Skin scraping is a diagnostic method that involves obtaining skin samples for testing in a laboratory. The method helps determine the type of disease, etiology (cause), and also helps select and evaluate the success of treatment.
COST OF SOME DERMATOLOGIST SERVICES IN OUR CLINIC IN ST. PETERSBURG
| Price for a dermatologist appointment | 1000 rub. |
| Removing a mole with a radio knife | 500 rub. |
| Analyzes | from 300 rub. |
| Call free: 8-800-707-1560 *The clinic is licensed to provide these services | |
When is a skin scraping test prescribed?
The main function of the skin is to protect human internal organs from various pathologies. The variety of skin diseases is due to the peculiarities of its structure and the large number of factors influencing it. Almost always, skin diseases are the result of the influence of microbiological factors (viruses, fungi, parasites).
An experienced dermatologist can suggest a particular disease after a visual examination. However, in order to be confident in the diagnosis, it is necessary to use other diagnostic methods.
Skin scraping, as a diagnostic method, is prescribed in the following cases:
- If you suspect skin diseases;
- To clarify the diagnosis and select a treatment method;
- To evaluate the therapy performed.
Most often, scraping is prescribed if a fungus or demodicosis (a disease caused by a microscopic mite) is suspected.
Why do analysis?
Treatment of fungal and bacterial diseases differs radically. It is important to establish the cause of skin problems in order to prescribe adequate therapy.
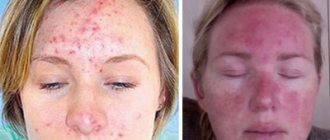
Fungi are one of the most resistant and contagious microorganisms. Mycoses occupy first place among all infectious skin diseases. Fungi do not threaten the patient’s life, but significantly reduce its quality. The situation is complicated by the fact that mycoses are very resistant to treatment. The earlier the disease is detected and the smaller the area it affects, the faster the recovery will occur.
What the analysis shows
Skin scraping shows the presence or absence of: fungi and subcutaneous parasites.
There are many types of fungal infections. It should be remembered that the fungus is contagious, and the carrier can be not only an infected person, but also an animal. Scraping the skin affected by the fungus will help identify the type of fungus and, accordingly, make it possible to choose the appropriate treatment.
Signs of skin damage by fungus:
- The affected areas differ in color, bumpiness, and peeling of the skin. In case of injury, the area may become larger in size and ulcers may appear. Itching bothers me;
- If the hands and feet are affected, severe itching and peeling appear; the skin becomes thinner and becomes covered with erosions. The nail plate may thicken in size and turn yellow;
- Fungus on the scalp makes hair dull and unhealthy. Peeling, itching, and plaque appear on the hair. Hair may fall out.
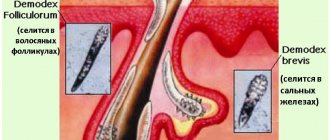
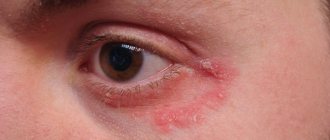
Demodex is a microscopic mite that parasitizes the sebaceous glands of the skin, hair follicles of humans and animals.
Signs of demodicosis can be confused with allergies and dermatitis. But there are such differences:
- The rash is accompanied by itching, burning, and discomfort. When the eyelids are affected, itching appears, the eyes become inflamed and swollen. Eyelashes become coated and fall out;
- There is an oily sheen on the face. The affected areas of the skin turn red, swell, and peeling and roughening may begin.
- Over time, scars appear. There is a feeling that something is moving under the skin.
It is impossible to see this mite without a microscope. Therefore, the dermatologist scrapes the skin, then evaluates the results and prescribes treatment.
Skin scraping will help identify scabies. Scabies is an infectious skin disease caused by the scabies mite. The tick can be seen with the naked eye (a white or yellow, small dot).
The tick can penetrate human skin very quickly - within 15 minutes. Scabies is highly contagious, with an incubation period of up to 14 days. The main route of infection is through touch.
Symptoms of scabies:
- Itching, especially intense in the evening and at night;
- Rashes;
- General malaise, fever in children.
Microscopic examination of scrapings from smooth skin and nail plates, as well as hair with hair follicles, used to diagnose superficial mycoses of the skin and its appendages.
Synonyms Russian
Microscopy of skin scrapings, nail plates and hair for fungi.
English synonyms
- Direct microscopy, Superficial mycoses
- KOH-test
Research method
Microscopy.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Nails, scraping, hair with hair follicle.
