Many people are bothered by white spots on their heads, and they can appear in both men and women. The etiology of the disease distinguishes between contagious and non-contagious types of disease. Symptoms of the disease may include peeling skin, dandruff, itching and partial or complete hair loss. At an early stage, the problem can be quickly treated, so it is important not to delay a visit to a specialist. What to do if white dots appear on your hair like bald spots on your head? To get rid of them, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist and undergo the necessary examinations.
Causes of alopecia
The causes of alopecia areata in men are different, and not all of them have been thoroughly studied by specialists. Negative factors can provoke the disease.
- Genetics. The likelihood of the disease is higher if one of your blood relatives has already been diagnosed with it.
- Autoimmune disorders. In many cases, focal baldness is of an autoimmune nature, in which lymphocytes perceive hair follicles as a threat to the body. Blood cells begin to attack “foreign agents,” destroying them and leading to hair loss.
- Chronic diseases. Baldness occurs due to endocrine diseases, problems of the digestive system, and dermatological pathologies. The causes of focal alopecia can be lichen planus and vitiligo, anemia and sexually transmitted diseases, helminthiasis and systemic lupus erythematosus, arthritis.
There are also so-called associated factors. These include:
- frequent nervous stress;
- infectious diseases;
- head injuries;
- activities that involve chemicals (acids, salts, alkalis).
There is an interesting theory called L-mosaic. According to it, different areas of the head have different sensitivity to male hormones. That is, if with age hair falls out only on the crown or only on the back of the head, why shouldn’t it fall out in round patches in other areas.
Before prescribing therapy, the trichologist will conduct a thorough examination and try to find out the cause of alopecia areata. All this will allow you to select the most effective methods and preparations for hair growth.
Safe Spots
The appearance of pigmentation on the head can be the cause of some disorder in the body. Unlike previous forms, this is not capable of harming health.
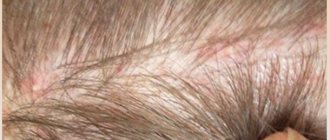
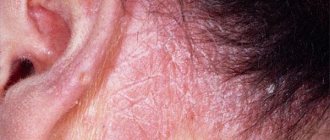
Contact dermatitis or an allergic reaction occurs after contact with an irritant. They can be household chemicals, cosmetics, food, pollen, jewelry and medicines. For treatment, it is necessary to eliminate contact with the allergen as soon as possible; without this, therapy will be ineffective. You can see what allergic spots on the head look like in the photo.
Hypomelanosis or albinism can be partial or complete and manifests itself in light spots. They occur due to a lack of melanin. The disease has 3 forms:
- with a partial decrease in melanin, single light areas appear on different parts of the body; the disease is congenital;
- the incomplete form can be seen by small spots under the hair; these areas of the skin do not darken even after tanning;
- The full type of albinism involves the cessation of melanin production, after which the skin on almost the entire body gradually acquires an unnatural white color.
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
The disease is not contagious. Experts have revealed that albinism is transmitted through genes, so you should not be afraid of communicating with people with hypomelanosis.
Piebaldism is a mild form of leukoderma and is a non-contagious disease. The disease is most often diagnosed in childhood, but it can also occur later. The reason is long-term exposure to ultraviolet rays on the skin. At first, you can only notice a small spot on the child’s head on the forehead, then the hair begins to turn grey. When dead skin particles accumulate, itching may occur. The most interesting thing is that the skin on the feet and hands remains the same color, white spots on the head photo.
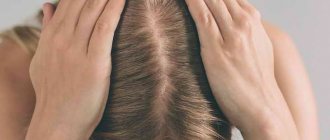
Symptoms of focal baldness
The danger of nested hair loss is that the symptoms occur suddenly and progress quickly.
- In a short time, bald spots form on the head.
- Eyebrows, beard, armpits and any other parts of the body can be affected.
- Often hair begins to fall out in clumps.
- Bald spots have clear edges.
- The skin in the area of loss is initially reddish and irritated, often accompanied by itching and burning.
Alopecia can be multilocular in nature. With this option, the lesions, growing, merge and form large bald spots.
