scales resembling oatmeal, as well as slight redness and dryness of the skin. The surface of psoriasis plaques is rough; mechanical action causes detachment of the affected particles of the epidermis.
- Candidiasis. The inguinal-femoral skin is susceptible to damage by saprophytic yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. With candidiasis of the skin folds, the skin between the legs peels off, a noticeable uncomfortable itching appears, and erosions of a bluish-crimson color form. This form of thrush is often diagnosed in workers in hot shops, baths, mines, etc. In the female body, fungal infection of the skin folds also spreads to the genital area.
If you look at the statistics, they claim that in 60% of cases, flaking in the perineum in women is caused by an allergic reaction to personal hygiene products (most often pads and synthetic underwear).
Dandruff treatment
If the process has not yet gone too far, then you can try treating dandruff at home.
First of all, you need to establish nutrition. For some time you will have to give up sweets, bread, carbonated drinks, strong coffee and tea. All kinds of bars, crackers and chips are also prohibited. Don't be afraid - it's only temporary. But you can eat vegetables, dairy products, cereals, lean meat, fish and other foods, baked, boiled and steamed.
You need to choose a medicated shampoo, sold only in a pharmacy. You should not use those products that are actively advertised as anti-dandruff shampoos - the effect, if any, will be short-lived. The pharmacy selects medicinal ointment and cream, which, if used correctly, can help very effectively.
You can try using non-drug remedies. There are quite a lot of recipes on how to remove dandruff.
These are, for example, masks.
- Egg yolk, orange juice: two teaspoons and aloe (also two teaspoons) mix well and apply to the head. Leave for forty minutes and rinse. Then it is advisable to use a decoction of horsetail to rinse your hair.
- Mix lemon juice and honey, a teaspoon each, olive oil (tbsp) and egg yolk, then rub along the parting lines. Next, put on a cap and wait for forty minutes, then wash your hair. It is recommended to do this twice a week for one month.
There are quite a lot of masks on offer; if a person finds it difficult to choose, you can consult a dermatologist or trichologist.
There are also rinses and lotions. For example, rinses:
- Boil chamomile inflorescences in the amount of two tablespoons and a liter of water for five minutes. Cool and rinse your hair.
- Thyme - four tablespoons and half a liter of water, boil for ten minutes. When the broth has cooled, you need to strain it and rinse your hair after washing.
Lotion: castor oil in the amount of 5 g, 2 g of salicylic acid and 100 g of vodka, mix thoroughly and lubricate your hair one and a half to two hours before washing. Use every other day until complete recovery.
And in folk recipes, the use of oils - castor, sea buckthorn and burdock - is widely recommended.
Lots of tips on how to get rid of dandruff. If all this does not help, you need to consult a doctor and follow his instructions. To avoid so much suffering with dandruff treatment, you need to try to prevent it.
Peeling skin on the pubic area in women photo
If the skin on the pubic area is peeling in women, it is necessary to promptly address this delicate problem with a doctor, who will prescribe an appropriate treatment regimen based on microbiological analysis of scrapings taken from the surface of the lesion. Uncontrolled self-medication can only aggravate the disease and provoke the development of severe complications.