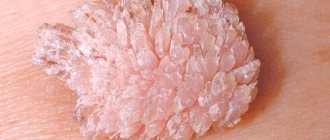
Improper and irregular oral care means there is a high probability of getting some kind of infection, which can lead to gum disease. Gum papilloma is a form of oral disease that requires immediate treatment. It may also occur on the lips, tongue, larynx, and throat. Papillomas can be quite painful, and their development threatens inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Reasons for the formation of papillomas in the mouth and possible locations of their localization
The appearance of all types of papillomas is associated with infection of the patient with the human papillomavirus (HPV). The prevalence of this type of viral agent is very high and reaches 90% of the population in some countries. However, HPV carriage is not always accompanied by the formation of skin tumors. The virus can remain latent for a long time without manifesting itself at all. The formation of papillomas is promoted by factors such as decreased immunity, bad habits, poor nutrition and hormonal imbalance.
Science knows more than 100 types of human papillomavirus. The location of the tumor directly depends on the type of HPV. Papillomas in the mouth, covering the surface of the mucous membrane, are caused by HPV types 13 and 32, affecting various parts of the oral cavity:
- Papillomas on the tongue. The tongue most often undergoes epithelial hyperplasia, which is usually manifested by the formation of fine granularity or single tubercles of the mucous membrane of the tongue. In the first case, multiple small growths are felt as an unpleasant surface roughness, while the second type of neoplasm, being quite large, is often injured and causes its owner not only discomfort, but also pain.
Papillomas on the tongue usually appear in the tip or lateral parts of the organ. Papilloma under the tongue can also be considered a frequent occurrence. The root of the organ is least likely to suffer from such growths. The color characteristics of papilloma vary from light pink to bright red.
- Papilloma in the throat. Papillomas in the throat can remain undiagnosed for a long time, since they usually do not cause significant pain in the patient. Owners of such neoplasms of the mucous membrane note minor discomfort and sore throat, which is not given any importance.
If the papilloma increases in size, it can interfere with normal food intake and even change the voice of its owner, making it more muffled. The growth itself usually looks like a soft whitish or one-time bump with a rough surface. Papillomas on the tonsil are especially common.
- Laryngeal papilloma. One of the most unpleasant types of localization of neoplasms. The fact is that the formation of laryngeal papillomas interferes with the breathing process, which can lead to acute hypoxia. This phenomenon is especially typical for young children who cannot clearly formulate complaints about difficulty breathing.
- Papilloma on the lip. Such epidermal growth usually causes more trouble from an aesthetic point of view than from a physiological point of view. However, excessive growth of the tumor increases the risk of injury during eating or active facial expressions.
- Papilloma on the gum. Usually characterized by the absence of symptoms and any pain. If a papilloma on the gum has formed in a place that is invisible to the patient. It can only be detected by visiting a dentist.
Sanitation of the oral cavity in the treatment of papillomas
Since pathogenic microorganisms present in the mouth can lead to an exacerbation of HPV, before operating on papilloma, special attention is paid to the sanitation of the oral cavity. This integral stage of wart treatment includes the following activities:
- Treatment of teeth affected by caries;
- Elimination of inflammatory processes;
- Elimination of plaque and tartar;
- Neutralization of pathologies affecting the gums;
- Enhanced oral care (regular brushing of teeth, removing food debris with dental floss, rinsing the mouth with prescribed medications).
Why are papillomas in the mouth dangerous?
The main danger of papillomas on the mucous membranes is the possibility of their malignant transformation, which is accompanied by an oncological process. It cannot be said that this probability is very high, but most doctors agree that if the epilelium grows excessively, atypical cell growth can become uncontrollable.
In addition, papillomas in the mouth are usually accompanied by constant discomfort, which is associated with the location of a large number of nerve endings and sensitive centers on the oral mucosa. Treatment of papilloma in the throat is necessary due to the likelihood of its growth with subsequent problems with speech activity.
Also, treatment of papillomas in the mouth is justified from the point of view that this particular localization is accompanied by the highest risk of injury to the neoplasm. This can happen while eating, talking, or making facial expressions. In this case, severe bleeding occurs, which is very difficult to stop. In addition, a constant humid environment with an abundance of microorganisms prevents the rapid healing of the wound surface and, on the contrary, contributes to wound infection.
Rehabilitation period after excision of papilloma in the oral cavity
After surgery for papilloma with any of the destructive methods, a recovery period follows, which includes drug treatment and compliance with a number of recommendations of the attending physician (treatment of the oral cavity with medications, proper nutrition, etc.).
As a rule, drug therapy after cauterization of papilloma includes taking antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, as well as vitamins. In the presence of infectious diseases that can provoke an exacerbation of HPV, appropriate medications are prescribed to combat this pathology. Complex treatment will block the virus, speed up the healing of mucous membranes and prevent infection of the postoperative wound.
