345
230
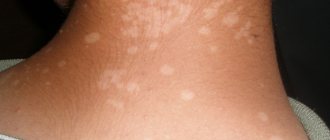
Newborns and infants have very delicate skin that requires special attention and care. Sudden peeling and redness of the skin are common occurrences in the first months of life. There are several causes of dry skin in children and ways to prevent it or help your child cope with the problem. What to do if a newborn’s skin peels? We will talk about this in our article.
Peeling is normal
The baby is born covered with vernix lubrication, consisting of the secretion of the sebaceous glands and epidermal scales. Scientifically it is called Vernix Caseosa, and is formed at 25-26 weeks of pregnancy. Its function is to protect the baby’s skin from the effects of amniotic fluid. When it goes away, you will notice that the baby's skin has begun to peel off. This is a completely natural process, because throughout your pregnancy the baby lived in amniotic fluid, and now he will have to adapt to a new, “dry” environment.
The intensity of skin exfoliation is individual for each baby, and the process usually takes one to two weeks. No special therapy is required, ordinary gentle procedures for caring for newborns are sufficient, for example, bathing with special products for babies.
Causes of peeling skin in babies
Young parents often worry unnecessarily about their baby's dry, flaky, and red skin. The first days after birth, the baby's skin is usually bright red. This is normal: this is how adaptation to the air environment occurs after the transition from the aquatic environment. At this time, small subcutaneous vessels dilate, so the skin is bright.
Don't be alarmed if you notice that skin flakes are peeling off - this is a completely healthy process. At about 6-8 days, the baby’s skin peels off especially noticeably, which is not a pathology, allergy or care defect. This is also part of the process of adaptation to life in the air; the skin changes its structure.
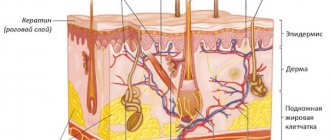
You need to know that in the first 6-8 months of a newborn, the sebaceous and sweat glands almost do not function, so the skin is deprived of the most necessary thing - a lipid film that helps retain moisture in the body. This is why babies' skin is especially prone to dryness.
Parents should remember that most processes, be it redness, peeling or specific discharge, are part of the formation of the child’s body and its adaptation to new living conditions, which are strikingly different from the mother’s womb. And the task of parents is to help (or not interfere) with the maturation of the baby’s skin, and, if necessary, to ensure its protection.
Peeling - as a result of improper care
Long, frequent bathing, aggressive soap, too warm water - a blow to the protective barrier of the child’s skin. This can often lead to dryness and flaking. There are opinions that the first bathing of the baby should be done with the addition of potassium permanganate to the water in order to disinfect it. So: it’s absolutely not worth doing this. There is no evidence that the method works, but the substance has a negative effect on the skin of a child.
According to the recommendations of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia, the water temperature for baths should be at 36.5-37.5 °C. Newborns do not need daily bathing; regular hygiene procedures and 2-3 baths per week are recommended.
What to do if your newborn has dry skin on his face?
In children, the sebaceous glands are developing, so they do not produce sweat. For this reason, infants have poor heat transfer. The surface of the epidermis is very sensitive because it is thin. Many people do not know why the epidermis peels off in a newborn, so they are very scared at the first signs.
The child should drink up to 150 ml of water per day. This will help you avoid dehydration.
To protect the surface of the face from inflammation, it is necessary to constantly monitor body temperature.
Try to dress your child as discreetly as possible, do not bundle him up in several sweaters, jackets and pants, and also use warm water for bathing. There should be no air conditioning or air heaters in the room where the baby is constantly located. The baby's body gradually adapts to the world around it. Peeling of the facial skin in a baby is very easy to treat if it is not caused by a disease.
The mother should periodically “bathe” the baby in an air bath - completely undress the baby and let her lie completely naked for a few minutes.
An air bath hardens and develops protective mechanisms. At the same time, it is necessary to monitor the temperature in the room so that the baby does not feel cold.
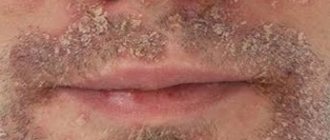
Infants often have too dry facial surfaces, this is mainly due to external factors. In newborns, the allergic reaction first appears on the face. It is caused by the food that the mother eats, hygiene products and clothing.
Seborrheic dermatitis
When the first symptoms appear, contact with these pathogens should be limited. You can soften dry skin of a baby with the La-Cri emulsion.
The product has proven itself well and has been chosen by millions of mothers. The emulsion heals cracks, moisturizes and normalizes the condition of the epidermis.
Peeling - as a symptom of the disease
Eczema and atopic dermatitis
Characterized by red, dry patches on the skin. In infants, it most often occurs on the scalp or face. Parents are advised to look for triggers that could cause an outbreak: it could be a reaction to baby cosmetics or an allergy to an item. There is no cure for eczema, but doctors prescribe medications to help relieve symptoms.
Ichthyosis
A very rare disease in which babies are born with an extra layer of skin on their body. It consists of a layer of skin cells that should have sloughed off before being born. Such children are observed in the intensive care unit until the skin condition returns to normal.
