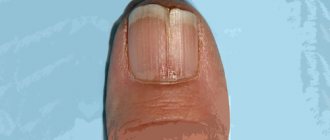
How does paronychia manifest?
The process itself takes place on the palms, but due to the thickness of the skin, the liquid penetrates through the lymphatic openings to the areas surrounding the nail plate. Often paronychia provokes the occurrence of periungual panacirium - acute purulent inflammation of the tissues of the finger.
The nature of the course of this disease can be:
- Acute , in which it lasts less than one and a half months. The disease is bacterial in nature and is accompanied by severe pain and suppuration, mainly on the back of the fingers. Tissues located closer to the palm may also be affected - in this case, the inflammation spreads deeply, involving the hand.
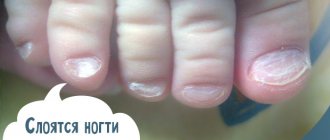
- Chronic , with a duration of more than one and a half months. As a rule, this type of paronychia is caused by chemicals, dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, and onychomycosis. In the chronic course of the disease (without the development of an abscess), the nail plate is affected: it becomes deformed, splits, becomes dull and yellow, crumbles, thickens (with fungal infection).
Causes of a sore finger near a toenail or hand nail
Improper manicure as a cause of paronychia
One of the most common causes of inflammation of the finger in the nail area is incorrect performance of pedicure and manicure.
Careless actions can damage the cuticle and provoke an inflammatory process with further accumulation of pus around the nail. Typically, such inflammation is caused by streptococcal and staphylococcal microorganisms that live on the skin of every person.
The development of the inflammatory process is influenced by certain conditions, such as:
- decrease in the body's immune forces
- presence of severe concomitant blood diseases
- metabolic disorders.
- fungus on the feet or nails.
Most cases of felon development occur after injury to the skin on the fingers. Moreover, the inflammatory process can occur even due to minor injuries - abrasions, scratches or splinters, cracks due to the skin being too dry and flaking. An infection penetrates the skin, which gives rise to purulent inflammation. For this reason, even minor wounds should be immediately treated with alcohol-containing solutions or iodine. Hangnails can also cause inflammation and the formation of pus in the tissues of the finger near the nail.
Causes of the disease
Hands and nails are an area of increased risk of injury. The skin surrounding the nail plate is quite thin, so it is easy to damage. The inflammatory process that develops in tissues is the result of injury. Women suffer from paronychia much more often than men, and the main reason for this is manicure done with instruments that have not been sterilized. Infectious agents such as staphylococci, streptococci, and fungi penetrate into soft tissues.
Factors that can lead to inflammation:
- constant mechanical impact on the hands or feet, work at elevated temperatures;
- frequent contact with aggressive chemicals or cold water;
- hangnails (in children, the habit of biting their nails and the skin around them);
- injury during manicure or pedicure;
- nail extensions;
- poor hand skin care, which results in cracks;
- weak immunity;
- insufficient hygiene;
- inappropriate or low-quality shoes, as well as using someone else’s shoes;
- thrombosis, thrombophlebitis and other diseases in which blood circulation in the feet is disrupted;
- lack of vitamins, unhealthy diet;
- stress;
- diseases of the endocrine system, especially diabetes.
Prevention of ingrown toenails
To prevent the nail from growing in, it is necessary to take the following preventive measures:
- Wear loose and comfortable shoes that do not put pressure on your toes.
- Trim your nails correctly, avoiding the formation of a nail plate that is too short at the root or too long, as well as hangnails that can grow into the nail fold.
- Walk barefoot as much as possible.
- Maintain regular foot hygiene.
- Treat fungus and other foot diseases in a timely manner.
- Use orthopedic insoles for flat feet.
- Protect your feet from injury, be careful and follow safety precautions at work.
- If you are injured or experience symptoms, contact your doctor immediately to receive professional treatment.
- Reduce body weight and treat diabetes.
Preventive measures will help significantly reduce the likelihood of an ingrown toenail.
Classification of paronychia and main symptoms
Characteristic forms
- Simple types of paronychia manifest themselves as an independent form of the disease, which is not a consequence of complications of other diseases. The skin around the nail turns red, swells, and minor pain appears. As a rule, with good immunity, the body copes with a simple form of paronychia in a few days; a visit to a doctor is not required.
- The purulent (pyococcal) form develops when microorganisms (staphylococci, streptococci) enter the tissues. The disease begins with the appearance of swelling and throbbing pain. After a couple of days, suppuration of the soft tissue occurs. Recovery begins after opening the abscess. Sometimes an abscess can spread to the hand; extremely rarely, it can spread throughout the body, affecting internal organs.
