Published: August 2, 2017
Human eyes are one of the most important and vulnerable organs; they are protected from the external environment for centuries; their skin is very thin and sensitive. Itching, redness or peeling of the upper eyelids occur quite often; about 10% of patients come to the ophthalmologist with this problem.
Many people ignore this symptom; of course, this is unacceptable. Redness and peeling of the eyelids may be a sign of a disease that leads to decreased visual acuity or complete loss.
What ophthalmological diseases cause the eyelids to swell and peel?
In this article
- What ophthalmological diseases cause the eyelids to swell and peel?
- Blepharitis of various etiologies
- Ulcerative blepharitis
- Scaly or seborrheic blepharitis
- Demodectic blepharitis
- Allergic blepharitis
- Conjunctivitis: symptoms of the disease
- Bacterial conjunctivitis
- Viral conjunctivitis
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Stye - bacterial inflammation of the eyes
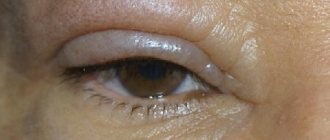
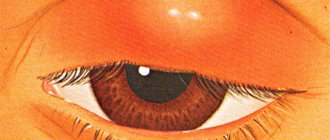
The reaction of the eyes to irritation, inflammation, and infection almost primarily manifests itself on the eyelids. Their pronounced redness and swelling most often indicate the presence of an inflammatory or infectious disease, even if other signs are not yet visible. Let's consider what pathologies these may be.
Scaly or seborrheic blepharitis
It is the most common form of pathology. When it occurs, the upper eyelids become red and swollen, and a sticky secretion may be released, which causes itching and sticks the eyelashes together. Yellowish scales are formed in the interciliary space, tightly attached to the tissues. Gradually, the swelling becomes more pronounced, and profuse lacrimation appears. Often the inflammatory process with scaly blepharitis moves to the conjunctiva, then blepharoconjunctivitis begins to develop. The disease can also be accompanied by seborrheic dermatitis in different parts of the head, which are covered with scales, and their peeling is observed.
Possible complications
The crusts that appear on the skin around the eyes can partially or completely peel off, and pathogenic microflora - from the environment, from the surface of the hands - enter small wounds. This causes the development of a secondary inflammatory process, after which, among other things, scars may remain.
Demodectic mange causes eyelash loss (rejection of hair follicles). Even after the disease is eliminated, their growth is not always restored.
Lacrimation, which is accompanied by blepharitis and allergies, creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora and intensification of the inflammatory process.
Demodectic blepharitis
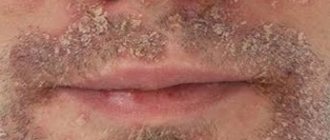
The cause of this type is the Demodex mite, which affects the upper eyelids and sometimes the lower eyelids. They become noticeably red and swollen, a sticky liquid is released, and the eyelashes stick together.
At the base of the eyelash row, sebaceous secretions and particles of the epidermis accumulate. Eyelashes look like they are covered with frost. This form of the disease is characterized by severe itching, dryness and burning, peeling of the eyelids, especially in the morning after waking up. The mite is detected at the roots of the removed eyelashes when examined under a microscope.
Diagnostics
Initially, the ophthalmologist conducts a visual examination of the patient, asking him in detail about the symptoms accompanying the course of the disease and illnesses suffered in the recent past.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a blood test is performed, eye secretions and tear fluid are taken for examination. To visually analyze the condition of the organ of vision, the doctor uses a slit lamp. To detect eyelash mites, four eyelashes are taken from the upper and lower eyelids for laboratory testing.
Allergic blepharitis
It develops during the flowering period of plants, and can also be caused by hygiene products, cosmetics, and household chemicals. In this case, not purulent, but mucous contents are released, increased lacrimation, a reaction to bright light are noted, the eyelids turn red and peel. Symptoms usually appear in both eyes at once. Sometimes gastritis, cholecystitis, tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, etc. can provoke the disease.