An interesting feature: single lesions can disappear as suddenly as they appear.
A symptom of focal baldness is often changes in the nail plates. They exhibit wavy deformations, thimble-shaped indentations and longitudinal stripes.
Types of alopecia areata
The clinical picture of the disease varies. Based on the symptoms, experts distinguish the following types of alopecia areata:
- Absent-minded. The focus of baldness is in one place. The spread of the disease to other areas of the head is not observed.
- Subtotal. The disease progresses, the lesions grow and occupy an increasingly larger area. Hair falls out on the head and body, from the eyebrows, beard and mustache.
- Total. Vegetation on the body and head completely disappears. The scalp becomes greasy, sweats, and turns pale. Treatment has virtually no results.
Types of Scalp Spots
The problem manifests itself for various reasons: a fungal disease, skin dermatitis or an allergic reaction to any irritant, albinism, as well as piebaldism. It is important to recognize the first signs in time so as not to trigger the disease. Some forms are non-contagious, but since they do not look very aesthetically pleasing, some measures must be taken to normalize the condition. White spots on the head are shown in the photo below.
The defect in the form of partial baldness and spots can appear at any age. Something like this on a child’s head indicates hormonal imbalances, gastrointestinal problems, or an infectious disease. At an older age, similar causes are disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, reactions to various substances and infections.
Diagnostics
When a patient comes to a trichologist with complaints of alopecia areata, diagnostic measures are carried out for him. Examinations help determine the type and degree of the disease. Even if the problem cannot be completely overcome, there is an option to put it into remission and ensure the safety of your hair.
Patchy baldness requires immediate medical attention. The pathology is poorly understood, and it is important to find out the reasons at the very beginning in order to prescribe adequate therapy. The treatment process requires patience and compliance with the specialist’s instructions.
Diagnostics may include:
- blood test for hormones;
- biochemical and general blood tests;
- microscopic hair analysis;
- analysis of cortisol levels;
- blood test for Epstein-Barr virus, toxoplasma and mycoplasma.
Additionally, the patient may be sent for consultation to a psychologist, dermatologist, or endocrinologist.
Message sent!
Treatment of alopecia
To treat focal baldness, men are prescribed complex therapy, which consists of medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. Sometimes traditional medicine recipes and alternative methods are effective.
Treatment for patchy hair loss is a long process. It involves constant use of medications. The doctor may make other appointments.
- Immunosuppressants. These are a number of immune suppressants. These include corticosteroids, cyclosporine, methoxypsoralen. The main task of such drugs is to slow down autoimmune processes, when hair follicles are perceived by the body as foreign cells that need to be destroyed. You need to take medications strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
- Irritant drugs. This could be dithranol, chrysarobin, croton oil. Their task is to divert the attention of the immune system from the destruction of follicles. The technique is applicable in cases where alopecia is caused by a malfunction of the immune system.
- Drugs that cause symptoms of contact dermatitis. Such an effect is also intended to “deceive” immune activity and change its vector.
- Preparations based on minoxidil. The products strengthen hair due to their direct action on the follicles. The purpose of such medications is to lengthen the growth phase of the hair shaft.
- Experimental drugs. In rare cases, your doctor may prescribe a new remedy. The medicine may be based on hormone-like peptides, cytokines or natural macrolides.
Medicines in the form of creams, ointments and gels are applied to the lesions. Injections are also given into the affected area. Treatment of this type can last 10–12 months. Tablet drugs are taken in short courses, since many of them have side effects and contraindications.
Physiotherapy is prescribed:
- massages;
- laser procedures;
- mesotherapy.
Transplantation
Transplantation is a radical method of treating alopecia. It involves transplanting your own hair follicles from a healthy area to a problem area. As a rule, the bulbs take root well and, growing, cover bald areas of the scalp.
There are several transplant methods. Some involve the transplantation of donor follicles along with the skin, others involve the introduction of single bulbs. The first option is quick to implement, convenient for surgeons, but traumatic for patients. The percentage of hair survival is low. Scars remain in the donor areas, making it impossible to wear short haircuts.
