Causes of peeling - external factors and improper care
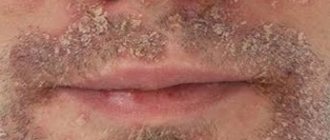
So, what are the causes of peeling skin on the face? There are three skin types: oily, normal, dry. People with dry skin suffer from flaking more often than others. This is natural. However, if the situation worsens over time, you should pay attention to the following factors.
why does the skin on my face peel?
One of them is lack of moisture in the body. Winds, frosts, scorching sun, dry indoor air during the heating season - all this dries out the skin, causing it to peel. Therefore, such environmental influences should be avoided in every possible way and skin care should be strengthened.
When caring for your face, it is important to remember that excessive frequent washing (especially with hot water), as well as the use of soap products, can negatively affect the skin, causing dryness and irritation.
If by leaving you have achieved the opposite effect, do not despair! Replace regular soap with a skin moisturizer and use a nourishing cream. This will help your facial skin recover.
Also, refrain from rubbing your skin after washing your face. It could hurt her. Better to gently pat your face dry with a soft towel.
Lack of vitamins
The lack of vitamins in the body or their deficiency also leads to flaking of the skin. What should you do in such a situation? It is necessary to help the body accumulate nutrients. To do this, include more fruits in your diet (especially during the period of autumn-spring vitamin deficiency).
Allergy
Peeling of the facial skin often occurs as a result of an allergic reaction to the lanolinic acid contained in face washes. Flowering plants, allergenic foods, and medications can also cause a skin reaction.
If the problem is with your cleanser, you should seek professional advice. If the itching persists, do not delay visiting your doctor. Since this phenomenon may not be a simple irritation, but a symptom of an infectious skin disease.
Dry skin
As we have already noted, the main problem of the skin is the lack of moisture. How to solve it? You should stop using soap when washing your face. It is recommended to replace it with soft, cleansing, non-alcohol-containing products, such as:
- foams,
- mousses,
- gels.
causes of peeling skin
Treatment of itchy skin
First of all, any cosmetologist will ask you to exclude from food all allergenic foods and other conditions that provoke itching (for example, a feather pillow or synthetic materials in clothing). In addition, you will need moisturizers: cosmetic ones, and you will also be recommended compresses from chamomile infusion. If these manipulations are useless, you should immediately use the services of a dermatologist, or even go to an allergist. What else will have to be done to establish a diagnosis:
- General urine test and general blood test;
- Biochemical blood test;
- Fecal analysis for helminths and occult blood;
- Skin scraping for fungus.
- Skin tests (to determine the nature of the allergy)
Based on the test results, after examination by a dermatologist, a diagnosis is made and treatment is determined. Taking into account the nature of the disease, either drug treatment or cosmetic procedures with a therapeutic focus are prescribed. Do not neglect the doctor’s advice, do not shirk the procedures, complete the full course of treatment, because the untreated allergy returns again and everything will have to start all over again.
Seborrhea
Indicators of this disease will be itchy skin, shine and flaking, and the appearance of pink spots.
It is treated using sodium thiosulfate, calcium chloride, corticosteroids, ointments and creams of antibacterial composition (bicarbonate, sulfur solution), salicylic alcohol, boric acid, as well as hawthorn tincture and lily of the valley tincture are used).
Psoriasis
You should think about psoriasis if the skin itches, becomes red, and becomes covered with flaky skin flakes.
Treatment is carried out using salicylic acid, sulfur-tar and naphthalan ointments, calcipotriol, diprosalic. Phototherapy, homeopathic remedies, icitretin, roaccutane, and cyclosporine have been successfully used.
Demodicosis
With this disease, severe itching occurs, eyelashes fall out, and the face becomes covered with acne.
First of all, with the help of drugs, they strengthen the immune system (in order to strengthen the body’s resistance) and try to ensure the normal functioning of the stomach and intestines. Antiparasitic drugs are prescribed in the complex: trichopolum, tinidazole, metronidazole. Ointments (sulfur, yellow mercury, ichthyol), pharmaceutical “talkers”, ointments of antibacterial compositions “Aversect”, “Permethrin” are used externally. To reduce inflammation, use Dexrdem Phyto cream-gel, which has a good anti-inflammatory effect.
