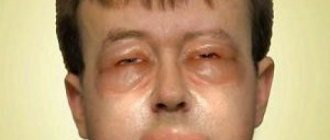
Hives are an allergic disease that appears as spots or red, intensely itchy plaques on the skin. Prevalence depends on age and environmental conditions, as well as comorbidities. The most common allergic dermatosis is recurrent urticaria.
The swelling and itching caused by hives can be severe. The feature that distinguishes this disease from others is red spots on the surface of the skin. They have irregular edges and small bubbles. Typically, hives are caused by allergies. When an allergen enters the body, histamine is released into the bloodstream and causes: swelling, redness and itching.
Causes of the disease
The causes of urticaria in children are:
- sensitivity to allergens;
- consumption of allergens in food, their inhalation;
- taking certain medications;
- bites of some insects;
- tactile contact with the allergen (urticaria in a child may appear after sleep due to a reaction to the dye in the bedding fabric or washing powder). Source: L.V. Luss Causes and treatment of urticaria in children, swelling in children // Medical Council, 2015, No. 14
Upon contact with an allergen, inflammation occurs, fluid accumulates in the body tissues, and a rash and swelling appear. This reaction of the body is an attempt to reduce the amount of harmful substances.
Chronic urticaria, which can appear as early as one year of age, occurs due to:
- chronic or long-term gastrointestinal diseases;
- chronic inflammation;
- viral infections;
- parasite infestation;
- fungal diseases;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system;
- hereditary predisposition.
The disease can be provoked by overheating or hypothermia of the skin, exposure to UV or water, when combing or injury by elements of clothing, due to severe stress. With such urticaria (it is called “cholinergic”), children do not have an elevated body temperature, and external manifestations quickly disappear (in a few minutes, maximum half an hour). Source: I.I. Balabolkin. Urticaria in children: clinical and pathogenetic variants, diagnosis and treatment // Russian Pediatric Journal, 2022, 20(2)
Types of urticaria
There are two forms of the disease: acute and chronic. Acute urticaria is often caused by food allergies, insect bites, medications, or exposure to an allergen. It lasts, as a rule, up to 1.5 months.
Chronic urticaria lasts more than 6 weeks. It can begin when the immune system attacks the body's tissues, thereby causing an autoimmune reaction. Antibodies (proteins that normally fight bacteria and viruses) cause the release of histamine, which leads to lesions on the skin.
The rash can be localized or appear anywhere on the body, from the neck to the knees. Rarely does the allergy affect the arms, legs and face, unlike angioedema. Characterized by the appearance of rashes and spots on the skin. There is also swelling in the eyelids, lips and larynx.
Angioedema urticaria is a medical emergency because it can cause breathing problems and suffocation.
It is believed that 30 to 50% of cases with chronic urticaria have an autoimmune cause. The reason why autoimmune urticaria develops is unknown, even though it often occurs along with other autoimmune diseases such as:
- rheumatoid arthritis – the immune system attacks the joints;
- lupus – the immune system attacks the joints and skin.
In rare cases, chronic hives can also be caused by other infections (eg Helicobacter), hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), hepatitis B or C (liver infections), intestinal parasites.
Table - Types of urticaria in children
| Name | Peculiarities |
| Immune (IgE-dependent - food, drug, helminth; complement components - anaphylotoxins C3a and C5a; complement-induced - hereditary or acquired deficiency of the C-1q inactivator) | Characterized by skin damage and itching. Quincke's edema, urticarial type of vasculitis and anaphylactoid urticarial reaction are possible. |
| Non-immune (based on a pseudo-allergic reaction) | There is no true reaction of interaction between antibody and antigen with the formation of an immune complex. Ig-E does not increase. Occurs due to consumption of foods that contain vasoactive amines. |
| Pigmented | Accompanied by an increase in the number of mast cells. Often found on the upper and lower extremities or trunk. May damage internal organs and be accompanied by systemic mastocytosis. |
| Vascular urticaria or vasculitis | It is characterized by several lesions that have an unusual shape and disappear after a few days. Other symptoms of urticaria vasculitis include fever, joint and muscle discomfort, abdominal pain and headache. |
Diagnostic methods
When this disease develops, the patient or his parents are interviewed and the symptoms are analyzed.
The doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis after examining the child’s skin. A rash with urticaria is difficult to confuse with another. However, to exclude errors and establish the cause, tests are prescribed:
- stool analysis, which will help identify parasites - they can be pathogens;
- general blood test - identifies or excludes inflammatory and immune processes;
- allergy tests - skin tests to identify the pathogen;
- liver tests - to determine liver function and exclude its pathologies.
Thyroid function may be tested because the disease can be caused by hypo- or hyperthyroidism.
Additional research:
- skin test when using autologous serum;
- rheumatological tests;
- nasal swab for the presence of eosinophils;
- TSH, T3, T4, antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin;
- culture of throat flora, throat culture for sensitivity to antibiotics and bacteriophages;
- stool analysis for sensitivity to bacteriophages and dysbacteriosis;
- antibodies to helminths, as well as roundworms and lamblia;
- coprogram;
- HBsAg, AT to hepatitis C, RW, AT to HIV;
- ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- consultation with a gastroenterologist to identify H. pylori, endoscopy, consultation with a neurologist, ENT specialist (VSD);
- ECG;
- if urticarial vasculitis is suspected, a dermatovenerologist performs a skin biopsy.
Types of disease
In medicine, there are five main forms of this disease:
- chronic with periodic exacerbations;
- acute, arising and spreading rapidly;
- allergic (affects 70% of children);
- pseudo-allergic (provoked by disturbances in the functioning of the liver and digestive organs);
- hereditary non-allergic (accompanied by Quincke's edema, similar to allergic). Source: L.P. Sizyakina, A.A. Lebedenko, C.B. Maltsev, A.N. Posevina, L.A. Averkina Urticaria in children: a modern view of the problem // Medical Bulletin of the South of Russia, Reviews, 2015
Let's take a closer look at the types of urticaria, depending on the triggering factor:
- Medicinal. A type of drug allergy is a reaction to certain drugs. The most common provocateurs are iodides, streptomycin, sedatives, NSAIDs, and drugs containing gold. The rash may be accompanied by a runny nose, conjunctivitis and bronchial asthma. To cure this form of urticaria, you need to eliminate the allergen, adjust the diet, removing the brightest allergens from it - citrus fruits, red vegetables and fruits, nuts, cow's milk, fish.
- Mechanical – appears when pressure is applied to the skin. Its causes have not been reliably studied, but the disease is associated with skin sensitivity, heredity and the condition of the blood vessels. Divided into several subspecies:
- dermographic – develops quickly due to friction or pressure, often caused by wearing tight clothing;
- cold - a reaction to contact with something cold, drinks or foods;
- heat – the rash appears when the environment is hot;
- solar - occurs during prolonged exposure to the sun, manifested by swelling and red spots on the skin;
- aquagenic - rare, but very dangerous, appears upon any contact with water;
- papular - the result of an insect bite;
- cholinergic - a rash appears when the child is nervous and sweats a lot.
- Generalized. It differs in that the rash spreads throughout the body, including the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, which makes breathing difficult. Quincke's edema may develop. Such urticaria appears in children with atopic diseases and can be caused by antibiotics and NSAIDs. Rarely are food products allergens.
- Idiopathic. The cause is unknown, but itchy blisters appear regularly over a period of 6 weeks at varying intervals. The process is considered chronic. Spontaneous occurrence and the lack of diagnostic methods make it difficult to control the course of the disease, treatment and prevention.
Skin symptoms of covid
There is not yet accurate summarized information about dermatological diseases associated with Covid from all countries. But data was obtained from America, China, England and Spain, where studies were carried out in medical centers where there were people infected with the virus. Experts have described about 400 cases of coronavirus accompanied by skin symptoms.
Research in China has shown that skin rashes rarely occur with the virus. Out of 1000 people, only 3 people were found to have skin problems.
Skin rashes have been noticed in patients seen in intensive care units and this is not surprising: they are under close supervision of doctors.