Transplanting individual hairs is manual, painstaking work. One operation can take several hours. The survival rate is high, and the morbidity rate is almost zero. There are no traces left after such a transplantation. The puncture spots disappear after a couple of days.
Hair and scalp diseases
What are the causes of alopecia? What is the differential diagnosis for focal baldness? How to manage patients with scalp psoriasis?
The problem of hair loss - diffuse or focal - and scalp diseases are the most common reasons for referral to a dermatologist. Hair is an important part of our body, and any damage to the hairline is associated with inconveniences that we are not inclined to underestimate.
| Figure 1. Bilateral receding hairlines characteristic of male pattern baldness. A new drug has recently been licensed - finasteride. |
There is an opinion that hair serves as a symbol of fashion and sexuality. People without hair seem unattractive to us and look unusual. Men feel less “masculine” and experience insecurity in their personal relationships and at work.
Hair goes through a cycle of growth (anagen) and loss (telogen); Normally, up to 100 hairs fall out per day. Only when this figure is exceeded does hair loss become noticeable. There is also a seasonal dependence: more hair is lost in summer than in other seasons.
- Diffuse baldness
Telogen effluvium hair loss. Diffuse alopecia can develop after a serious illness or surgery and can be quite severe. As a rule, two to three months after childbirth or illness, a large amount of hair shifts from anagen to telogen and falls out. This manifests itself as excess hair loss, but not complete baldness, and it is important to reassure the patient that the hair will grow back. The same thing is observed after exhausting diets.
The nature of hair loss after a course of chemotherapy differs from that described above, since it occurs in the anagen phase. Iron deficiency and thyroid disease can also lead to diffuse hair loss.
Androgenic alopecia. Up to 60% of women over 30 experience some degree of male pattern baldness, and the incidence increases after menopause.
As in men, the frontal part and crown of the head mostly go bald; Once again, women need to be reassured that this type of hair loss is rarely severe. However, receding hairlines do not tend to grow over. Minoxidil lotion helps slow hair loss, but although 30% of patients experience some improvement, only 10% of men and women achieve effective hair restoration.
This expensive treatment is not available under the national health care system. In addition, the effect of this treatment lasts only during the use of the drug, then the hair condition gradually returns to its previous state.
Androgenetic alopecia develops to some extent in women with polycystic ovary syndrome, they also have acne, hirsutism and irregular periods. For hormonal disorders, cyproterone acetate at a dose of 50-100 mg per day in combination with estrogen, as in the Diane contraceptive pills, helps well.
Men with androgenetic alopecia begin to lose hair from the temples and then from the crown. The severity of baldness varies widely. The number of men with this type of baldness increases with age, until by the age of 70 it reaches 70%.
| Figure 2. Up to 60% of women over 30 years of age suffer from male pattern baldness to varying degrees. |
As a rule, there is a family predisposition to this type of baldness, and most men perceive it as an attribute of aging. For those who feel differently about this, we can recommend minoxidil; There are many clinics, often illegal, offering hair transplants and implantation. Baldness is a problem that many people seek to make money from. Finasteride, a 5-a-reductase inhibitor, has recently been licensed for use in androgenetic alopecia in men. It is taken orally, but there may be side effects such as loss of libido or impotence.
Many teenage girls and young women who complain that their hair is falling out and thinning actually have beautiful hair with no signs of thinning. It looks like the thick thick hair they had in
| Figure 3. Alopecia areata can develop at any age and in both sexes, but it is more common in adolescents and young adults. |
childhood, they simply come to a state corresponding to a different age norm. No objective reasons have been found for this phenomenon, but although we do not know why the hair becomes thinner, girls can be reassured by assuring them that this will not continue indefinitely: soon the condition of their hair will stabilize at a new, completely acceptable level.