- Candidiasis is a form caused by fungi of the genus Candida. The nail fold loses the inner layer that protects the nail from damage. This form is chronic and is accompanied by minor inflammation. The purulent process is usually absent or not very pronounced. When fungi affect not only the skin, but also the nail plate, it begins to peel, crumble, thicken, and change shade. Most often, workers in the confectionery industry suffer from inflammation in the chronic stage.
- Ulcerative form - usually caused by pathogenic microorganisms or household chemicals, temperature exposure, injury, eczema or psoriasis. Ulcerative paronychia sometimes manifests itself as a complication of a simple form. Sores form on the skin around the nail, which can cause secondary infection.
- Horny form - occurs infrequently, mainly in patients with syphilis, characterized by the appearance of hyperkeratotic papules.
- The dry form is characterized by mild inflammation and the absence of suppuration. At the same time, the nail fold noticeably becomes coarser and flakes off.
- Tourniol is a form in which beta-hemolytic streptococci, staphylococci, and fungal microflora enter the tissue through wounds and burrs. Loose bubbles appear on the skin, the contents of which begin to fester. After opening the blisters, horseshoe-shaped wounds remain around the nail. Symptoms such as weakness and increased body temperature may appear. Tourniol is dangerous due to complete detachment of the nail and the development of lymphadenitis.
- Eczematous and psoriatic forms - the nail fold swells, becomes slightly inflamed, blisters appear, peeling, and the skin becomes thick. When the vesicles break open, crusts form. The nails acquire a lattice surface, longitudinal grooves, turn yellow, crumble and peel.
With the development of a purulent process, only the smallest ulcers open on their own. Therefore, to avoid an abscess, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Possible complications
With timely treatment of paronychia, fingers or toes are quickly cured. If you delay it and wait for everything to go away on its own, then the infection will even reach the muscles, tendons, bones of the finger, and enter the systemic bloodstream. Accumulations of pus can undermine the nail and lead to its detachment from the nail bed. In advanced stages, partial or complete removal of the nail plate with long-term rehabilitation is often required.
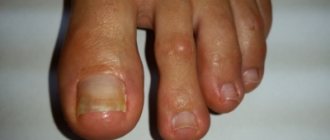
The main complication of chronic paronychia is nail dystrophy, caused by inflammation in the nail matrix. It manifests itself in the form of fragility, delamination of the nail plate, distortion of the shape, and the formation of grooves and grooves. The color of the nail plate may change.
Symptoms
Typically, the signs of paronychia are quite pronounced, which allows you to make a diagnosis quickly and accurately. They are expressed as follows:
- the patient complains of pain in the area of the nail plate; the nature of the pain can be different: throbbing, constant, pulling;
- swelling of the nail fold occurs and can spread to the entire upper part of the finger;
- due to swelling and pain, it is difficult to bend your fingers and work with your hands; if parochinia has developed on the foot, it hurts to put on shoes;
- damaged skin becomes red, burgundy, dark purple, and if there is suppuration, then yellow-green;
- if the process affects several fingers, body temperature often rises and pain appears.
The doctor determines the presence of the disease and determines the cause of the pathology: it may be associated with professional activity or with exposure to pathogenic microorganisms. In the second case, a microbiological test is prescribed to determine which pathogen caused the disease.
To confirm the inflammation process, the patient undergoes a general blood and urine test.
Based on the type of pathogen, paronychia is divided into:
- bacterial: in acute cases the culprit is Staphylococcus aureus, and in chronic cases – streptococci and pseudomonads;
- viral, the causative agent of which is the herpes simplex virus;
- fungal, in which infection occurs with fungi of the genus Candida;
- non-infectious, developing from exposure to adverse and irritating environmental factors, as well as as a side effect from taking certain medications; may be associated with skin diseases.
The “leaders” are bacterial and fungal forms of paronychia.
First aid
Let's look at this in more detail. As a rule, a patient seeks help from a surgeon only when the affected area does not allow him to lead a normal lifestyle. Pus on the toe near the nail can be the start of more serious complications. In severe cases, amputation is even required. The cause of an abscess can be an unsuccessful pedicure, fungal diseases and microscopic injuries. In addition, an abscess is a harbinger of diabetes. Inflammation can gradually spread to deep tissues. Then the process will become irreversible. What to do at the first signs of defeat?
So:
- Try to reduce the load on your sore leg.
- Apply a compress with potassium permanganate or alcohol to the affected area.
- Treat your foot with an antiseptic composition.
- Take an antipyretic.
- During treatment, limit contact of the affected area with water.
Consult a qualified physician at the earliest opportunity. Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis. After all, inflammation is often similar to a simple fungal infection.