Rosacea
The symptoms of this disease are lumpy, inflamed skin. The skin constantly itches, turns red, and the spider veins become very noticeable.
It is treated with metronidazole in ointments and tablets, a certain diet is prescribed, lotions are made with boric acid, and a special massage is prescribed. Rosacea is treated with antibiotics, immunocorrective medications, cold treatment and psychocorrection.
"Panthenol"
An effective remedy for protecting against flaking of facial skin is the drug “Panthenol”. Particularly convenient to use thanks to the spray form. This drug is sprayed onto problematic facial skin; after a few minutes, the remaining drug must be removed with a cotton pad. The drug can be used up to four times a day. The use of Panthenol stops the inflammatory process, relieves skin irritation, and eliminates flaking. The drug softens and restores problematic facial skin.
why does my face itch
Eczema - symptoms and treatment
During the course of the disease the following stages :
- Erythematous - skin redness, swelling and itching appear.
- Papular - red papules (nodules) form.
- Vesicular - grouped bubbles with liquid appear, reminiscent of air bubbles when water boils.
- Weeping - the covers of the bubbles open and weeping and erosion are formed.
- Cortical - areas of weeping dry out and become covered with crusts.
- Peeling – exfoliation of crusts and restoration of the skin surface [2].
As eczema enters the chronic stage, the skin undergoes changes: it becomes rougher and drier, as a result, it flakes and pigmentation appears.
Forms of eczema depending on the clinical picture and causes of occurrence [5]:
- true;
- seborrheic;
- microbial;
- nummular;
- mycotic;
- intertriginous;
- varicose;
- sycosiform;
- nipple eczema;
- children's;
- professional.
True eczema
True eczema most often affects the face and limbs. Areas of healthy and affected skin alternate. Other areas may be involved in the process, including erythroderma (generalization of the inflammatory reaction and fever). The process is usually symmetrical. In the acute stage, the disease manifests itself in the form of blisters (vesicles), redness of the skin, erosions with weeping, crusts, excoriations (mechanical damage to the skin when scratching), there may be papules and pustules. Eczematous lesions have uneven boundaries. When the disease enters the chronic stage, redness becomes stagnant, areas of cracks and lichenification (thickening of the skin with increased skin pattern as a result of prolonged scratching) appear, the skin becomes rough and dry. Often the process is complicated by the appearance of ulcers caused by the addition of an infection: beta-hemolytic streptococcus or Staphylococcus aureus [1].
Monetoid (nummular) eczema
Nummular eczema occurs mainly in adults. Men get sick more often than women. The highest incidence occurs between 50 and 65 years of age, in both sexes. In women, the first peak occurs between the ages of 15 and 25, when puberty passes and the woman reaches adult height and weight. But in children, nummular eczema is extremely rare. The lesions are often located in the elbows and behind the knees, with the arms being affected more often than the legs.
The pathogenesis of the disease is still unclear. In some patients, foci of chronic infection are detected, including in the oral cavity and respiratory tract. Allergens, such as house dust mites, play an important role in the development of nummular eczema. With the disease, clearly defined coin-shaped plaques of papules and vesicles appear. Characteristic signs include pinpoint weeping and crusting. Crusts can cover the entire area of the plaque, the diameter of which varies from 1 to 3 cm. Itching can be either minimal or severe. In ring-shaped forms of the disease, the manifestation decreases in the central part. Chronic plaques become dry, flaky, and the skin thickens.
Microbial eczema
Microbial eczema is a polyetiological disease. In the pathogenesis of microbial eczema, the skin barrier plays an important role, because one of its main functions is protection. Itching provokes scratching of the skin, damaging the integrity of the skin, and this, in turn, forms an entry point for infection. Exudation (the release of the liquid part of the blood into the inflamed tissue through the vascular wall) creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of microbes.