There are many types of blepharitis. There are also meibomian, drug-induced blepharitis and some others. However, all diseases in this group are characterized by common symptoms: redness and inflammation of the eyelids, their peeling, itching and dryness. If such signs appear, you should visit an ophthalmologist to make a diagnosis. Symptoms may also be a manifestation of another eye pathology - conjunctivitis.
How to get rid of peeling eyelid skin
Any eye disease, even minor, requires proper treatment. Such a seemingly harmless symptom as peeling on the eyelids should not be ignored.
If, apart from dry eyelids, there are no other symptoms (pain, photophobia), or there is no opportunity to get to an ophthalmologist, you can try to alleviate the condition yourself:
- Provide rest to your eyes - limit watching TV, do not use the computer. Wear sunglasses when going out into the sun.
- Apply brewed and squeezed tea bags to your eyes, make compresses with natural rose water and herbal infusions.
- Do not use decorative cosmetics.
- Do not eat possible allergens.
- Relax and get a good night's sleep.
- Do not use contact lenses
If the cause of peeling of the eyelids is minor (overwork, allergies to cosmetics), your health will improve after eliminating the irritant, and after a few days the skin condition will normalize.
If peeling is accompanied by severe pain and unresponsiveness to bright light, a visit to the ophthalmologist cannot be postponed.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the eyes of a bacterial nature if not treated in a timely manner poses a great danger to adults and children. The causative agents of the disease are various pathogenic bacteria: staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci, chlamydia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other microorganisms. Even a newborn baby can get bacterial conjunctivitis if it is infected from a sick mother.
If the eyelids are swollen, red, or flaky, this may most likely indicate the onset of a disease. Purulent discharge, severe itching and eye irritation also occur. Some types of bacterial conjunctivitis, for example, gonococcal and chlamydial, can lead to serious damage to the visual organs if not treated promptly. In an advanced stage, the disease becomes chronic, and the corneal tissue is destroyed and becomes cloudy, keratoconjunctivitis, blepharoconjunctivitis develops, scars form - this is what bacterial conjunctivitis can result in if you neglect it.
Which doctor should I contact?
Initially, when your eyelids peel and itch, you need to make an appointment with a therapist. Then, depending on the type of suspected disease, you will need to contact an ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist). If a relationship between peeling and hormonal imbalance is established, you need to make an appointment with an endocrinologist.
When inflammation of the tissues around the eyes is caused by intolerance to certain substances, an appointment with an allergist is indicated. Demodectic mange and fungal infection are eliminated by dermatologists with the simultaneous assistance of ophthalmologists.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a therapist online
Viral conjunctivitis
The disease develops when various viruses enter the body. The most common of them is adenovirus, and pathology can also be caused by herpes simplex virus, enterovirus, Coxsackie virus, and herpes zoster. Viral conjunctivitis often develops against the background of colds - influenza and ARVI.
Here are its main features:
- redness and swelling of the eyelids;
- the eyelid peels and itches;
- formation of follicles and ulcers on the edges of the eyelids;
- the lymph nodes located in front of the ears become inflamed;
- there is a feeling of “sand” in the eyes, dryness, photophobia;
- The cornea may become cloudy and the quality of vision may decrease.
To treat the viral form of conjunctivitis, medications are prescribed in the form of ointments and drops. You should definitely contact an ophthalmologist instead of looking for advice on the Internet.
Prevention and care of eyelid skin
It is impossible to 100% eliminate the risk of flaky skin around the eyelids, since the symptom is associated with various processes occurring in the body. But it can be reduced with simple preventive measures:
- Buy high quality cosmetics, do not skimp on yourself and your health. Be sure to remove your makeup before going to bed;
- To wash your face, use clean water and toners that suit your skin type;
- Apply soothing compresses once every seven days;
- Give your eyes rest, do not overstrain the organ of vision;
- Create a balanced diet, eat healthy foods and, if necessary, take vitamin complexes;
- Avoid touching your face and eyes with unwashed hands.
| To prevent the development of this or that pathology, carefully monitor your health and listen to your body. If peeling occurs, seek medical attention immediately. |
Allergic conjunctivitis
The reaction occurs due to contact with the mucous membrane of the eyes of any irritant. In the world in recent decades, there has been a noticeable increase in the number of allergic manifestations, regardless of region. Doctors attribute this to widespread deterioration of the environmental situation, water and air pollution, and poor food quality. The human immune system weakens and begins to react incorrectly to ordinary substances, perceiving them as dangerous to the body.
