General information
If the scalp is flaky, itchy and inflamed, causing a person significant discomfort, most likely it is a fungal disease. Hair fungus ( mycosis ) is a disease that can be caused by various reasons.
Fungal infections are widespread in the modern world. There are about 500 species of fungi that infect humans. They are resistant to external influences. Often people who experience unpleasant symptoms believe that their causes are trivial - an incorrectly chosen headdress, too dry skin, etc. As a result, they do not treat the disease, and the situation gets worse. Since hair fungus can be caused by different types of fungal pathogens, it is necessary to visit a doctor, undergo an examination and apply the appropriate treatment regimen. This article will discuss how to recognize fungal diseases of the scalp and what treatment can be practiced after diagnosis.
Features of hair damage with trichophytosis
Trichophyton ectothrix
Zooanthropophilic trichophytons belong to the group Trichophyton ectothrix (ecto - outside). They have large and small spores, which form sheaths at the base of the hair: the wider ones are large-spored, the narrower ones are small-spored. Along with spores, short or long chains of rounded spores are found in the peripheral region of the hair. Trichophyton ectothrix are the cause of the development of infiltrative-suppurative processes and purulent melting of follicles.
Trichophyton endothrix
Anthropophilic trichophytons belong to the group Trichophyton endothrix (endo - inside). The spores of these fungi are found inside the hair. They have a round shape, are large in size (5 - 7 microns), densely fill the hair inside without going beyond their limits, are arranged either in the form of chains, or fill the hair like a bag of nuts.
Rice. 10. Trichophyton ectothrix: pathogen spores envelop the outside of the hair, like a muff (photo on the left). Trichophyton endothrix: The inside of the hair is filled with spores (photo on the right).
Pathogenesis
An excessive increase in the number of fungal microorganisms may be due to systemic disorders in the body. Fungal infections of the head occur against the background of deteriorating immune system function, metabolic and endocrine disorders, deterioration of skin condition, as well as concomitant diseases. Gender, age, and professional factors also play a certain role. Thus, children's skin is especially favorable for the introduction of fungi and the transition of fungal flora into pathogenic skin.
Pathological changes in the scalp depend on the type of pathogen. As a rule, as a result of the active development of fungal microflora , the inflammatory process of the skin is activated. of alopecia or areas covered with dry scales appear on the scalp These signs are often combined.
Classification
Photo of fungus on the head
The course of the disease depends on the type of fungus affecting the skin.
- Microsporia is a fungal disease that develops when the pathogen Microsporum is infected. Infection occurs from other people or animals. Very often, these microorganisms affect children who often come into contact with animals. The incubation period is 5-6 weeks, after which the hair gradually becomes brittle and dry, and eventually begins to fall out. The skin turns red in the affected areas, small blisters appear on top. Hair turns gray at the base - this causes active proliferation of fungi on the hair follicle.
- Trichophytosis - damage is caused by trichophyton fungi. Most often, such a lesion is observed in children, but it is also diagnosed in adults. The disease can only affect the scalp, but sometimes the lesion also appears on the skin and nails. Trichophytosis can be superficial and deep. With the superficial form, small multiple foci of peeling appear on the head under the hair. They have blurred borders and a whitish color. Some of the hair on these lesions breaks off, and the broken hair rises several millimeters above the skin level. That is why this form of fungal infection is also called ringworm . Black dots from broken hair are visible on the lesions, and white-gray scales cover the skin. The deep form of the disease appears due to infection by trichophyton fungi, which live in the skin of animals. This form is acute. First, red spots appear on the scalp, then signs of an active inflammatory process appear. Gradually, the lesions merge and form a continuous lesion that protrudes above the skin. Hair growing on this area falls out easily. When the ulcers open, the disease may go away on its own. After it, scars remain, and the hair on them does not grow back. The disease lasts a long time - up to 10 weeks. Often the deep form of the disease affects men, developing in the mustache and beard area. It is also diagnosed in children.
- Nodular trichosporia (white piedra) - this pathological process is characterized by anthroponotic mycotic damage to the hair cuticle. Trichosporia is most often diagnosed in people who live in warm or tropical climates. White piedra develops under the influence of the pathogen basidiomycete Trichosporon beigelii. Trichosporia nodosa affects the beard, mustache, scalp, pubis, and armpits. It can occur both acutely and chronically. The source of infection is a sick person. You can become infected by using hygiene items from a carrier of the pathogen. As the disease develops, dense white nodules of irregular or oval shape appear. These nodules, which are collections of fungal spores, envelop the hairs. They can stick together to form bundles. The hair shaft is affected, but it does not break off.
