The skin protects the human body from harmful environmental influences. In addition, there are a number of internal factors that affect the condition of the skin (hormonal changes, stress, poor nutrition). Internal failures and negative exogenous effects are increasingly becoming the cause of the development of benign skin tumors. Any growths on the human body cause psychological discomfort, and when located in injured areas they can be accompanied by pain, bleeding, inflammation, and infection. Benign neoplasms also include moles, and many people know that not all moles are benign. Removing skin tumors is the most effective method of treating them.
Reasons for the development of skin tumors
- prolonged exposure to direct ultraviolet rays;
- global disruptions in the immune system (granuloma annulare);
- decreased protective functions of the body (plantar and palmar warts);
- bad habits;
- frequent stress;
- disturbance of metabolic processes in the body (keratomas, fibromas, nevi, xanthomas);
The main danger to human health is due to the fact that many benign tumors are prone to malignancy (malignancy).
Only complete removal of the tumor can prevent its malignancy. Patients of the multidisciplinary medical center have access to a full range of services in the field of detection and treatment of dermatological tumors. Surgical treatment of tumors in our clinic is carried out by highly qualified plastic surgeons and dermatosurgeons; advanced equipment is used during the procedures. During surgical treatment of tumors, our patients are provided with the maximum therapeutic and aesthetic effect.
How does HPV infection occur?
The mechanism of transmission of the virus is contact; the source of infection is the patient or the virus carrier. HPV can be released not only from growths on the skin, but also circulate in the blood, saliva and urine. In this case, infection can occur in 4 main ways:
- through contact and everyday life;
- sexually;
- during childbirth from mother to child (which may be the cause of laryngeal papillomatosis);
- during autoinoculation (self-infection or dispersion of the pathogen from existing foci during combing, shaving, or using a hard washcloth).
The risk of HPV infection usually depends on the state of the human body’s immune system, viral load and the presence of microtraumas and other inflammations on the skin and mucous membranes.
Even when infected with the HPV virus, papillomas do not always form on the skin and mucous membranes. The virus is localized in the basal layer of the epithelium and can remain inactive for a long time. Only under certain conditions (weakening of the immune system, stress, exposure to unfavorable environmental factors) do the processes of its replication start, which leads to cell proliferation and the appearance of tumors.
Indications for removal of skin tumors
- genetic predisposition (skin cancer pathologies in a related line);
- frequent injury (location in the axillary area, neck, arms, scalp);
- location of a large number of formations (20 or more) in a small area of the body;
- viral origin (genital warts, papillomas);
- color change (uneven or variegated color);
- localization in open areas, often exposed to direct sunlight (face, neck, hands);
- uneven growth, unclear boundaries;
- discomfort, pain, bleeding, itching, redness of the skin around the tumor;
- a pronounced cosmetic defect that affects appearance and provokes psychological discomfort.
Since neoplasms on the skin are dangerous due to the risk of complications in the form of malignancy, you should never try to remove them yourself. Only an experienced doctor can recognize the nature of the tumor and select the optimal removal option based on a thorough examination of the patient.
When contacting the Mother and Child clinic for treatment of skin tumors, the patient first of all receives highly qualified advisory assistance, after which, together with the patient, the most acceptable option for removing the tumor is determined. Before removing or destroying a tumor, the doctor must determine its nature (benign, oncological). If the tumor is located in the upper layers of the skin, atraumatic diagnosis using an electron-optical device (dermatoscope) is often sufficient.
Contraindications for the procedure
Laser removal of benign tumors is prohibited if the following contraindications are present:
- Diabetes mellitus of the first and second degree.
- Oncological pathologies.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Aggravated herpes.
- Epilepsy, thrombocytopenia, photodermatosis.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Inflammatory processes accompanied by fever.
If contraindications are neglected, undesirable consequences may develop after removal of the tumor. For example, pigmentation due to photodermatosis, allergies, swelling due to autoimmune pathologies, keloid scar due to endocrine system disorders.
What skin tumors are removed in the clinic?