- Patchy baldness
Alopecia areata. Patchy baldness usually develops as a result of alopecia areata, an autoimmune disease in which antibodies are produced against the hair follicles. The patient experiences bald areas on the scalp. The beard and eyebrow areas may be involved, and in severe cases, all the hair on the head (alopecia totalis) or body (alopecia universalis) will fall out.
| Figure 4. In tinea capitis, the scalp shows flaking, broken hair, and random patches of baldness. |
Alopecia areata can develop at any age and in both sexes, but teenagers and young adults are more often affected; it may be associated with other autoimmune diseases such as thyroid disease and vitiligo. The scalp is healthy, with smooth, rounded bald patches and characteristic single hairs that look like exclamation marks. In 70-80% of cases, the nests heal spontaneously, but there remains a possibility of relapse: more than half of the patients will develop new areas of baldness over the next five years.
The occipital sockets overgrow worse, and the larger the area of baldness, the less chance of a successful outcome. In 5-10% of cases, the disease ends in total or universal alopecia. Only 10% of patients recover from total alopecia; if hair loss begins before puberty, the prognosis is less favorable. In some patients, small indentations are visible on the nails.
| Figure 5. Dermatomycosis of the scalp. Visible typical greenish-blue glow under Wood's lamp |
Differential diagnosis for focal hair loss includes ringworm and trichotillomania. In the first case, there is flaking of the scalp, and in both cases the hair breaks rather than falls out completely.
For alopecia areata, strong steroid drugs such as clobetasol propionate or topical triamcinolone are used to stimulate hair growth. It is difficult to say with certainty that the overgrowth of lesions occurs due to treatment, since in many cases the hair is restored spontaneously. At least the patient feels that he is being helped, and the use of the ointment for six to eight weeks or periodic injections does not cause skin atrophy.
Some patients are happy to hear that the chances of spontaneous recovery are good and no treatment is required. Typically, hair grows naturally within a year, in most cases within the first six months.
| Figure 6. Trichotillomania. Typically, the patient needs treatment for an underlying mental illness |
In severe cases, a regimen of PUVA (oral psoralen followed by long-wave ultraviolet light), high-dose systemic steroids, and irritants such as dithranol, dinitrochlorobenzene, or diphencipron may be tried. But most often the effect turns out to be too insignificant compared to the severity of the side effect.
Dermatomycosis of the scalp. It develops as a result of a fungal infection and affects exclusively children. The scalp is flaky, showing random patches of hair loss with broken hairs; the appearance of such areas resembles woven lace.
| Figure 7. Cicatricial alopecia seen in lichen planus and discoid lupus erythematosus |
Skin scrapings are taken to identify fungi. Culture takes four to six weeks, so a Wood's lamp examination of the scalp may be helpful. When Microsporum canis (the most common fungal agent) is present, a greenish-blue glow is visible over the affected areas. This allows you to start treatment earlier.
Topical treatment is ineffective for tinea capitis, and a six-week course of griseofulvin is required to control the infection. In severe cases with a pronounced inflammatory component (kerion) due to peeling, permanent hair loss is observed.
| Figure 8. Moderate hairline psoriasis. Scalp psoriasis produces thicker scales than eczema |
Trichotillomania. With this disease, the patient intentionally or unconsciously constantly pulls and twists the hair, which breaks due to this. As a rule, hair problems are not resolved until the underlying mental illness is eliminated. The treatment process can be quite lengthy. During this time, the patient often continues to lose hair. The prognosis is better in children than in adults.
- Scarring alopecia
Cicatricial alopecia is seen in conditions such as lichen planus (LP) or discoid lupus erythematosus, as well as after injury. The scalp is tense to the touch, with patchy areas of alopecia and erythema. It is difficult to restore the skin at the site of the scar, but it is possible to stop the further spread of the disease by treating the blooming edge of the area of active damage with a local steroid in cases of PL or discoid lupus. A biopsy confirms the presence of a scar and often determines the cause of the disease. You should also look for other cutaneous manifestations of PL or discoid lupus erythematosus.
- Peeling skin
This is another common dermatological problem, and flaking can affect just the scalp or be part of a larger skin lesion, as with eczema or psoriasis. The leading symptoms are itching and dandruff - both of which bring significant inconvenience to the patient.
| Figure 9. Severe form of scalp psoriasis. If thick scales form, a cream with 10% urea or olive oil can soften the scales |
Scalp eczema is usually a consequence of seborrheic dermatitis; At the same time, the skin itches and is covered with thin scales. The nasolabial folds, as well as the chest and back are often affected.