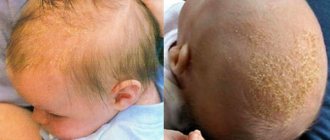
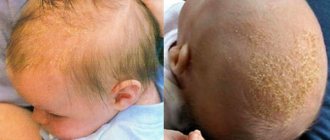
Seborrheic dermatitis
In the first three months of your baby's life, you may notice that his scalp is flaking. Most likely, this is seborrheic dermatitis, which occurs in children of this age and goes away on its own. But if the condition worsens or drags on, do not delay a visit to the pediatrician.
What is epidermolysis bullosa
This is a whole group of hereditary skin diseases characterized by excessive fragility of the skin and the appearance of blisters and wounds on it.
The diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa is made at birth or in the first month of life. With such a disease, the baby is born with erosions on the skin, blisters that can appear on any part of it.
There are four forms of epidermolysis bullosa: simplex EB, borderline EB, dystrophic EB and Kindler syndrome.
For newborns with epidermolysis bullosa, careful management is essential to avoid the development or worsening of wounds. Erosion or wounds appear from any mechanical, thermal impact or even without it. So, for example, if you take your baby by the armpits, his skin may remain in your hands.
The main principles of treatment of epidermolysis bullosa:
- Daily use of a special atraumatic dressing material - a regular bandage or cotton wool will not work.
- Application of external products that will have protective or barrier properties and promote healing of damaged skin areas.
- Mandatory drainage or puncture of blisters.
- Do not use alcohol-containing antiseptics, ordinary adhesive plasters and aniline dyes such as “green stuff”.
Regular bathing of infants with epidermolysis bullosa is important to reduce the risk of infections associated with open skin wounds. Special bath salts are added to the water to create isotonic, pH-neutral water to reduce pain. To prepare a seawater bath for babies with epidermolysis bullosa, add five teaspoons of salt to every liter of water.
Child care checklist
- Bathe your baby in warm running water if it meets hygiene standards - this is stated in the recommendations of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia. That is, it is not necessary to boil the water at all.
- Bathing time for babies in the first month of life is 5-10 minutes. Long contact with water deprives the skin of its natural protective barrier.
- Choose detergents with a mild composition and a pH level (5.5) close to the physiological values of the skin. Liquid bath products tend to be less irritating to the skin and wash off more easily than soap.
- Hypoallergenic moisturizers suitable from birth can be applied to your baby's skin. But it is better to minimize the use of any means.
- It is better to choose washing powders and fabric softeners without fragrances - babies have very sensitive skin.
Useful links: [1] verywellhealth: Why newborns' skin peels [2] Bathing a child (Moscow Regional Center for Public Health and Medical Prevention (MOCP) [3] Skin care for a newborn baby, 2016
How is seborrheic dermatitis treated in children?
If seborrheic dermatitis appears in newborns, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor. If seborrheic dermatitis is detected in an infant, treatment is carried out with external means. To loosen the crusts on the head and remove them painlessly, use products based on salicylic acid and oil compresses, which are applied about half an hour before water procedures. To treat seborrheic dermatitis in newborns , you can use drugs with a keratolytic effect. This will help remove excess gland secretion and cleanse the scalp. After softening and removing the crusts, anti-inflammatory agents may be prescribed.
For treatment to be more effective, it is necessary to ensure that the skin is well hydrated and supplied with nutrients in the right quantities. This helps restore and strengthen the water-lipid barrier and restore the proper functioning of the sebaceous glands. Suitable for care are dermatological creams created for children, which contain vegetable oils, sebum-regulating and wound-healing components. If treatment for seborrheic dermatitis in newborns turns out to be ineffective, the following may be included in the therapeutic regimen:
- topical corticosteroids;
- antibiotics and antiseptics;
- antihistamines for severe itching.
What to do if a child has diathesis
Local therapy using ointments is one of the components of complex treatment. But both hormonal and non-hormonal drugs should be prescribed by a doctor individually for each baby, taking into account the characteristics of the diathesis.
Self-medication in such a situation is not only ineffective, but also dangerous for the child’s health. Therefore, it is better to contact competent specialists. PsorMak employs doctors with extensive experience in treating diathesis.
We take a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment, and for local therapy we use ointment made according to our own recipe without the addition of hormones.
She has been helping our patients at our clinic for more than 25 years, so we guarantee a complete cure without side effects. Contact us for a consultation so we can begin solving your problem. April 5, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
How to identify the pathogen
It is almost impossible not to notice peeling, but there are still certain criteria that help to accurately identify the problem. Symptoms that are considered normal:
- the presence of a white or yellow crust;
- absence of any odor;
- problem areas make you want to scratch;
- the flaked pieces of skin resemble dandruff.
If you have any disease, slight swelling and redness may appear. In some cases, ignoring the symptoms can lead to the crust moving from the head to other parts of the body. Situations like this require medical attention.
Is it necessary to remove crusts from a baby's head?
If an infection gets into the skin, it is necessary to use antifungal ointments.
The crusts, as a rule, go away on their own by one year, so there is no need to do anything to eliminate them. According to pediatrician Komarovsky, measures should be taken in the following cases:
- suppuration forms;
- an unpleasant odor appears;
- a weeping surface is formed with the release of ichor;
- there is redness and swelling around the crust.
These symptoms indicate that an infection has penetrated the skin. These cases require contacting a clinic.