- Favus (scab) - it is caused by the fungus Achorion, which only affects humans. With such a lesion, yellow crusts appear on the scalp, tightly covering the hairs, and gradually leading to atrophy of the hair follicles and complete baldness. Each such crust is a cluster of fungi. In the early stages, it is difficult to determine this disease, since at first there are no symptoms. This type of fungus mainly affects residents of Asia and the Middle East.
- Dermatophytosis - the causative agents of this form of fungus are the molds Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Microsporum canis. With this form of the disease, round foci of hyperemia appear on the head, with a clearly defined edge. The hair becomes dull and a white coating appears on the roots. Sometimes with dermatophytosis, a kerion - a large soft formation on the skin under the hair. Kerion is an inflammatory response to a dermatophyte. This formation can subsequently lead to alopecia.
Causes of fungal scalp infection
Microsporia is the most common infection of the scalp. Causes of the disease:
- In 98% of cases, the cause of microsporia is the zooanthropophilic fungi Microsporum canis (dog microsporum) and Microsporum folineum (cat microsporum). Cats (more often) and dogs (less often) get sick and transmit the infection to humans. These pathogens cause superficial microsporia.
- In 2% of cases, the cause of microsporia is the anthropophilic fungi Microsporum audouinii (more often) and the more contagious Microsporum ferrugineum (less often). These pathogens cause infiltrative-suppurative microsporia.
- Microsporum gypseum and Microsporum nanum live in soil. This type of microsporia is very rare.
Trichophytosis of the scalp is less common than microsporia. Its causative agents are:
- Anthropophilic fungi Trichophyton tonsurans, less commonly Trichophyton violaceum. They cause superficial trichophytosis and are also the cause of chronic trichophytosis in adults.
- Zooanthropophilic fungi Trichophyton mentagraphytes (var. gipseum) and Trichophyton verrucosum (var. faviforme). Infection occurs from large domestic animals and rodents. Fungi are the cause of the development of infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis.
Favus or scab is extremely rare in the Russian Federation. Its cause is the anthropophilic fungi Trichophyton Schonleinii. Cases of infection from mice and cats have been reported.
Rice. 3. Colonies of fungi Microsporum canis (photo on the left) and Trichophyton mentagrophytes (photo on the right).
Causes
Mycosis of the scalp develops for the following reasons:
- Infection with pathogenic microorganisms is infection by a number of pathogenic fungal microorganisms.
- The impact of external factors on the natural microflora of the head. As a result, fungi that are part of the normal microflora behave like pathogens.
In turn, factors that can affect this process are:
- Poor nutrition, in which the body does not receive enough proteins, microelements, and vitamins. B vitamins, zinc, selenium, and iron are especially important for the normal condition of hair and scalp. When there is a deficiency of these substances, fungi quickly become active.
- Violations of the functions of the internal secretion organs. As a result, changes occur in the composition of the secretion of the sebaceous glands. As a result, the microflora, not receiving the necessary nutrition, exhibits pathogenic activity.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Chronic intoxication due to poisoning with alcohol, salts of heavy metals, drugs, etc.
In addition, there is a hereditary predisposition to some fungal diseases.
You can become infected with pathogenic microorganisms when a person comes into contact with a carrier of the infection or uses his personal hygiene products. There is a risk of infection in public places - sauna, bathhouse, swimming pool. Sometimes the pathogen enters through broken skin.
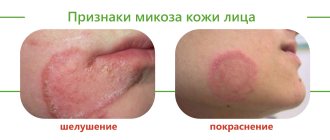
Symptoms of fungus on the head
Photos of symptoms of fungus on the head
Signs of fungal infections largely depend on their type. But we can identify some common characteristic symptoms of mycosis.
With the development of this disease, the following symptoms of scalp fungus appear:
- The first sign of problems may be the appearance of roughness, redness and dullness of the hair.
- You should be wary of prolonged itching, which intensifies over time. In such a situation, you should not comb the skin, because if the epidermis is damaged, the infection process is inevitable.
- As the pathological process develops, dandruff , gradually its number and size of scales increases.
- Seborrhea develops - the skin under the scales becomes red and irritated. As a result, seborrheic plaques form, and dandruff becomes denser, acquiring a yellowish color. If adequate treatment is not carried out at this stage of the disease, the hair in the affected areas will begin to fall out.