Here are the types of allergic conjunctivitis that are common in adults and children:
- Hay fever, also known as seasonal rhinoconjunctivitis, or “hay fever,” is the most common type of allergic reaction that occurs when certain plants bloom. Wind-borne pollen reaches mucous membranes, causing an irritant reaction in people sensitive to it. Symptoms of hay fever are often confused with viral conjunctivitis - outwardly their manifestations are quite similar.
- Eye irritation that occurs as a reaction to products from pets. Allergies often do not arise from fur or fluff, as many people believe. In this case, an allergy can occur even to hairless cats - Sphynx cats. The body reacts to certain secretions of animal glands - saliva, sweat. For example, cats constantly lick themselves, so particles of saliva are present on their fur or skin - they cause inflammation of the eyes.
- Allergic conjunctivitis that develops from taking medications. It happens that the body is too sensitive to any component of the drug, and this leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes. Most often, inflammation occurs after taking antibiotics, administering local anesthetics during surgery, and also when instilling liquid medications into the eyes.
Allergic conjunctivitis can also develop due to careless care of contact correction products, as a reaction to food products, or due to other factors. Here are the signs characteristic of this type of pathology:
- peeling of the eyelids, their swelling and redness;
- itching and lacrimation;
- sensitivity to bright light;
- nasal congestion, snot, cough.
When an allergy occurs, normal life activities become difficult. The eyes begin to itch very much, in this state it is difficult to go to work or school. The patient should urgently contact an ophthalmologist for diagnosis and prescription.
Treatment with drugs
Therapy is selected for each patient individually after identifying the factor that triggered the development of the disease. It is important to treat not the manifestation of the disease, but its source. Otherwise, any measures will not bring results.
Most often, medications are the first to hit the target. The doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed eye drops are Okomistin, Albucid and Tsipromed. For damage to the mucous membrane, tetracycline ointment is used;
- Antiallergic and antihistamine medications. Helps get rid of itching and relieve swelling. This could be Claritin, Loratidine, or hormonal ointments that contain hydrocortisone;
- Antiseptic drugs. Block the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. Use the most gentle means, such as “Vitabakt” or a solution of boric acid;
- To combat the fungus, Levorin or Nystatin is prescribed;
- Antiviral drugs. These include “Anaferon”, “Solcoseryl”;
- If the cause of peeling lies in inflammation, then Sofradex or Maxitrol eye drops will help;
- To relieve visual fatigue, doctors recommend taking Visine.
To strengthen the immune system and increase the body's resistance to negative factors, take a course of Vitrum Vision or Complivit Oftalmo vitamins.
| Often, to get rid of unpleasant symptoms, doctors prescribe topical medications (ointments and drops). They affect the source of the disease and almost never enter the circulatory system. If you need to use several types of drops, use them with a break of fifteen minutes. |
Stye - bacterial inflammation of the eyes
Barley, or hordeolum in other words, is a purulent acute inflammation of the organs of vision, which is characterized by noticeable external manifestations in the upper or lower eyelid. It usually occurs due to a bacterial infection or a weakened immune system. What are the signs of stye, what to do if you notice them in yourself?
According to statistics, about 80% of the population suffers from barley. This is a common illness in childhood - children often become infected with bacterial infections by touching their eyes. Inflammation usually occurs very quickly, but the abscess itself does not form immediately, but 3-4 days after the first signs. Here are some of them that may indicate that you or your child is developing stye.
At the initial stage, the eyes begin to experience severe itching, peeling, redness of the edges of the eyelids, and their swelling. When pressing on the swelling, quite painful sensations occur. Sometimes the swelling is so severe that the eyelids close completely. If the external symptoms of gordeolum are also accompanied by headache, fever, and enlarged lymph nodes, then this indicates that, most likely, several purulent formations are ripening at once or the process has progressed into another disease.