Today, there is an online registry that collects information from all over the world about skin rashes due to coronavirus. The main goal of such a resource is the high-quality and prompt collection of medical data that can be useful in treating the disease.
Treatment methods for urticaria in children
This disease should be treated depending on its form. The pseudoallergic variety requires examination for the underlying disease. Allergic – allergen exclusion and immunotherapy.
In the acute period:
- eliminate contact with the allergen;
- the child is prescribed a hypoallergenic diet for several days;
- remove the allergen from the body, prescribe plenty of fluids;
- use sorbents and antihistamines (types and dosage regimen are determined only with a doctor);
- for severe swelling, a specialist may prescribe a diuretic;
- Prescribe antipruritic ointments for the arms, legs, or other areas of the child’s body that are prone to hives.
Parents should carefully monitor the cleanliness of the house and promptly wash clothes and bedding with hypoallergenic products.
Frequent skin symptoms
The most common variant of skin diseases associated with coronavirus are erythematous-edematous lesions. The spots may vary in diameter and have different shades of red. They do not itch and do not cause any particular discomfort or pain. The affected areas of the skin become warm and sometimes hot.
There are also pink rashes. They are oval in shape and flaky. They are usually found on the sides of the body and can itch, causing severe discomfort.
Skin rashes do not appear in a chaotic manner. Most types of rashes are characteristic of a certain age category or form of the disease.
Are there any complications?
Acute urticaria in children can have a dangerous complication - Quincke's edema (giant urticaria, angioedema). It consists of swelling of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. The child has coughing attacks and has difficulty breathing. Very young children may experience swelling of the gastrointestinal mucosa (the reaction to this is vomiting). In severe cases, the membranes of the brain and nervous system are affected. Any of these conditions is very dangerous and can be fatal. Therefore, it is very important not to delay visiting a doctor if there are signs of illness.
Important! Many parents do not know what to do with Quincke's edema. You should immediately give your child an antihistamine (any one from your home medicine cabinet) and call emergency medical help.
Manifestation of skin rash
Cases of skin problems have only been documented in observational studies, so we cannot say with 100% certainty that they are symptoms of Covid. Skin rashes may appear as a reaction to medications. But still, WHO classified skin rashes as a symptom of a viral infection.
The prevalence of the rash is also not yet clear. If in China skin problems are observed in 0.3% of patients, then in Italy this value is 21%. Skin rashes can also appear with many other diseases, such as chicken pox, measles and herpes.
Disease prevention methods
There are no special preventive measures. However, you can minimize the risk of developing the disease by following these recommendations:
- control the child’s diet;
- exclude contacts with potential allergens - food, volatile, contact;
- have an antihistamine in your home medicine cabinet;
- buy your child loose clothes made from natural fabrics;
- do not provoke stress in the child;
- do not trigger chronic diseases.
Sources:
L.V. Luss. Causes and treatment of urticaria in children // Medical Council, 2015, No. 14
I.I. Balabolkin. Urticaria in children: clinical and pathogenetic variants, diagnosis and treatment // Russian Pediatric Journal, 2022, 20(2)
L.P. Sizyakina, A.A. Lebedenko, C.B. Maltsev, A.N. Posevina, L.A. Averkin. Urticaria in children: a modern view of the problem // Medical Bulletin of the South of Russia, Reviews, 2015
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Advantages of NEARMEDIC clinics
The NEARMEDIC network of clinics will provide you with effective assistance because:
- any clinic has certified adult and pediatric allergists on staff who will conduct a preliminary examination, prescribe laboratory tests and provide professional treatment;
- our Diagnostic Center provides laboratory services of guaranteed quality, which is confirmed by the appropriate certificate;
- The Laboratory Diagnostics Center is equipped with the most modern equipment for conducting all types of examinations and analyses;
- Any data about the patient obtained during the examination and treatment is confidential and is not transferred to other persons.
Allergists have extensive experience in successfully treating acute and chronic allergic diseases. If symptoms appear, please contact one of the network clinics in a timely manner using a general telephone number or through the call back form on the website.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an allergist-immunologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) - maintenance course (excluding the cost of the drug) | 8100 rub. |