Oncologist
Zhukova
Elena Nikolaevna
13 years of experience
Oncologist, member of the Russian Society of Mammologists, member of RUSSCO (Professional Society of Chemotherapy Oncologists), member of the European Cancer Society ESMO, American Society for Melanoma Research - SMR
Make an appointment
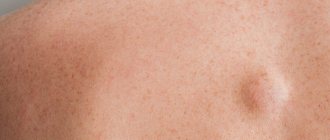
Among benign breast formations, a significant proportion is lipoma - a fatty tumor, the development of which is provoked by the action of several internal and external factors. Breast lipoma, or fatty tumor, is diagnosed in more than 10% of patients who contact specialists about the discovery of a dense formation in the breast structure. Modern medicine has studied such cases well and is ready to offer optimal treatment for the pathology with a guarantee of safety for the body.
Causes of breast lipoma formation
Factors that can trigger the process of lipoma formation in the breast are divided into several groups:
- Hormonal. Associated with the premenopausal period, when global hormonal changes occur in the body. The size of the ovaries decreases, the inner layer of the uterus becomes thinner, and glandular tissue in the breast is replaced by fatty deposits. If these processes are disrupted, there is a possibility of excess formation of adipose tissue, which becomes the cause of tumor formation. There is also a risk of wen formation in women of reproductive age, which may be associated with menstrual irregularities, the use of oral contraceptives and the use of hormonal drugs for a long time.
- Metabolic, associated with impaired fat metabolism in the body. High-density lipoproteins can form large accumulations and become covered with a sheath of connective tissue. The reason for this phenomenon is physical inactivity, a diet with a predominance of animal products, diseases of the endocrine system, etc.
- Genetic, associated with the influence of a hereditary factor. Defects in the HMG IC gene cause lipomatosis, diseases associated with the deposition of adipose tissue in various parts of the body.
- External. The formation of a wen can be caused by uncomfortable underwear, breast injuries, previous surgeries, bad habits, frequent stress, etc.
The simultaneous impact on the body of several of these factors leads to excessive production of adipose tissue and its encapsulation - encapsulation in a dense shell, which gives mobility to the tumor structure and makes it easy to palpate under the layer of skin. In medicine, there have been cases of transformation of a benign formation into an oncological process in patients with oncology or in those women in whose families there are cases of breast cancer.
Lipoma removal methods
If you do not pay attention to the lipoma and do not remove it in a timely manner, the risk of its degeneration may increase. The doctor decides how to treat and which method to choose on an individual basis.
- Operation (surgical method).
The doctor treats the surgical field and numbs it. He carefully makes an incision over the lipoma, grabs the capsule and removes it. After the tumor is separated from the surrounding tissue and removed, the wound is sutured. A bandage is placed on top. If regular threads were used, the sutures are removed after about two weeks. Sometimes, to avoid making an incision, a small lipoma is removed with a needle, simply sucking out its contents. To prevent the tumor from reappearing, special medications are injected into the appropriate area. It should completely disappear within about 3-4 months. However, this option takes quite a long time, and there is a risk of re-development of the lipoma. - Removal of lipoma with laser.
The doctor cuts the skin with a laser beam, then removes the capsule and burns its remains. After about two weeks, complete healing occurs. However, this method is not suitable if part of the tissue needs to be sent for histological examination or if it is very large. In addition, the laser method is contraindicated in patients with diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states, and during pregnancy and lactation. It is also prohibited to carry out such removal of a lipoma in the presence of an oncological process, herpes in the acute stage and inflammatory skin diseases, especially localized at the site of the intended intervention. - Removing lipoma using radio waves.
This is a completely bloodless method. There are usually no scars left after surgery. It is used when the size of the lipoma does not exceed 6 cm. The essence of the technique is the removal of the lipoma along with the capsule and coagulation of the blood vessels passed through a tungsten filament. The removed tumor can be sent for histological examination. However, this method cannot be used if the patient has metal prostheses or suffers from diabetes.
Symptoms
Fat formation can be detected accidentally during examination or palpation of the breast. The nodule is designated as it reaches a size of about 1.5-2 cm. most often the area of its localization is the upper outer part of the mammary gland. Education can be single or paired. When palpated, the following symptoms of breast lipoma can be identified:
- Round or oval shape.
- Smooth surface with clear contours.
- Elastic, dense or doughy consistency, the nature of which is associated with a specific type of tumor.
- Painless.
- Mobility.
Pain syndrome with lipoma is extremely rare. Its appearance is associated with tumor growth and compression of muscle tissue or blood vessels, which causes circulatory problems and tissue injury.
Kinds
Lipomas are classified according to several criteria.
By localization:
- Subcutaneous - the formation is located between the dermis and glandular tissue.
- Intramammary - the tumor is located between the milk lobules.
- Deep - formed in the thickness of the gland, closer to the chest.
By degree of distribution:
- Nodular - a clearly demarcated formation.
- Diffuse - with germination into other layers.
According to morphological structure:
- The classic form - the tumor is represented only by adipose tissue.
- Lipofibroma is a combination of connective tissue and fatty structures with a predominance of the latter.
- Fibrolipoma – represented predominantly by a connective tissue structure with small lipid areas.
- Myolipoma is a fatty tumor with penetration into smooth muscle fibers.
- Myxolipoma - formation cells produce a pathological mucous secretion inside the capsule.
The last 2 species are much less common than the others. In menopausal women, wen with a fibrous component is more often diagnosed.
Diagnostics
A preliminary diagnosis of “breast lipoma” is usually made during an initial examination by a mammologist and palpation of the breast. To accurately establish the nature of the formation, differentiated diagnosis is required, which involves excluding other diseases with similar symptoms. The list of required studies includes:
- Consultation with an oncologist, gynecologist and mammologist.