Two to three days after the first signs appear, a purulent head forms on the inflamed area (usually around the base of the eyelash), and the pain decreases slightly. After a day or two, the head opens, the pus comes out, the swelling of the eyelids subsides, after which all symptoms gradually disappear. Usually this process takes about seven days, and the abscess leaves no traces.
The cause of barley is a bacterial infection, in almost 90% of cases it is Staphylococcus aureus - a pathogenic bacterium, the causative agent of a large number of dangerous diseases. It can also be triggered by a fungus, the microscopic demodex mite that lives on the eyelashes, or various types of fungi. Microorganisms entering the cavity of the hair follicle or sebaceous gland provoke blockage of the excretory duct, inflammation of the cavity walls and accumulation of pus.
The abscess can be located on the edges of the upper or lower eyelid so that it is visible from the outside - this type of stye is characterized as external. But it can also be internal, forming under the eyelid on the mucous membrane. In its external form, the purulent formation usually opens and goes away without consequences (with proper treatment of barley). But the hordeolum, which appears on the inside of the eyelid, is dangerous. It causes great inconvenience: it rubs against the eyeball and feels like a foreign body, causing discomfort. In addition, if the stye breaks through and pus enters the internal bloodstream, very serious consequences can occur: chalazion, chronic meibomitis. Vascular thrombophlebitis occurs when pus spreads into the vessels of the eye. The danger is phlegmon of the orbit - this is a purulent inflammation of the retina with its subsequent melting. Against the background of phlegmon, meningitis can also develop. All these ailments can lead to atrophy of the eye structures and loss of vision. Therefore, in this case, it is recommended to immediately go to the hospital, and not wait until the stye on the eye bursts inside on its own.
So, if you find that your eyelids are swollen and red, and have begun to peel, these may be signs of a viral or bacterial infection or allergic eye inflammation. In such cases, it is imperative to contact a specialist to establish a diagnosis and receive recommendations for treatment.
Help from traditional medicine
If the cause of the anomaly does not lie in a serious illness or you simply don’t have time to visit the clinic, try using the gifts of nature and grandma’s recipes. Some of them are excellent substitutes for medications and successfully fight the disease. However, despite their effectiveness, there is no need to abuse traditional medicine. Before using any recipe, consult your doctor.
To moisturize dry skin, use melt water and wash your face with it every morning; herbal decoctions or tar soap are also suitable for this purpose. Tinctures from medicinal plants are an excellent option for compresses. The most commonly used plants are calendula, chamomile, and St. John's wort. At the stage of epidermal regeneration, you cannot use string and celandine, as they are very drying. Use the latter with extreme caution, as it is poisonous.
To prepare a medicinal decoction, no special knowledge or skills are required. Take a tablespoon of herb, pour a glass of boiled water and keep in a closed container until the infusion has cooled. Next, strain it and use it in the following way:
- As lotions. Soak a cotton pad in the liquid and apply to the affected organ of vision for half an hour;
- For washing. Soak a cotton swab well in the solution and wipe the eye in the direction from the nose to the temple;
- For rinsing. Dilute the broth with boiling water in a ratio of 1:5, and irrigate your face with it every time after washing.
Several proven traditional medicine recipes will also help get rid of peeling.
Camomile tea
Take one tablespoon of dried chamomile flower and pour boiling water over it. After the composition has infused, strain it. Soak a cotton pad in the liquid and apply to damaged eyes. If the infusion is diluted with water, it can be used as eye drops. It relieves fatigue, relieves dryness and irritation.
Tea brewing
They help with visual fatigue and as therapy for a variety of ophthalmological pathologies. It is better to use loose leaf tea, but you can opt for bagged tea. The brew should be very strong, soak the discs in it and apply for about fifteen minutes.
Aloe juice
Cut the aloe leaf and place it in the refrigerator, this will help achieve the desired consistency. Within seven days, the juice is saturated with enzymes and becomes liquid. Lubricate damaged skin with it. The juice moisturizes well, eliminates redness and itching, and restores the epidermis.