An important component of pathogenesis is the skin microbiota. In scrapings from the affected skin of patients with microbial eczema, Staphylococcus aureus and hemolytic staphylococcus, yeast fungi, mainly of the genus Candida, are found. Microbial eczema can also be caused by external physical or mechanical irritants. Often, foci of microbial eczema appear around purulent wounds and in places of long-term pyoderma (a purulent skin disease resulting from the penetration of bacteria).
In microbial eczema, the lesions are round or irregular in shape, with clear boundaries, located asymmetrically and limited by a border of exfoliating epidermis. In the center of the lesions, purulent and serous crusts can be seen; after their removal, weeping, reminiscent of “wells,” is discovered. The rash is characterized by intense itching [2].
Seborrheic eczema
Inflammation begins on the scalp and is localized in areas of the skin with the largest number of sebaceous glands. In this way, seborrheic eczema is similar to seborrheic dermatitis. The lesions are localized behind the ears, on the chest, neck, between the shoulder blades, and on the flexor surface of the limbs. The skin within the lesion is hyperemic, edematous, on its surface there are small yellowish-pink papules and greasy yellowish scales and crusts [2].
Varicose eczema
Varicose eczema, as the name suggests, occurs when the patient has varicose veins. The skin of the legs next to varicose ulcers is predominantly affected. The development of this type of eczema is caused by irrational and untimely treatment of varicose ulcers, skin maceration (wrinkling of the skin during prolonged contact with water), and trauma. Varicose eczema causes severe itching. Differential diagnosis, first of all, must be made with myxedema and erysipelas [3].
Sycozyform eczema
The disease occurs against the background of vulgar sycosis - inflammation of the hair follicles as a result of the penetration of staphylococci into them. The pathological process can go beyond the boundaries of hair growth; as a rule, lesions can be found on the upper lip, armpits, chin and pubis. Clinically, sycosiform eczema is manifested by serous wells, severe itching and weeping, and later areas of skin thickening appear [2].
Childhood eczema
The first symptoms can be noticed at the age of 3-6 months. Eczematous areas are symmetrical, the skin within the lesions is brightly hyperemic, swollen, hot to the touch, has a shiny smooth surface, there is weeping, layering and milky crusts. Eczema primarily affects the cheeks, forehead, scalp, ears, buttocks and extremities (usually extensor surfaces). It is characteristic that eczema does not affect the skin of the nasolabial triangle. When sick, children complain of itching and insomnia. Eczema often transforms into atopic dermatitis[5][10].
Eczema of the nipples
Skin breakdown occurs after nipple trauma during breastfeeding. Externally, eczema manifests itself as slight redness, weeping, crusts of blood collections, and in some cases pustules and cracks, usually without hardening of the nipples. As a rule, the eczematous process spreads to both breasts [5].
Occupational eczema
Occurs under the influence of various industrial allergens. The disease can be caused by mercury, various metal alloys, penicillin and semi-synthetic antibiotics, resins and synthetic adhesives. Occupational eczema is more common among workers in various industries, people who deal with various chemicals (chemists and biologists), as well as those whose work involves constantly immersing their hands in water (for example, cleaners and orderlies). Under the influence of allergens, a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction develops. Clinically, occupational eczema occurs like ordinary eczema. The lesions are located mainly in the area of contact with allergens and on open areas of the skin. Occupational eczema is characterized by rapid recovery when the cause disappears [6].
Paratraumatic eczema
Occurs in the area of postoperative scars or with incorrectly applied plaster casts. Manifests itself in the form of acute inflammatory erythema (redness), pustules or papules, and crusting. Hemosiderin, a yellow pigment formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin, can be deposited in the affected tissues [5].
Summer care goals for combination skin
When choosing products for the care of combination skin in the summer, it is necessary to take into account not only the impact of provoking factors, but also the reactions of different areas of the facial skin to them.
- Regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands in the T-zone . It is in summer that activity is most increased, which leads to blockages and subsequently rashes.
- Regular elimination of hyperkeratosis , which inevitably appears on all areas of the facial skin. You need a product that works effectively and delicately and does not dry out the skin of the entire face.