If a patient develops ringworm, symptoms appear fairly quickly. Painful swellings and bubbles - vesicles - may form.
Tests and diagnostics
At the first signs resembling the symptoms of a fungus, you should immediately consult a doctor to determine the exact cause of the pathological process. The specialist examines and interviews the patient, and also takes tissue from the scalp for microscopic examination. Specific tests and Wood's fluorescent lamp diagnostics are carried out.
A blood test for this disease is not an indicator, since it does not determine the presence of mycobacteria.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes other tests.
Diagnosis of mycosis of the scalp
Diagnosis of scalp fungus is based on collecting an epidemiological history, clinical picture of the disease and laboratory diagnostics.
Microscopy
With this type of study, spores and mycelium of fungi are detected, but it is impossible to differentiate microscopy from trichophytosis. Microorganisms are identified using the culture method followed by microscopy. The material for the study is the patient's scales and hair taken from the peripheral zone of the lesion.
Rice. 20. Microscopic picture of Microsporum canis (fluffy microsporum). The mycelium (photo on the left) and numerous exospores (photo on the right) are clearly visible.
Cultural examination
The most reliable sign of scalp fungus is the detection of growth of pathogens on nutrient media. Microscopy of the obtained material makes it possible to identify the type of mushroom.
Rice. 21. Type of colonies of Microsporum canis (fluffy microsporum). It is detected in patients with microsporia in 98% of cases.
Establishment of the tissue form of trichophytons
Microscopy of affected hair reveals the tissue form of trichophytons:
- Zooanthropophilic trichophytons belong to the group Trichophyton ectothrix (ecto - outside). The spores of these fungi are found on the outside of the hair. Trichophytons of this species are the cause of the development of infiltrative-suppurative processes on the scalp.
- Anthropophilic trichophytons belong to the group Trichophyton endothrix (endo - inside). The spores of these fungi are found inside the hair.
Rice. 22. Trichophyton ectothrix hair lesion.
Rice. 23. Trichophyton endothrix hair damage.
Diagnosis of scalp fungus using a Wood's fluorescent lamp
The emerald-colored glow in the rays of a fluorescent lamp (Wood's lamp) is characteristic only of microsporia.
Rice. 24. Fluorescence (glow) of hair in the rays of a fluorescent lamp during microsporia.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies can be used as auxiliary methods in the process of complex treatment of fungal diseases.
- Onion and garlic . You need to prepare a paste from these vegetables and apply it to the scalp, leaving it for half an hour. It is better to do this procedure on weekends, as your hair may smell sharp after it. It is carried out once a week.
- Herbal decoctions . They are used to wash your hair twice a week. Decoctions for washing can be prepared from chamomile, burdock root, calendula, nettle, plantain leaves, etc.
- Burdock and castor oil . You need to make compresses from them, applying the selected oil to the scalp. Next, you need to cover your head with plastic and wait half an hour, then wash your hair. Such procedures should be carried out twice a week.
- Oak bark . You need to prepare a decoction, pour 1 tbsp. l. bark 200 ml water. After 5 minutes, cool, strain and mix with 1 tbsp. l. honey Rub into scalp, cover with film and towel. Wash off after an hour. This mask can only be made if you are not allergic to bee products.
- Vinegar . Mix table vinegar with distilled water in equal proportions and wipe the scalp with the solution using a cotton swab. After half an hour, wash your hair. After this procedure, itching decreases.
- Soda . Add soda to shampoo for washing hair using 1 tsp. for one wash. You can also use it by diluting it in 1 glass of water and adding 1 drop of essential oil. This solution should be applied to the scalp and wait half an hour before washing.
- Salt mask . You should grind two soaked rye bread crusts and mix them with 1 tsp. salt and 2 yolks. Apply to scalp and leave for 40 minutes.
- Essential oils . It is recommended to add a few drops to your balm or shampoo. Melissa, eucalyptus, cypress, and tea tree oils are effective against fungus.
Treatment of fungal infections
Thrush is treated with antifungal agents that are applied to the skin or mucous membranes. Systemic therapy is also prescribed. If you treat only the symptoms, a relapse will soon occur. The cause of the disease should be combated by strengthening the body’s protective functions.