Treatment is carried out with local steroid drugs in the form of lotion or mousse, as well as tar or an antifungal shampoo, for example containing ketoconazole. Symptoms may return during stress or illness. When using coloring solutions, contact dermatitis may occur. The diagnosis in most cases follows from the anamnesis; To confirm the diagnosis, the plaque is examined.
With psoriasis of the scalp, the scales are thicker, the peeling is located at the border of hair growth and moves to the forehead or neck. It can be in the form of plaques or cover the entire scalp.
If the scales are not very thick, you can try the same treatment methods as for eczema, or a lotion (ointment) with calcipotriol. However, this is not enough to combat thicker scales. First you need to take measures to reduce the thickness of the scales. To soften and reduce peeling, use a cream with 10% urea or olive oil.
An alternative is coconut oil, a mixture of tar, coconut oil and salicylic acid.
This product stains your hair and has an unpleasant odor, but it is very effective when used regularly. Coconut is applied in the evening and left overnight. The drug stains clothing, so instruct the patient to use an old pillow. As the peeling decreases, you can move on to less unpleasant treatment methods. Further reading 1. Mortimer CH, Rushton H., James KC Effective medical treatment for common baldness in women // Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1984; 9: 342 – 348. 2. Olsen EA, Weiner MS, Amara LA et al. Five years folloe-up of men with alogenic alopecia treated with topical minoxidil // J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1987; 16: 643 – 649. 3. Kligman AM Pathologic dynamics of human hair loss. 1. Telogen effluvium. Arch. Dermatol. 1963; 87: 609 – 611. 4. Simpson NR Alopecia areata. In: Desiases of Hair and Scalp // Eds Rook AJ, Dawber RPR Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford 1991: 296 – 333.
Note!
- Hair goes through a cycle of growth (anagen) and loss (telogen); normally, a person loses up to 100 hairs per day. Only when this figure is exceeded does hair loss become noticeable
- Alopecia areata can develop at any age and in both sexes, but teenagers and young adults are more often affected; it may be associated with other autoimmune diseases such as thyroid disease and vitiligo. Most of the nests spontaneously overgrow
- Up to 60% of women over 30 years of age suffer from more or less severe androgenetic alopecia; After menopause, the incidence increases. Like men, hair loss occurs primarily at the front and top of the head. In this case, women should be reassured by saying that such hair loss is rarely severe
- Scalp eczema is usually caused by seborrheic dermatitis and is accompanied by itching. The skin is covered with thin scales. Treatment consists of topical steroids and tar or an antifungal shampoo such as ketoconazole
- Diffuse baldness can occur after pregnancy, serious illness or surgery (telogen effluvium) and can be quite severe.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine can be used to treat alopecia. In order for them to have at least some effect and not cause harm, you should use traditional recipes only after consulting a doctor.
Often, to prepare formulations for home use you will need:
- burdocks;
- onion;
- hop;
- hot pepper;
- burdock.
Masks with these components help strengthen hair roots and awaken dormant follicles.
To improve blood microcirculation, masks are used:
- from aloe, honey, garlic;
- mustard;
- red pepper.
Some traditional healers recommend rubbing regular salt into the scalp. The method helps exfoliate dead skin particles.
Traditional medicine is usually used in courses. Each is 2 weeks, then a break of 5–7 days is recommended.
Care
Experts are sure to give recommendations on hair care.