General information about the study
Superficial mycoses of the skin are a group of diseases of the skin and its appendages (nails and hair), the causative agents of which are fungi that are capable of superficial invasion of the epidermis, hair and hair follicles and the nail apparatus. Most often, superficial mycoses are caused by the presence of fungi of the genus Dermatophytes (in this case we speak of dermatophytosis), but the disease can also be caused by fungi of the genus Candida, Malassezia, Trichosporon and Hortaea.
Clinical examination may suggest the presence of smooth skin mycosis or nail mycosis (onychomycosis), but is not used as a definitive diagnostic method, since many other diseases may have a similar clinical picture (for example, nail psoriasis may resemble onychomycosis). The main method for diagnosing this group of diseases is direct microscopy, in which the material under study (skin flakes obtained by scraping at the lesion, or fragments of the affected nail plate) is examined under a microscope after treatment with a solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH). Microscopy makes it possible to identify hyphae/pseudohyphae and yeast cells of the fungus and characterize their morphology, on the basis of which the diagnosis of “superficial mycosis with clarification of its nature” can be confirmed. For example, dermatophyte fungi (Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton) are represented by multiple tube-like structures with true septa and spore formation. Fungi of the genus Candida, on the contrary, are represented by elongated yeast cells (pseudohyphae), and do not form true spores. Fungi of the genus Malassezia produce round yeast cells and elongated pseudohyphae.
The pathogens of superficial mycoses are in fact often part of the normal skin microbiota or temporarily colonize it (“healthy carriage”) and can be identified by microscopy of scrapings from normal skin or scrapings from the distal part of the nail plates in many healthy people. For this reason, a positive test result in the absence of any clinical signs of mycosis has no clinical significance. This statement, however, does not apply to the analysis of the subungual contents of the proximal nail plates, which normally do not contain any microorganisms, including fungi.
It should be noted that microscopy does not allow specifying the type of fungus: for these purposes, inoculation on a nutrient medium is used (microbiological method). A negative test result does not completely exclude superficial mycosis.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of superficial skin mycoses (dermatophytosis, candidiasis, pityriasis versicolor and others) and onychomycosis.
When is the study scheduled?
- With symptoms of superficial mycosis of the skin (single or multiple foci of peeling and hyperemia with a clear edge, accompanied by itching);
- in the presence of symptoms of onychomycosis: changes in color (yellow, whitish), thickness (subungual hyperkeratosis) and shape of the nail (cracks, onychogryphosis).
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
Positive result:
- dermatophytosis, candidiasis or other superficial mycosis;
- "healthy carrier"
Negative result:
- norm.
How to do scraping
First of all, the doctor conducts a survey, identifies complaints and medical history.
Before taking a scraping, the dermatologist cleans the surface of the skin from dust and sebum. To carry out scraping, a scalpel, a special spatula, and scissors (to take a nail sample) are usually used. If a scraping needs to be taken from the scalp, the doctor will trim the affected area.
The procedure is absolutely painless. The material obtained during the analysis is delivered to the laboratory. Based on the results, the dermatologist selects a course of treatment.
Get tested for skin fungus in Moscow
Our clinic works with one of the largest laboratory complexes in Moscow, which allows us to perform tests quickly, efficiently and at an affordable cost. The price of scraping for skin fungus does not include a consultation with a dermatologist on the results of the study and treatment of mycosis, but you can sign up for it separately.
Reception is carried out at a time convenient for the client. You don't have to wait in line or adjust to your local doctor's schedule.
Are you looking for where to have your skin scraped tested for fungus in Moscow quickly and efficiently? Come to the Kutuzovsky Children's Center.
Leave feedback
Dermatologists
- Ayvazyan Linda Volodyevna
Experience: 5 yearsDermatovenerologist, mycologist, trichologist
Rating: 0/5 — 0 votes
Make an appointment
- Osipova Daria Sergeevna
Experience: 14 years
Deputy chief physician for medical work. Dermatovenerologist
Rating: 0/5 — 0 votes
Make an appointment
Demodex is a small-sized mite that causes an unpleasant disease - demodicosis. If you suspect demodicosis, you need to take a demodex test.
The mite is usually localized on the surface of human skin and often lives in the hair follicles of skin derivatives: for example, hair or eyelashes. The skin of the face is its favorite localization. A demodex test will instantly help confirm or refute the presence of a mite in a patient, which means the doctor will begin treatment in a timely manner.
So, do you suspect you have demodex because of the alarming symptoms? Make an appointment with a dermatologist, and then get tested for demodex mites at the Kutuzovsky Children's Center. You will need to carefully prepare for the study.
Our clinic will help you with this!
How do you know when it's time to sound the alarm?