- Taking a blood test for tumor markers.
- Ultrasound of the breast.
- Blood chemistry.
- Mammography.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
- Biopsy of tissue obtained by puncture using a long needle.
The results of the conducted studies make it possible not only to identify the nature of the formation, but also, with a high degree of probability, to name the reasons for its occurrence.
Diagnosis of lipoma
There are no typical signs of breast lipoma. It is important to differentiate the neoplasm from other benign tumors and breast cancer.
Patient examination algorithm:
- Consultation with a mammologist, and, if necessary, related specialists (gynecologist, endocrinologist, oncologist).
- Donation of blood tumor marker CA 15-3 to exclude breast cancer.
- Biochemical blood test. Panel of hormones of the reproductive system, thyroid gland.
- Ultrasound of the breast.
- Mammography is an x-ray of the breast. The nodal form is visualized well. The method is not informative if the growth pattern is diffuse; it is technically impossible to carry out with a small size of the gland.
- CT, MRI according to indications. Tomography determines the exact location and blood flow characteristics of the lipoma.
- Biopsy. The procedure for collecting a tissue sample is carried out using a long needle puncture. The cellular structure of the biopsy specimen is studied. A biopsy is required to confirm the benign nature of neoplasia and determine its type.
Lipoma treatment
If the tumor is growing extremely slowly or is in a stable condition, surveillance tactics with ultrasound examination are provided at least once every six months. If concomitant pathologies are detected in the body, specialized treatment is prescribed with mandatory monitoring of the lipoma.
The decision to undergo surgery for breast lipoma is made if:
- The formation quickly increases in size.
- The patient notes persistent pain.
- The tumor is large in size, distorting the natural shape of the breast.
- There are signs of necrosis of gland tissue.
- There is a high risk of malignant degeneration of the tumor due to a hereditary factor.
The surgical technique for the treatment of breast lipoma is selected taking into account the size and location of the lipoma:
- Enucleation is the removal of a wen with a capsule using classical surgery or endoscopic intervention, which is carried out through thin punctures of the skin. The destruction of the tumor is carried out under the influence of radio waves or a laser beam.
- Removal of fatty tissue while preserving the membrane (aspiration). The procedure is low-traumatic and leaves no marks on the skin. However, preservation of the capsule may cause re-accumulation of excess adipose tissue inside.
- Partial resection (removal) of the mammary gland. It is used in cases of high risk of degeneration of wen tissue into a malignant formation. The operation covers the tumor area and adjacent tissues. The extracted contents are subjected to histological analysis; if symptoms of oncology are detected, adjacent tissues and lymph nodes are subject to removal.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, vitamins and immunomodulators.
Causes
The reasons for the development of fibrolipoma have not been precisely established. Some researchers believe that the neoplasm occurs as a result of embryogenesis disorders (intrauterine formation of atypical adipose tissue cells in the mammary gland). Other scientists believe that the main factor in the development of the disease is systemic metabolic disorders. In addition, experts focus on the possible connection between breast fibroids and changes in hormonal levels - this connection is supported by the frequent manifestation of the disease during the period of hormonal changes in the body (during menopause or premenopause). Other factors contributing to the development of fibrolipoma include diseases of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, liver and pancreas. There are suggestions that the risk of breast fibrolipoma increases with alcoholism, diabetes, living in unfavorable environmental conditions and prolonged psycho-emotional stress. In some cases, a hereditary predisposition is revealed.
Diagnosis and treatment of breast lipoma at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
Specialists from the clinic of JSC "Medicine" in the Central Administrative District of Moscow invite patients with suspected benign formations in the tissues of the mammary glands. Our own diagnostic center with high-precision equipment will allow you to conduct the necessary examinations and accurately identify the nature of the pathology, as well as make a decision on the need for surgical intervention. It is possible to participate in the diagnosis and treatment of other specialized specialists. Call to make an appointment with a mammologist and get additional consultations. The recording is also available on the clinic website.
Types of lipomas
Lipomas are distinguished according to several characteristics.
By the number of neoplasms:
- Single wen (formed in the form of one compaction);
- Multiple lipomas (formed throughout the body, most often this disease is inherited).
According to tumor consistency:
- Nodular formation (formed from adipose tissue, has a soft elastic consistency);
- A diffuse tumor is divided into: fibrolipomas (in the formation of a tumor, in addition to adipose tissue, connective tissue cells also participate, and this formation has a fairly hard consistency);
- lipofibroma (the wen is formed in exactly the same way as with fibrolipoma, but in this type adipose tissue predominates, so upon palpation the formation is very soft);
- Angiolipoma (the tumor itself has a network of blood vessels).
- Myxolipoma (in addition to blood vessels during the formation of a tumor, there is also mucus tissue).
- Myolipoma (a rare type of tumor that consists of adipose tissue and muscle fibers).
Table: research methods and analyzes - norm and deviations
| Survey | Norm | Deviations |
| Mammography | The structure of the mammary gland is uniform, there are no compactions or darkening. | Visible oval or round formation. In the case of a cancerous tumor, the contours are unclear and uneven. |
| Ultrasound examination of the mammary glands | The thickness of the glandular tissue is no more than 14 mm. The condition of the milk ducts without expansions and deformations in the areolar segment and along the periphery. | Excessive decrease or increase in glandular tissue by more than 20 mm. Formations with a heterogeneous structure are visible. |
| Biopsy | No atypical inclusions or bodies were found. | An abnormal collection of cells, or unusual connections. Obvious changes in cells. |
| Blood for biochemistry | Protein 63-87 g/l. Protein fractions: albumins – 35-45 g/l, globulins – 21.2 – 34.9 g/l. | A deviation is considered to be an increase or decrease in protein levels. |