- Moisturizing the skin - it is important to monitor the water balance of the skin, preventing dehydration.
- Protecting the skin from the sun - prevents dehydration, photoaging and pigmentation.
What you need to know about peeling skin
If untidy white scales appear and the skin becomes rough, it means that the barrier functions of the skin have been impaired.
The formation of scales signals problems in the skin © iStock
“Peeling indicates damage to the protective hydrolipid mantle and increased evaporation of moisture from the surface of the skin.
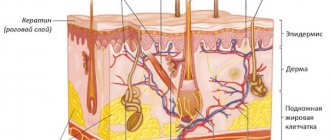
The structure of the stratum corneum is disrupted: corneocytes cannot evenly and quickly exfoliate from the total mass of cells.
Typically, peeling is accompanied by a decrease in NMF, a natural moisturizing factor consisting of uric and lactic acids, amino acids, metal ions and other components of the intercellular fluid. And also by the destruction of the hydrolipid layer and aquaporin proteins - water conductors.” Elena Eliseeva, medical expert at Vichy
Skin types
Structurally, different people's skin looks the same. The main difference is the intensity of the sebaceous glands. Let's look at each of the four main skin types in detail.
Normal skin
Main characteristics:
- smoothness and dullness of the cover;
- pores are narrowed;
- wrinkles appear after 35 years;
- the influence of the menstrual cycle on the condition of the skin is absent or minimal;
- no irritation, peeling, acne;
- pinkish tint.
The most problem-free type, which can be found extremely rarely - only 6% of the world's population can boast of this. Most often these are children under eleven years of age. Such people are not bothered by acne during adolescence. Age-related changes are slow.
Oily skin
Key Features:
- clogged, wide pores;
- oily, shiny surface (even after washing);
- there are comedones, inflammation, black spots on the nose (sometimes also on the forehead, chin);
- makeup fades a couple of hours after application;
- grayish color.
The good news for people with this skin type is that it fades more slowly, thanks to the increased activity of the sebaceous glands. After thirty, as a rule, the skin type becomes mixed.
Dry skin
Main differences:
- the cover is thin;
- pallor, dullness;
- there is peeling, a feeling of tightness;
- frequent allergies to cosmetics;
- makeup stays on well;
- In the morning, the skin is often irritated.
Age-related changes are noticeable after 25 years. The skin loses turgor, becomes less elastic, small wrinkles form around the eyes and mouth, as well as on the forehead. Any temperature changes affect the appearance of the skin - heat or cold can cause redness.
Combination skin
It is distinguished by:
- the face has dark shades;
- The T-zone is often shiny;
- enlarged pores in certain areas;
- in the area of the neck, cheeks, and temples the dermis is thinner;
- before the onset of menstruation, rashes are possible;
- uneven complexion.
Aging is unpredictable.
Folk remedies
To treat and get rid of such a phenomenon on the face as red spots, you can also resort to traditional methods:
- For this method, you need to grate one cucumber on a fine grater and mix the resulting gruel with one teaspoon of white clay. Apply the mixture to the face and keep for 10 minutes, then rinse with running water and apply a moisturizer.
- For the next recipe you will need a spoon of honey and one chicken egg yolk. You need to mix all this and apply it to your face for about 5 minutes. Then rinse and moisturize.
- Also, a mixture of sour cream or heavy cream can help you , which must be mixed with one finely grated potato and add 3 drops of orange or tangerine oil. Apply the paste to your face, wait until it is absorbed, then rinse and apply a nourishing cream.
- One of the simplest and most effective masks is a mixture of oatmeal, which must be crushed and poured with a tablespoon of boiling water. You can add half a teaspoon of honey or three drops of juniper essential oil. Apply to face, leave for 10 minutes, then rinse and moisturize with nourishing or moisturizing cream.
- Another of the most effective folk remedies is considered to be a mixture of one spoon of full-fat sour cream, honey, lemon juice and olive oil. You need to mix all the listed ingredients, apply to your face for 10 minutes, then rinse and apply cream.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3ZMtBONbHCQ