Treatment options
The initial stage of the disease can be treated conservatively. If slight redness and mild swelling occur, you can use home methods. If a purulent process is noticeable, emergency assistance from a specialist - a podologist, surgeon, or dermatologist - will be required. For any inflammation accompanied by the accumulation of pus, surgical intervention is necessary.
During the treatment process, you need to remember the following rules:
- When doing housework and any other work, hands must remain dry, all actions are carried out wearing protective gloves;
- if the cause of the disease is chemicals, you need to temporarily stop or at least limit contact with them;
- if parochinia is localized on the feet, you should wear only comfortable, spacious shoes of good quality.
Treatment of purulent form
If an abscess is present, the abscess is opened surgically. If this is not done, the patient's condition will inevitably worsen. This operation is performed with or without local anesthesia. In the first case, small incisions are made on the skin, in the second, punctures are made with a needle. Immediately after opening the abscess, a bandage with ointment is applied, the pain stops, and the patient feels relief. Ointments must be effective against Staphylococcus aureus. Drainage is almost always installed to speed up the separation of pus. In more serious cases, where the abscess has spread to the nail bed or there is an ingrown nail, partial removal of the nail may be necessary. Oral antibiotics are also prescribed, especially if the immune system is weak.
If the cause of parochinia is a fungus, antifungal drugs are used, for example, clotrimazole. Sometimes the doctor prescribes antifungal medications for internal use, such as fluconazole.
Parochinia, which has developed against the background of eczema, psoriasis or syphilis, requires specific treatment methods. Conventional therapeutic measures are supplemented by physiotherapeutic procedures (corticosteroids, ultraviolet irradiation).
After the operation and installation of drainage, the patient should come back for a follow-up appointment some time later to assess the condition. Usually, with adequate care and compliance with all medical recommendations, paronychia is completely cured and has no relapses. The patient is recommended to take multivitamin complexes to strengthen the body's protective reserves.
Treatment of paronychia with home methods
You can engage in independent treatment only if there is no purulent inflammation. Under no circumstances should children be treated at home!
If there is definitely no abscess, then baths with antiseptics (chlorhexidine, povidone-iodine), which are done several times a day for 15 minutes, will help.
Herbs such as calendula and chamomile also have antiseptic properties. Decoctions of them can also be used in the form of baths.
A good effect is obtained by using a solution of sea salt, as well as soda and potassium permanganate for baths.
The listed solutions can also be used for compresses.
Herpes infection of sore finger
If there are blisters on the inflamed finger or toe , filled with clear liquid or mixed with pus and blood, the cause of panaritium is most likely caused by herpes pathogens. Most often, herpes infection on the fingers occurs in children , but such blisters are also present on other parts of the body - in the mouth, on the lips.
| The difference between herpes inflammation on the fingers and others is that it does not respond to treatment with antibacterial drugs. For abscesses caused by these pathogens, surgical intervention is not performed, as there is a risk of infection spreading throughout the body and causing serious complications. |
If you suspect herpes inflammation of the finger, treatment should be carried out as follows: 1. Apply Acyclovir ointment to the inflamed area for a week. After this treatment, the skin will return to normal in 1 or 2 weeks. 2. A bandage can be applied to the site of inflammation in order to reduce the risk of the herpes infection spreading to healthy parts of the body, especially the mucous membranes. If the use of the ointment does not bring results and the inflammatory process only intensifies, you need to make an appointment with a doctor to choose further treatment tactics.
Prevention of paronychia
Prevention:
- keep your hands and feet clean and dry at all times;
- get rid of the bad habit of biting your nails and surrounding skin;
- After washing your hands, apply cream to the skin;
- When contacting aggressive chemicals, be sure to use gloves;
- do not cut the cuticle, especially on the toes;
- do not bite off hangnails;
- disinfect manicure and pedicure tools;
- trim toenails correctly to prevent ingrown nails;
- fight sweaty feet;
- monitor blood glucose levels;
- wear comfortable, high-quality and dry shoes.
If infection does occur, paronychia begins to develop, without wasting time, seek medical help. This will allow you to cure the disease painlessly, in a short time and without the risk of complications.
Rehabilitation after removal of an ingrown toenail
The recovery period after excision of an ingrown nail is on average 1 month. During the rehabilitation period it is recommended:
- Ensure the patient remains calm.
- Regular treatment of the nail with antiseptic agents and bandaging.
- Applying medications prescribed by a doctor to the wound.
- Taking painkillers for pain.
- Wearing loose shoes that do not put pressure on the toe.
- Other procedures indicated by the surgeon.
During the recovery period, you must strictly adhere to the doctor's instructions for a successful recovery.