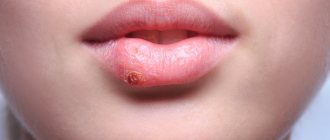
Every person has several nevi on the surface of the skin. A mole on or near the lip is a fairly rare occurrence. Some consider pigment formations to be a highlight of appearance, while others consider them to be an undesirable defect.
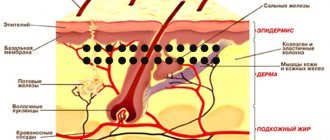
Nevi occur due to the accumulation of melanocytes - cells responsible for the production of melanin. The bulk of moles are formed during global changes in the body. This includes puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. The process of secretion of hormones by the pituitary gland is accompanied by excessive production of pigment. Many doctors believe that the algorithm for the development of nevi is embedded in the genetic code. Members of the same family often have similar numbers and locations of pigment formations.
A mole on the lip can appear throughout life. This is due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Visiting a solarium and prolonged exposure to the sun lead to intense melanin production. The reasons for the formation of nevi also include:
- radiation and x-rays,
- pathologies of internal organs,
- taking hormonal drugs,
- inflammatory skin diseases,
- allergic reactions.
Causes of moles on the lip
A mole is the result of the proliferation of a certain number of subcutaneous cells. Where do nevi come from and what causes their formation? Medicine puts forward several possible answers to this question:
- Heredity is a tendency to the appearance of birthmarks, which is passed on to children from parents.
- Ultraviolet radiation - exposure to open sunlight or irradiation in a solarium.
- Changes in hormonal levels - taking hormonal medications, pregnancy and childbirth, stress, illness.
- The influence of harmful factors such as x-ray or radiation exposure, trauma or viruses.
Some doctors also note the appearance of moles on the lips of people who smoke, but this theory has not yet been properly confirmed.
Diagnosis of melanoma of the mucous membranes
When diagnosing mucosal melanoma, mistakes often occur. Due to its hidden position and lack of noticeable early signs, detection of mucosal melanoma is usually delayed.
When diagnosing a primary melanoma, especially a rare one, it is important to exclude the possibility of metastatic lesions from the primary cutaneous or ocular melanoma.
If melanoma of the mucous membranes is suspected, endoscopic examinations are performed:
- tracheobronchial tree;
- upper respiratory tract;
- esophagus and stomach;
- large intestine;
- rectal segment.
During the diagnostic procedure, the doctor takes fragments of the changed mucosa for analysis. A biopsy of a sample of suspicious tissue and subsequent pathological examination are the main points in the diagnosis of mucinous melanomas.
Amelanotic forms of tumors, which are often found among mucosal lesions, further complicate diagnosis. Immunohistochemical staining of the material to detect tumor protein (S-100, HMB-45, Melan-A, Mart-1) and the tyrosinase enzyme helps in the diagnosis of non-pigmented forms of the tumor.
If the prevalence and metastasis of mucous melanomas is suspected, a body scan with visualization is performed: CT, PET CT, MRI.
Types of moles on the lips
In medicine, nevi are classified into vascular, which arise due to the rapid growth of capillaries, and pigmented, which appear due to excess melanin.
Moles on the lip can vary significantly in appearance: shape, size and color. Based on this, the following types of moles are distinguished:
- Flat - small formations located in the upper part of the epidermis. They are practically invisible and do not create any discomfort.
- Convex - their appearance occurs in the deep layers of the skin. These moles usually contain hair follicles.
- Vascular - have a pronounced blue or purple color and a compacted structure.
- Hemangioma - this neoplasm looks like a nodule or wart.
- Age spots are most often congenital. They can reach large sizes and pose the greatest risk of forming a malignant tumor.
How are moles removed with laser?
The content of the article
The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia - before removing the mole, the doctor administers local analgesics. The effect of the drug lasts from half an hour to 3 hours. After the procedure, a wound remains, which, depending on the size and location of the removed mole, heals in 2-4 weeks.
After the procedure for removing the bandage, the doctor writes a prescription for an ointment, which must be used at home until healing. This prevents infection and provides a beautiful aesthetic appearance and helps prevent scarring. Depending on the size and location of the mole, the procedure takes 10-15 minutes, and several moles can be removed in one visit.
The laser, which is used to remove moles or other skin lesions, works on the principle of evaporating water from cells. This means that water evaporates from the affected cells and the cells die, while the surrounding tissue remains intact. True, in some cases, a post-procedure wound on the skin caused by heating may seem deeper than it actually is, but after a few days everything returns to normal, and the skin defect fills in during the healing period and leaves a small spot.
The effect of laser on moles
The surgical laser used for mole removal (and other soft tissue procedures) is highly accurate and is by far the best choice for this type of procedure.
Possible danger
Often, a mole on the lip does not cause much discomfort. Most often, the desire to remove it appears only when it does not have an aesthetic appearance. However, we should not forget about the danger that can hide behind even the smallest and most defenseless neoplasm.
The first thing you should pay attention to is that the face is the most unprotected part of the body that is exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Under the influence of sunlight, especially in the warm season, a mole on the lip can grow and change, which may be one of the signs of a malignant tumor. Therefore, you should carefully monitor its visual transformations and, if possible, protect it from direct sunlight.
In addition, if a mole has a convex structure, it may be subject to mechanical damage, which is completely unacceptable.
Changes in the structure, shape and color of the nevus should be constantly monitored and if any of the following symptoms appear, immediately consult a doctor:
- Mechanical damage to a mole;
- Discharge of blood or ichor;
- Itching and peeling;
- Painful sensations;
- Inflammation of a mole;
- Rapid increase in size;
- Color change.