Every person thinks that bad things will happen to anyone, but not to him. That is why in most cases people turn to a mycologist at an advanced stage of the disease. If you suspect that you have nail fungus, our advice is to immediately get tested and begin treatment.
Look at what changes are tested for nail fungus:
- Change in nail color. The nail has become opaque and it is impossible to see the nail bed. The surface of the nail has a yellowish tint.
- The appearance of a gap between the nail bed and the nail. In this interval, a focus of infection is formed.
- Thickening (keratinization) of the nail plate. The thicker the nail, the more deeply the fungus has taken root.
- The appearance of white dots. The surface of the nail becomes loose and rough.
- Swelling and redness of the skin around the nail. As a result, after some time the nail plate begins to deform.
- Painting nails grayish-yellow or brown. This sign is an indicator of the advanced stage of the disease. At this stage, the nails begin to peel off.
How to prepare for a demodex test?
Analysis for demodex in Moscow can be done at the Kutuzovsky Children's Center. Our doctors will quickly detect a microscopic mite. The cost of undergoing a skin examination is low, so you can contact us with your suspicions.
At the Kutuzovsky Children's Center, eyelashes will be analyzed for demodex, as well as skin analysis for demodex. Let us describe in more detail how to prepare for demodex analysis:
- 24 hours before testing for the presence of demodex mites is a key time, because a person should not apply cosmetics or even wash his face. You should also not use eye drops. An exception to this rule is considered to be a pathology of the eye apparatus, in which the use of drops cannot be skipped.
- If you use soap or shampoo to wash your hair before analyzing the scraping for demodex, you need to do this as carefully as possible so that the product does not get into your eyes.
Preparation for demodex analysis of eyelashes, and the face in general, has some features. For example, a tick activates at night, and during the daytime it hides, avoiding sunlight.
Therefore, at the Kutuzovsky Children's Center, when examining eyelashes, skin, hair, even such minor areas as the skin of the eyelids, they will help you choose the best time to analyze demodex on the face.
References
- Basal cell skin cancer. Clinical recommendations. Association of Oncologists of Russia, 2022. - 85 p.
- Squamous cell skin cancer. Clinical recommendations. Association of Oncologists of Russia, 2022. - 31 p.
- Kumar, V., Abbas, A., Fausto, N. et al. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 2014. - Vol. 1(7), 3(25) — 1464 p.
- Ferrante di Ruffano, L., Dinnes, J., Chuchu, N. et al. Exfoliative cytology for diagnosing basal cell carcinoma and other skin cancers in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2018 - Vol 12.
Analysis methodology
Analysis in the form of scraping for demodex is carried out as carefully as possible, the patient does not feel pain or discomfort. Using a scalpel, the doctor removes material from a particularly inflamed area of skin.
If a person does not have clear foci of inflammation, then the material for demodex analysis is taken from standard zones. They are the forehead, cheeks, chin.
The material is placed on a glass slide and subjected to microscopic analysis. The specialist will immediately tell whether the patient has demodicosis and will also count the number of mites.
The normal result of a healthy person is the absence of both mites and demodex eggs.
Another diagnostic method is the eyelash test, which is performed by an ophthalmologist by taking a few eyelashes and eyebrow hairs. Cytology is often used to test for Demodex, in which a section of the upper layer of the epidermis is carefully removed.
The price of demodex analysis at the Kutuzovsky Children's Center is as affordable as possible for all patients.
It is very easy to get tested for demodex in Moscow at our clinic! Call for advice at the phone number listed on the website!
Leave feedback
general characteristics
Fungal skin diseases (dermatomycosis), caused by pathogenic dermatomycete fungi (dermatophytes), are divided into 4 groups. The first group is keratomycosis. Pathogens parasitize in the most superficial parts of the stratum corneum of the skin or on the cuticle of the hair. This group includes pityriasis versicolor, erythrasma, nodular trichosporia and axillary trichomycosis. The second group is epidermomycosis. The pathogens also parasitize in the stratum corneum, often affecting the nails, but, unlike the pathogens of keratomycosis, they cause an inflammatory reaction from the underlying layers of the skin. This group includes: athlete's foot, athlete's foot and superficial yeast lesions of the skin and mucous membranes (candidiasis). The third group is trichomycosis. They differ from the causative agents of epidermomycosis in their ability to infect not only nails, but also hair, growing into their cuticle and penetrating into the cortex of the hair. This group consists of: trichophytosis, microsporia and scab. The fourth group is deep dermatomycosis: actinomycosis, deep blastomycosis, chromomycosis, sporotrichosis, as well as visceral forms of candidiasis and mycosis caused by certain molds. This study determines only the presence of a dermatophyte, without determining the species.