Allergies in children are as common as colds. While many parents may find it intuitive to distinguish between runny nose symptoms and allergies, in some cases it can be quite challenging, especially if symptoms appear when plants are in bloom.
If persistent symptoms of a runny nose, cough, sneezing and itchy eyes persist for more than a week while pollen is flying, then an allergy is most likely to blame for your runny nose. But with one important caveat - if your child is an infant or a toddler under the age of three, then he is much less likely to have seasonal allergies. While there are exceptions to every rule, most children don't begin to experience hay fever symptoms until they are 3 or 4 years old, after they have been seasonally exposed to large amounts of pollen and have developed a sensitivity to the allergen. Interestingly, pollen allergies and food allergies are linked: more than half of children who suffer from hay fever also have food allergies.
How do allergies occur in children?
Allergy symptoms occur when a child's body overreacts with a protective immune response to normally harmless substances. Instead of not reacting to dandelion, an allergic child's body will quickly release a series of chemicals (including histamines) upon encountering the flower that cause itchy and red eyes, swollen mucous membranes, a runny nose and sometimes a cough. There is no clear, accurate way to tell at a glance whether your child has seasonal allergies when they start sneezing in the spring (or fall).
Causes
A child develops a food allergy due to:
- genetic predisposition;
- decreased protective functions of the intestinal mucosa;
- large amounts of food consumed, etc.
In circumstances where tolerance fails, the immune system produces an Ig E antibody response against the specific food. The process begins in the intestines (although it can also affect other areas, such as the respiratory system or skin).
When a patient consumes a “dangerous” product, the antigen associated with Ig E is detected on the surface of basophils and mast cells. At this time, they are activated, and histamine and other inflammatory substances are released.
What is hay fever and why does it occur?
Hay fever is the most common type of allergy and is an allergic reaction to pollen in the air and environment. Children with seasonal allergies exhibit symptoms at certain times of the year when certain allergy triggers (such as grass or tree pollen) are circulating. However, some children and adults may be allergic to more than one pollen or trigger, causing symptoms to appear at different times throughout the year. Most children with hay fever experience a noticeable change in symptoms around the same time each year, which is during the flowering season.
Seasonal allergies typically first appear after preschool age, although they can develop at any time during childhood, usually before age 10. Allergy symptoms typically change with age, peaking in your 20s, and then often disappear as you get older. Allergies are usually inherited. If one parent has allergies, there is a 25% chance that the child will also have allergies. And if a child is lucky enough to have both parents with allergies, the risk of developing allergies increases to more than 60%.
Characteristic symptoms
It is important for young parents to figure out whether the rash that appears is an allergic reaction or is it a source of dangerous infectious diseases.
Characteristic features of an allergic rash in a child are:
- Swelling of the face (with an infectious etiology of the rash, swelling is not observed)
- Skin itching (often accompanies a rash of an allergic nature, less often - infectious)
- No high fever (infectious infection is accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature).
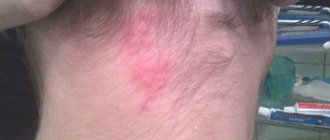
An allergic rash on the back, abdomen, neck, and arms is often accompanied by clear mucus discharge from the nose. In infectious diseases, mucus quickly thickens, becomes cloudy, with a greenish tint.
The nature of possible rashes can be seen in the photo.
The skin reacts with the appearance of pimples, blisters, papules, round spots, often with exudate, then they can develop into a continuous swollen surface, sometimes covered with a crust. With severe itching, irritability may appear.
An allergic rash in infants mainly appears in the upper part of the body, in the folds, and may be accompanied by swelling of the facial organs: tongue, larynx area, which causes risks of suffocation. If symptoms such as nasal congestion, lacrimation, swelling of the cheeks occur, parents should not hesitate, but call an ambulance, since the development of Quincke's edema may become a complication.
How to treat seasonal allergies in children?
Over-the-counter antihistamines are most often used for allergy symptoms. Typical antihistamine active ingredients found in over-the-counter medications include diphenhydramine, loratadine, cetirizine, or chlorpheniramine. Most often, antihistamines that do not have a sedative effect are used for children - loratadine or cetirizine.
Over-the-counter allergy medications should only be used in children over 6 years of age. If your child is under 6 years of age and has allergy symptoms, talk to your pediatrician about prescribing the best medications available at the lowest appropriate dose.
Treatment of urticaria
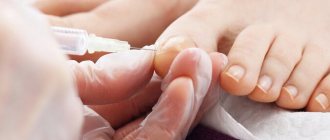
The only way to get rid of the disease is to avoid contact with the allergen, which is previously detected by laboratory tests.
If testing does not reveal a provoking factor, and the urticaria is episodic, then taking antihistamines will quickly eliminate the symptoms. During treatment, it is recommended to follow a diet that, in case of urticaria, will help prevent the recurrence of the disease. The menu should include only hypoallergenic products: lean boiled meat, soups with recycled meat broth or vegetarian. It is better to choose rice, buckwheat, and oatmeal from cereals. Low-fat cottage cheese, natural yogurt, apples, dried fruit compote, excluding raisins, and whole grain bread are recommended.
Citrus fruits, nuts, fish and all seafood, chocolate products, smoked meats, coffee, eggs, honey, and store-bought baked goods should be excluded from the menu during treatment.