When to see a doctor?
Nevi located in the lip area or on their surface need to be closely monitored. Moles are not protected by clothing and are constantly exposed to sunlight. Pigment formations are often injured during shaving or hair removal, eating, etc. Regular damage to the nevus increases the risk of developing melanoma several times.
Signs indicating malignant degeneration include:
- nevus growth - an increase in size by more than 4 mm in a short time;
- color change - sudden fading or darkening, inclusions, uneven coloring;
- lack of skin pattern - the mole is flaky or has a glossy surface;
- asymmetry - asymmetrical halves when visually dividing the nevus;
- dynamics of the process - pain, tingling, itching, hair loss, blurring of boundaries, bleeding, etc.
If you identify at least one alarming sign, you must contact a dermato-oncologist. With a 95% chance, skin cancer can be defeated at the initial stage. During the diagnosis, the doctor will determine the type of formation, establish the process of degeneration, and select the optimal treatment regimen. If necessary, he will prescribe fluorescent microscopy and a blood test to determine the level of tumor markers.
Diagnostics
If you have a black mole on your body, it is not at all necessary to remove it, but you need to contact a specialist. The dermatologist will conduct a diagnosis, which consists of examining the neoplasm and studying it using optical or digital dermatoscopy (under magnification).
During the examination, the doctor evaluates the size of the tumor, its density, structure, consistency, surface character, symmetry, edge, color and other signs. As a rule, examination and dermatoscopy are sufficient to make a diagnosis. Biopsy and histological examination are carried out only before removal. In other situations, dermatologists prefer not to injure black moles unnecessarily.
Melanoma-dangerous nevi
Listed below are specific types of black moles that are melanoma-dangerous. This means that when exposed to unfavorable factors, they can degenerate into melanoma; the risk of malignant transformation is higher than in the case of ordinary nevi.
Dysplastic nevi. This type of nevi is characterized by the presence of melanocytic dysplasia, an atypical arrangement of melanocytes. Only a dermatologist can diagnose melanocyte dysplasia. The patient needs to know that a dysplastic nevus has a smooth surface. It does not rise above the skin, or only its central part rises. The shape is irregular, with uneven edges. The coloring is uneven, with black areas located in the center.
Blue nevus. Despite the name, the formation can be not only blue, but also black. Usually has the shape of a regular hemisphere and rises above the surface of the skin. The surface is smooth, the edges are even. Typical localization is the scalp, feet and hands, and gluteal region. The risk of malignancy increases after injury, including independent attempts at removal.
Nevus Ota. This type of tumor appears only on the face. Characteristic mainly for representatives of the Mongoloid race. The color is black or bluish. The differential sign is the presence of pigmentation of the sclera, iris or conjunctiva of the eye.
Borderline pigmented nevus. The neoplasm is formed in childhood. Subsequently, birthmarks increase in size throughout life, reaching one and a half to two centimeters in diameter. The differential feature is an uneven ring-shaped coloration, with a decrease in color intensity from the center to the periphery. The color is brown, darker in the central part.
Giant pigmented nevus. Refers to congenital. Increasing in size, such birthmarks reach gigantic sizes, up to 15 centimeters or more. A characteristic feature is an uneven surface with “potholes”, nodules and cracks. Hair growth from the nevus may occur.
For melanoma-dangerous moles, the risk of malignancy is higher than for ordinary skin tumors. Such nevi and birthmarks require observation by a dermatologist or oncologist. Malignant degeneration can be caused by exposure to external factors - mechanical or chemical damage, ultraviolet irradiation.
Treatment of mucosal melanoma
Today, surgery is the main treatment option and can be combined with adjuvant radiation therapy. However, the prognosis for melanomas of the mucous membranes remains unsatisfactory. Local relapses occur in half of the cases. Radiation therapy for melanomas of the head and neck mucosa somewhat stabilizes the condition, but does not improve survival in common forms of the disease.
At the same time, due to the complex topography of some tumors, it is not always possible to perform a sentinel lymph node biopsy.
For urogenital melanomas, the most accessible method is surgical. The combination of wide excision of the tumor after a course of radiation gives good results only in the initial stages of melanoma.
Immunotherapy and targeted therapy have good prospects for the treatment of common mucosal melanomas complicated by metastases to distant organs. Tumor genotyping and detection of BRAF mutations in melanoma make it possible to introduce a new generation of antitumor drugs into clinical practice.
Drugs such as Ipilimumab and Pembrolizumab are being introduced into oncology protocols, which makes it possible to expect a reduction in tumor growth rates and an increase in life expectancy for patients with mucosal melanoma.
Dangerous symptoms
Only a very few black moles pose a potential threat. The risk of malignant transformation to melanoma is low, but caution should be maintained. In any case, it is advisable to show the skin lesion to a specialist. You definitely need to see a dermatologist or oncologist if you have the following symptoms:
- The black mole increases in size. Even small growth should be alarming; a rapid increase in size is an unfavorable sign.
- The surface has changed (becomes “glossy” or loose).
- The formation peels off or bleeds.
- Unpleasant sensations appear in the form of pain, burning or itching.
- The shape has changed, the edge has become striated, uneven, asymmetrical.
- The color changes: an ordinary mole becomes black, bluish or dark brown.
Any dynamics should be alarming. There is no need to panic, but you need to make an appointment with a specialist. What you definitely cannot do is try to remove the tumor yourself using traditional medicine. Injury by mechanical or chemical influence is one of the main causes of malignant degeneration.