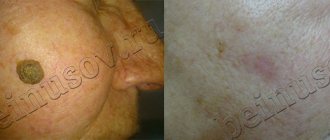
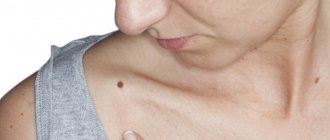
Moles (nevi) are formations with clearly defined edges, with increased pigmentation, developing due to the accumulation of a large number of nevus cells in the upper and lower layers of the dermis. Nevi develop at a very early age, their development peaks in middle age, and in old age they often disappear or undergo age-related changes. According to statistics, most adults have, on average, twenty moles.
Moles can be congenital or acquired. Depending on their size, nevi are divided into small, medium and large. Based on the depth of their location, nevi are differentiated into epidermal, intradermal and borderline.
Small congenital nevi that do not change their shape and color, as a rule, do not require radical interventions. The treatment tactics for modified moles are determined by a dermatologist. If indicated, after excision of the nevus, Mother and Child specialists send samples for histological analysis.
Treatment methods for nevi: surgical excision, laser destruction.
Lymphangioma is a benign neoplasm that affects the lymphatic vessels. Benign tumors of the lymphatic vessels are divided into:
- primary (congenital), they are often combined with hemangioma;
- secondary (acquired). Secondary tumors develop against the background of an infection and act as a symptom of impaired lymph circulation (lymphostasis).
The key diagnostic symptom of lymphangioma is the release of lymph when the tumor is punctured.
Treatment method for lymphangioma : surgical excision.
Hemangioma is a benign tumor that forms in the womb at birth from vascular tissue structures.
The following forms of hemangioma are distinguished:
- port-wine stain (flaming nevus) - contrasting pink spots on the skin, most often localized on the back of the head, back, and facial skin;
- cavernous - convex seals on the skin, flesh-colored or bluish in color, soft to the touch;
- capillary (strawberry nevus) - bright red convex tumors with clear outlines that affect the skin of the face, scalp, chest, and back.
Treatment tactics for hemangioma: In the absence of intensive growth of capillary and flaming nevus, dynamic observation is indicated. If indicated, hemangiomas are removed using the classical surgical method or through laser destruction.
Papilloma (wart) is a benign growth of epidermal tissue on a thin stalk or wide base, having a papillary surface. The diameter of papillomas ranges from three millimeters to one and a half centimeters, the color varies from white to brown. Papillomas develop against the background of the penetration of the papillomavirus into the body and are transmitted by contact. Usually papillomas affect the skin of the face and body, in some cases they are located on the mucous membranes, including internal organs. In the absence of timely treatment, the papillomavirus quickly progresses, which is manifested by reproduction and an increase in the diameter of the growths.
Treatment of papillomas: excision with a scalpel, laser removal.
Fibroma is a benign reproduction and proliferation of connective tissue structures. Soft fibroids are visually similar to pouches, have different sizes, and are pink or brown in color. Solid fibroids have a dense consistency, a wide base, a light pink tint and are smooth to the touch.
Fibroma treatment: surgical removal.
Atheroma is a cystic formation in the form of a capsule with serous or purulent contents, developing due to blockage of the sebaceous gland. Atheromas are round in shape, soft to the touch, their sizes range from five millimeters or more. Dermal cysts are most often localized on the face, earlobes, head and torso. During inflammation, the serous contents of the atheroma can suppurate; such processes are often accompanied by a local or general increase in body temperature and recur until the capsule is peeled off.
Treatment of atoroma : the neoplasm is surgically removed along with the capsule “in the cold period”, when there are no signs of inflammation. During the inflammatory process, as a rule, the atheromas are opened and drained, and the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy.
Lipoma (fat) is a tumor of fat cells. Lipoma is a soft, painless subcutaneous nodule; its course is benign. Wen have different localizations and appear on any part of the body where there are fat cells. Most often, these tumors are diagnosed on the neck, hips, and abdominal area.
Lipoma treatment: surgical excision.