Treatment is carried out by a dermatologist and an allergist-immunologist. For topical application, ointments for urticaria are effective; they not only relieve itching, but also eliminate swelling, redness and a burning sensation on the skin. One of the most effective is Dimetinden gel, which must be applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the skin up to 4 times a day.
A course of antihistamines is prescribed in the form of tablets. Your doctor may also prescribe calcium gluconate or calcium chloride for urticaria. They help reduce the symptoms of allergies, but they should only be administered under the supervision of a doctor in the treatment room.
If antihistamines do not provide the desired effect quickly, or for severe forms of hives, corticosteroids are used, which can be applied to the skin or taken in the form of tablets or injections.
What else do parents need to know?
One in five people suffers from allergies at some point in their lives. Hay fever is the most common type of allergy. It is easily treated by avoiding allergens, washing the child in the shower after returning from outside during flowering season, over-the-counter medications, and sometimes additional prescription medications. Most children with hay fever only need allergy medication during seasonal outbreaks.
Allergy symptoms often change with age. Allergy symptoms can worsen during early childhood and often disappear as people get older.
Drug labels list the ingredients of allergy medications. Use the lowest dose possible to treat symptoms, and check with your child's doctor if he is younger than 6 years old before giving him an over-the-counter antihistamine.
Possible complications
The danger is that this condition gradually worsens if no measures are taken over time:
1. First, against the background of sensitization, the body develops dermatitis.
2. Then the respiratory system is damaged in the form of atopic rhinitis.
3. If the antigen is not excluded, then bronchial asthma manifests itself.
The most dangerous complication is anaphylactic shock. It develops rapidly – 1-3 minutes after contact with the antigen. It is characterized by bronchospasm, laryngeal edema and collapse, which can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Food allergies
Hives and facial swelling are the most common symptoms of food allergies. Hives appear as raised pink bumps with pale centers, similar to insect bites. Other symptoms include itching and swelling in the mouth, runny nose and cough, vomiting and diarrhea. Life-threatening allergic reactions may also include difficulty breathing and/or swallowing. The medical name for this phenomenon is anaphylaxis. Most of these reactions occur suddenly within 10-20 minutes. All this happens within 2 hours after eating a certain food containing allergens.
Diagnosis of rashes in babies
Due to the huge variety of causes and types of skin rashes in young children, it is necessary to immediately seek advice from a pediatrician, especially if an allergic rash is observed in a newborn. The body's reaction to a particular allergen can be rapid.
During diagnostics the following is performed:
- Study of the biochemical composition of blood
- Allergy tests are carried out
- The state of immunoglobulin in the blood is revealed
For a doctor to make a correct diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment, it is important to know what the baby’s diet was like the day before, whether the diet has changed, whether medications have been taken, or whether there has been contact with chemical ingredients.
Main allergens in children
An allergic rash on the neck, abdomen, arms, legs is often the result of a child’s immune system reacting to provoking factors. Allergens can be:
- Food: eggs, milk, fruits, honey, nuts, seafood
- Medicines: antibiotics, vitamins and other drugs
- Chemical factors: soap, washing powder used to wash the child’s clothes
- Dust, wool, pollen from flowering plants
- Insect bites, burns from plant leaves
- Effect of ultraviolet
An allergic rash on the stomach or arms may appear as a result of contact dermatitis. Doctors consider the most dangerous reaction of the body to an allergen or irritant, when the symptoms of an allergic rash in children manifest themselves within 15-30 minutes after interaction with the allergen.
Genetic inheritance is considered a significant factor in the susceptibility of children to atopic dermatitis. Provided that one of the adults (mother/father) often suffers from malaise as a result of food or drug allergies, the likelihood of the disease developing in the child increases.
Main causes of food allergies
8 foods cause 9 out of 10 food allergies.
In the first year of a child's life: cow's milk, soy milk and egg.
Older children: peanuts, tree nuts, fish, seafood and wheat.
Seafood includes shrimp, crab, lobster, clams, oysters and scallops.
Tree nuts include all nuts (such as almonds and cashews) except peanuts. Peanuts and tree nuts are the most common triggers for severe reactions.
Of children with a proven food allergy, 40% have severe reactions. The remaining 60% have a mild reaction.
Still have questions?
Get an online consultation from leading allergists in St. Petersburg!
A professional and experienced pediatrician will answer your questions.
Medical care for a child without leaving home at a convenient time.
sign up for a consultation
A Skype consultation lasts 45 minutes.
Prevention measures
Complete recovery is possible only with early identification of factors and their exclusion from the diet. By following nutritional recommendations, relapses of the disease can be prevented. Some children experience spontaneous recovery as oral tolerance increases. Many people “outgrow” the disease, but you shouldn’t count on it.
Cross-reactions with other foods
Children with allergies to the following foods may react to other foods:
Cow's milk allergy: 90% also react to goat's milk and 40% to soy milk.
Egg: in 5% there is a reaction to chicken meat
Peanuts: In 5% of cases there is a reaction to other legumes (such as peas or beans). In 30% there is hypersensitivity to tree nuts.
Fish: in 10% a reaction to seafood is also observed.
Melon: 90% reacts to bananas and avocados
Ragweed pollen allergies can cause a cross-reaction with all melons, bananas and tomatoes.
Birch pollen allergies can cross-react with raw potatoes, carrots, celery and apples.
Grass pollen allergies may cross-react with tomatoes and kiwis.