It is important not only the quality of cosmetics, but also the correct selection. Treatment of total alopecia Alopecia, or baldness, is quite common in men, but it also occurs in women and children. There are several types - focal, nested, diffuse, scar, non-scar. The most severe form is considered to be total alopecia, which leads to complete hair loss. It progresses gradually, appearing first in small areas, and over time affecting more and more areas. The intensity of the flow can vary from two to three months to a year or longer. Hair loss due to stress The statement that all diseases are caused by nerves is not unfounded. Against the background of emotional stress, chemical processes occur in the body that negatively affect health. Caring for porous hair Why do some people have curls that shine in the sun, flutter beautifully in the wind and look like they came out of a salon procedure, while others don’t even with regular care? It's all about porosity. Baldness in the temples and back of the head in men In most cases, baldness in men begins in the temple area - the hair becomes short, vellus and sparse. If you contact a trichologist at this stage, you can stop the progression of alopecia and restore aesthetics. Causes of hair loss on the back of the head Modern research methods make it possible to most accurately determine the cause of baldness on the back of the head in men, assess the current condition of the hair and scalp, and select home care. Treatment of androgenic alopecia in men Every hair on our body grows from a follicle - the shell of the hair follicle, consisting of epithelium, sebaceous and sweat glands, blood vessels and nerve endings.
Treatment options
To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor and undergo diagnostics. It is also necessary to find out the causes of the disorder; the therapeutic regimen will directly depend on this. If white spots appear on the head as pigmentation, then first of all you should visit a dermatologist, and then, possibly, an immunologist.
It must be said right away that piebaldism and albinism have no cure. There is only surgery to eliminate the defect. It consists of transplanting healthy donor skin or cells with endogenous melanocytes. After the intervention, it takes up to 1 month for healing and the onset of effect.
With contact dermatitis, it is important to identify and eliminate the irritant. To relieve itching, it is allowed to use antihistamines in the form of tablets or creams, as well as ointments for local anesthesia. It is recommended to adjust your diet by removing sweet, salty and spicy foods from your diet, and you should also give up alcoholic beverages for a while.
Seborrhea requires complex therapy. First, you need to adjust your diet by eliminating harmful foods. Patients are also prescribed vitamins or dietary supplements. Vitamin deficiency is very dangerous, so it is necessary to consume more foods that contain the necessary substances. More detailed information can be found in the table.
| Vitamin | Products where to find | The danger of lack |
| A | Citrus fruits, cod liver, cheese, butter, chicken eggs, carrots | Dry skin, wrinkles, hair loss, weakened immunity, gastrointestinal disorders |
| AT 2 | Mushrooms, (chanterelles), wheat sprouts, liver, bread, egg yolks, cheeses, cottage cheese and broccoli | Skin rashes, chapped lips, poor sleep and appetite |
| AT 5 | Broccoli, rice, legumes, liver, offal, peanuts | Hair loss, brittle nails, worsening mood, tendency to depression |
| AT 6 | Chicken eggs, milk, meat, seafood, salad, bananas, walnuts, wheat | Peeling, irritation and dry skin, seborrhea, loss of appetite |
| AT 9 | Legumes, various nuts, citrus fruits, eggs, bananas | Anemia |
| WITH | Oranges and lemons, currants, sea buckthorn, strawberries, kiwi | Dry dermis, long healing of scratches and wounds, insomnia, stress, infectious diseases |
| D | Fatty fish, cod liver, cow's milk | Fluctuations in blood pressure, development of rickets (in children) |
| E | Almonds, oils (especially olive), fennel and spinach | Infertility, early aging of the body |
| Nicotinic acid (PP) | Rabbit, mushrooms, turkey meat | Coarsening and flaking of the skin, bleeding gums, stomach pain |
| Biotin (N) | Beef liver, eggs (yolks) | Seborrhea, dermatitis, sleep and appetite disorders, stunted hair and nail growth |
It is also necessary to use medications to get rid of dandruff; sometimes antibiotics or antifungals are required. Proven ointments are Clotrimazole and Pimafucort; Skin-Cap and Triderm are common creams. It is recommended to change your hair care by changing the shampoo to a medicated one, for example, Sulsena or Nizoral. It is possible in addition to use tar soap for washing your hair. The duration of treatment is at least 14 days.
If the cause of white spots on the head is psoriasis, you must adhere to another treatment. In general, it is similar to antifungal therapy, but other agents must be used. To wash your hair, you can use special shampoos - Algopix, Psorilom or Libriderm zinc. It is recommended to treat the head with Fluorocort, Elocom, Losterin or Lorinden. Treatments with ultraviolet rays have a positive effect.