You can remove papilloma in the oral cavity using one of the destructive methods in our specialized medical center, where experienced and highly qualified specialists work. After the necessary examination, taking into account the patient’s wishes and medical indications, the doctor will select the most appropriate tactics to combat warts. An individual approach to the patient, high professionalism of doctors and the use of advanced equipment will ensure successful and safe treatment of papillomas in the oral cavity.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 6401 Date of publication: 08/06/2018
Dermatologists - search service and appointment with dermatologists in Moscow
Removal of papillomas
Removal of papillomas is a method used in 80% of cases. The surgical intervention is painless, because before it the oral cavity is anesthetized. High accuracy is achieved through the use of the latest surgical methods. It is not always possible to get rid of a tumor in one visit; in this case, complex therapy will be required.
Removal methods:
- Removal with a scalpel. This method is old and is used if the patient has a limited financial budget and there are no other options for removal. The formations are cut off and there is a possible risk of scarring. It is prohibited to use it to remove papillomas on the lips.
- Laser. The growth is burned out layer by layer, while the remaining tissue remains undamaged. The method is modern and effective, no scar remains. Its only disadvantage is the high cost of the procedure.
- Medical loop. The papilloma is captured and gradually removed from the tissue. The method avoids re-infection and is characterized by rapid healing.
- Ultrasound. High-intensity ultrasound destroys infected tissue while sparing others. The method is effective and safe, but it costs a lot.
- Electrocoagulation. Removal occurs by microwave or electric current. Used primarily to work with formations under the tongue.
- Conchotom. Extracting the affected areas of the mucosa using biopsy forceps. The method is effective and safe, indicated for growths in the oral cavity, and not outside it.
- Radio waves. The impact of the waves is painless and safe for the patient. Histology confirms the benign nature of the neoplasm.
Nutrition
Since in most cases of disease the patient does not experience any complications or pain symptoms, there is no need to follow a diet for leukoplakia. However, most often the cause of the formation of plaques is a low level of immunity, and therefore, nutrition should be complete, healthy and rich in vitamins.
In advanced and severe forms of the disease, when it is difficult for the patient to open his mouth and chew food due to the formation of erosions and ulcers in places where the mucous membrane is damaged, it is recommended to switch to a porridge-like and puree-like consistency of food. It is also necessary to avoid eating too spicy and too hot foods.
Diagnostics
Even with the current high level of medicine, it is impossible to determine leukoplakia by eye with one hundred percent accuracy. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to perform a biopsy under local anesthesia. After a histological examination of the damaged mucosa and determination of the type of leukoplakia, the diagnosis is considered successfully completed.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor prescribes treatment, which may include removing the source of irritation, local treatment of the damaged areas with retinol acetate or other oil solutions, and taking immunostimulating and vitamin-mineral preparations. Or, in case of a serious precancerous form and the presence of cellular atypia, the doctor will recommend cryodisruption of the lesion.
What it is
It is believed that leukoplakia occurs against the background of chronic irritation of the oral mucosa and is a kind of protective reaction of the body. This is a local reaction and is not transmitted through contact with a sick person.
The disease is not so harmless, since it most often occurs shortly before the development of oral cancer. Many people mistakenly believe that leukoplakia itself is cancer, however, this opinion is incorrect. This disease affects the epithelial covering of the oral cavity in response to constant external irritants; vitamin deficiency, a decrease in the level of immunity and the presence of chronic foci of inflammation in the oral mucosa serve as an additional impetus for its development.
Leukoplakia of the oral cavity is a significant lesion of the mucous membrane of the lips, tongue, cheeks, upper and lower palate, manifested by keratinization (hardening) of the epithelial cover to varying degrees. Doctors usually classify leukoplakia as a disease that precedes the development of a tumor.
The greatest risk of developing this disease are men in the age group from 30 to 70 years, who abuse alcohol, smoke and wear dentures. Leukoplakia does not occur overnight, and its development can last for years.
Pregnancy with papilloma virus
The papilloma virus passes from mother to fetus during childbirth in 98% of cases. The child passes through the birth canal, which is literally strewn with condylomas. As a result, the virus enters the fetus's mouth and eyes. For this reason, every woman who is planning a pregnancy should be pre-tested and, if necessary, treated for HPV and STDs. Only after finishing the therapy process can you start thinking about your future child.
If the disease was latent and was detected only during pregnancy, which often happens (the body’s defenses weaken during pregnancy), then you should immediately consult a doctor.
Consequences
Many patients, having received a similar diagnosis from a doctor, are interested in whether leukoplakia is dangerous. Most doctors consider simple forms of this disease to be safe and do not require special treatment. Leukoplakia in the initial stage has a favorable prognosis, especially if it is caused only by external irritants, and not by a functional disorder of the internal organs.
However, there are also frequent cases of precancerous leukoplakia - the danger of this form is clear to everyone. If atypical cancer cells are detected in the histological analysis of the obtained material, this type of disease requires immediate surgery. If left untreated, the consequences of leukoplakia at the cancer stage can be disappointing. After the operation and the end of the rehabilitation period, the patient is recommended to undergo periodic examinations and take a course of medications aimed at a speedy recovery.