Clinical picture
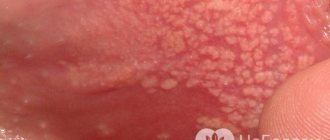
Condylomata acuminata are formations of flesh-pink color, lobulated, ranging in size from 2 millimeters to ten centimeters, with exophytic growth, in which the apex of the genital condyloma is often wider than the base. Externally, the growths may resemble cauliflower or cockscomb.
The incubation period can range from 2-3 months to 2-3 years or more. The growth rate of formations varies, which is often associated with the state of local immunity, the presence of concomitant STIs, and sexual activity.
Methods for removing dermatological tumors in our clinic
Classic surgical excision
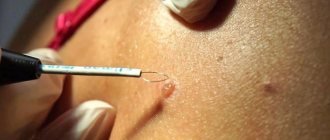
Removal with a scalpel is one of the most radical methods of treating tumors. After excision of the tumor tissue, cosmetic sutures and an aseptic dressing are applied to the wound. The mini operation takes place under local anesthesia. Surgery is indicated for large tumors and if a malignant process is suspected. The practical skills of highly qualified medical specialists make it possible to prevent the appearance of pronounced scars and achieve maximum aesthetic effect.
Laser destruction (laser removal)
Laser destruction is the most progressive and safe method of treating dermatological neoplasms. The procedure is practically painless; for small tumors, anesthesia may not even be used. During laser destruction, the doctor projects a laser beam on the tumor for several seconds. The use of a laser is advisable when there is no need to study tissue morphology, since the tumor structures are completely destroyed.
Advantages of this method:
- absence of complications in the form of bleeding, metastasis and infection (blood vessels are completely coagulated);
- rapid tissue regeneration, absence of cosmetic defects;
- short rehabilitation period, painlessness.
Removal of tumors at the Mother and Child clinic is carried out after a comprehensive diagnosis of the patient and examination by an oncologist (if indicated).
At the slightest suspicion of a malignant process, specialists at our medical center submit tissue samples for morphological examination and develop further treatment tactics depending on the histology results.
Papilloma virus. Diagnostics:
- Consultation with a dermatovenerologist . Only a dermatovenerologist can make a diagnosis during an initial examination, assessing the clinical picture, conducting a test with acetic acid, and, if necessary, using the dermatoscopy method.
- Laboratory diagnostics. It is necessary to conduct a HPV test using the PCR method, which will allow you to estimate the amount of the virus, as well as determine which type of HPV is present in this case (they are divided into types with high and low risk of oncogenicity). A PCR test must also be performed on all sexual partners of a patient with genital warts. A positive test result in the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease means that treatment is necessary to suppress the development of the virus in the body.
- Urethroscopy is a study of the condition of the urethral mucosa using special endourethral endoscopes. Considering the increase in recent years in the number of patients with endourethral condylomas, this study is necessary for all patients, both men and women.
- Extended colposcopy - examination of the cervix using a colposcope and performing a test with acetic acid and the Schiller test. It is necessary for all women to undergo laboratory confirmation of papillomavirus infection, since the presence of flat condylomas on the cervix is possible.
- Immunogram is a study of the state of the immune system. This will allow for the most effective HPV therapy.
Rehabilitation after removal of dermatological tumors
The duration of rehabilitation after radical and low-traumatic treatment of a dermatological formation depends on its size, morphological characteristics, as well as on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. To reduce the recovery period, the patient must adhere to the following recommendations:
- During surgical removal, regular wound dressings and examination by a specialist are performed on days 4-7.
- After laser destruction, it is necessary to avoid injury to the resulting crust.
- You cannot peel off the crust yourself; this can lead to infection of the wound and cause the development of a scar. The crust will come off on its own.
- It is necessary to treat the wound with prescribed medications according to the recommended regimen (developed individually).
- After the crust is rejected, the skin at the site of laser exposure must be protected from the sun (use sunscreen and not be in direct sunlight until complete recovery), since these areas are very susceptible to hyperpigmentation.