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is necessary only in case of severe disease and in the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Treatment of fungal infections in children has the following approach:
- prescribing monotherapy or a combination of systemic and external antimycotic agents;
- the use of immunostimulants, glucocorticoids and antihistamines.
To increase the effectiveness of drug therapy, multivitamin complexes and physiotherapeutic procedures (DMV, therapy, darsonvalization, magnetic therapy, medicinal electrophoresis) are prescribed. Treatment should be carried out 2-3 times a day. The hair is shaved and the crusts are carefully removed.
When localized on the feet and hands, it is recommended to use special pastes, creams and ointments based on clotrimazole, neftifine or terbinafine. If a bacterial infection occurs, it becomes necessary to use antibiotics. For protracted and severe fungus of the nails, face and body skin, and hair in a child, antimycotic drugs containing fluconazole, itraconazole or griseofulvin are indicated.
For onychomycosis, it is necessary to use the drug until the nail grows completely. If drug treatment is ineffective, then surgical removal of the nail plates is performed.
To permanently defeat an infectious disease, you need to use the right medications and adhere to a certain diet. Self-medication in this case can lead to the development of serious complications.
Foods that should be excluded from the diet:
- Sugar, in any variety - honey, cane sugar, dextrose, fruit, malt and beet sugar, maple syrup, etc.
- Refined carbohydrates - white bread, buns, cakes or cookies, light noodles, white rice, etc.
- Products containing yeast.
When treating fungal infections in children, it is recommended to keep the affected area dry by frequently changing underwear or diapers. After showering and bathing, it is advisable to pat your skin well with a soft terry towel.
Prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to follow important rules of prevention:
- Infection with pathogenic fungi should be prevented. To do this, it is necessary to avoid contact with sick people and animals with signs of disease. It is important to always use personal hygiene products.
- It is important to wash your hair regularly and choose shampoos that suit your hair type.
- You should eat right and avoid strict diets.
- You need to move a lot and practice physical activity regularly.
- It is important to avoid stressful situations.
Epidemiology
- Microsporum canis fungi are infected from sick cats and dogs (usually kittens). Mostly children get sick. They become infected through direct contact with animals. By the time of puberty, self-healing is noted, which is associated with the normalization of cellular-humoral immunity.
- Infection with the fungi Microsporum gypseum and Microsporum nanum occurs in adults cultivating the soil.
- Anthropophilic species of fungi that cause microsporia and trichophytosis are infected from sick people and infected household items (pillowcases, hats, scarves, scissors, combs, etc.).
- The source of Trichophyton mentagraphytes mushrooms is domestic animals: cattle, horses, calves, goats and donkeys, as well as wild animals. The source of Trichophyton verrucosum are small mouse-like rodents, rabbits, gophers and guinea pigs. Transmission of infection from a sick person is possible. Infection from animals occurs through direct contact, as well as through the hair and scales that animals leave on the soil, hay and feed. Rural and urban residents - workers of hippodromes, circuses, zoos and veterinary institutions - are getting sick. In addition to animals, the role of grasshoppers in transmitting infection has been proven. Trichophytons were found in corn stalks and straw.
- Favus spreads mainly among members of the same family. Low levels of sanitation and personal hygiene contribute to the appearance of mycosis.
Rice. 4. Kittens, cats and dogs are the main sources of microsporia.
Rice. 5. Cattle and horses are the main sources of zooanthroponotic trichophytosis.
Diet
Antifungal Diet
- Efficacy: no data
- Terms: 3-6 months
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles. in Week
The diet should contain many foods containing vitamins A, B, C, zinc, selenium, and nicotinic acid. It is recommended to consume the following foods:
- Dairy products - sour cream, cottage cheese, milk, homemade yoghurts, kefir.
- Eggs.
- Dark rice, whole grain pasta, buckwheat, millet, oatmeal.
- Lean meat, steamed or boiled.
- Greens, fresh fruits and vegetables - beets, onions, garlic, cucumber, dill, parsley, raspberries, apples, cranberries are useful.
- Legumes.
- Walnuts.
- Whole grain bread without yeast.
The following foods are excluded from the diet:
- White sugar.
- Broth, fatty foods.
- Milk.
- White rice, white bread, pasta made from premium flour.
- Alcohol – beer, vodka, sweet wines, fizzy drinks.
- Dried fruits.
- Store-bought confectionery, soda, packaged juices.
- Jam.
- Canned food.
- Pears, bananas, grapes.
- Peanuts, cashews, sunflower seeds.