Expecting a baby is one of the most wonderful periods in a woman’s life. Her thoughts are focused on dreams of the future baby and joyful worries about children's things, a stroller, and toys. But changes in the body sometimes prepare unpleasant surprises for the expectant mother. Thus, many women feel dryness, itching and burning in the intimate area during pregnancy. What caused them?
Why does itching and burning occur in the intimate area during pregnancy?
While expecting a baby, a woman’s hormonal background is completely restructured, as a result the vaginal microflora changes, which leads to the appearance of pathogenic bacteria and fungi that cause discomfort. If you add to this the wearing of synthetic underwear, the use of sanitary pads with fragrances, and too hot weather, then unpleasant symptoms such as dryness, burning and itching in the intimate area may appear during pregnancy. Many women are ready to sacrifice good health for the health of their baby. Fearing taking medications, they endure discomfort until the birth. However, itching, pain and burning during pregnancy force the expectant mother to be in a state of constant stress, which only increases the discomfort. If you feel discomfort in the intimate area, consult a doctor who will tell you what is causing it and help you choose the right treatment.
Itchy hands during pregnancy: eliminating the causes
Skin itching in pregnant women can be both a natural reaction of the body to the current situation, and a symptom of some serious abnormalities. In any case, you should consult your doctor about this.
To alleviate the unpleasant condition when your arms, fingers, and palms itch during pregnancy, you can follow these recommendations:
- Proper care of the skin of your hands and entire body should begin from the very beginning of pregnancy. Then you will be able to avoid increased dryness and flaking of the skin.
- For care, it is better to use products marked “hypoallergenic”; if allergic symptoms appear, you should temporarily abandon decorative cosmetics and try not to come into contact with chemicals and irritants.
- Watch your diet, eat properly and balanced.
- Drink enough clean water to replenish the lack of fluid in the body.
- Try to avoid stressful situations, get more rest and relaxation, walk in the fresh air, and provide gentle physical activity (after consulting a doctor).
- If itching persists for a long time and other symptoms appear, immediately inform your doctor.
What diseases of the intimate area can occur during pregnancy?
Often, during pregnancy, the expectant mother is bothered by irritating discharge with an unpleasant odor, itching, and dryness. The cause may be one of the following infections:
- thrush.
Its appearance is caused by the proliferation of yeast fungi on the mucous membrane of the intimate area. The infection can be transmitted to the child during childbirth, affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals; - bacterial vaginosis.
Caused by pathogenic bacteria and manifests itself in the form of gray discharge with an unpleasant odor; - urinary tract infections
. Hostile microorganisms penetrate the urinary organs when urinating from the intimate area. Cutting and burning are the first signs of this condition. This does not harm the baby, but can lead to kidney inflammation, which is dangerous for the expectant mother.
If you see a doctor in time and undergo the necessary treatment, you can avoid dangerous complications.
Allergies during pregnancy: the effect of allergies on the fetus
25.05.2021
Epidemiological data show that 15-30% of women of childbearing age suffer from allergic diseases. Allergies often worsen during pregnancy and can complicate pregnancy.
Allergies during pregnancy
Allergies can be a group of disease symptoms caused by contact with environmental factors that do not cause allergic reactions . Exposure to external factors, called allergens , activates the immune mechanisms of the allergic person. After this, the immune system begins to stimulate the body's cells to release various substances that cause inflammation.
Allergens can be divided into:
- inhaled;
- food;
- contact.
Depending on which allergen is the source of sensitization, different symptoms will appear. Inhaled allergens mainly cause respiratory diseases, and contact allergens cause skin reactions.
Allergies may worsen during pregnancy . This mainly applies to allergic rhinitis and asthma . Moreover, some allergic diseases appear for the first time during pregnancy . One of them is atopic dermatitis , which is the most common dermatosis among pregnant women.
The effect of allergies on the fetus
Allergies can negatively affect fetal development.
The following allergic diseases can affect the course and outcome of pregnancy:
- asthma;
- allergic rhinitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- hives;
- anaphylaxis;
- food allergy;
- drug allergy .
Women with asthma are primarily at increased risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth . Experts estimate that up to 10% of pregnant women suffer from asthma . Research into asthma during pregnancy suggests it can slow down a baby's development. It can also lead to premature birth and low birth weight of the fetus. Because of the above complications, pharmacotherapy during pregnancy will be much less of a threat to the fetus than untreated asthma .
Allergy medications during pregnancy
During pregnancy , many changes occur in a woman's body. They concern almost all systems, especially the cardiovascular, respiratory, urinary, digestive and endocrine systems. The body of a pregnant woman is preparing to create appropriate conditions for the development of the fetus.
Due to changes in the functions of many organs and direct effects on the fetus, a pregnant woman needs to be especially careful when taking medications. Moreover, the annotations of most medications indicate that they are contraindicated in pregnant women.
Most allergic diseases are treated with antihistamines, which block the physiological effects of histamine. Histamine is the main mediator of allergic reactions . Antihistamines that are safe for pregnant women include: cetirizine, loratadine, clemastine, cyproheptadine and diphenhydramine.
Pregnant women should absolutely not take:
- antazolines;
- fexofenadine;
- hydroxyzine;
- promethazine;
- ketotifen;
- Levoceterizine.
Women with asthma may take bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory drugs during pregnancy Safe drugs include sympathomimetics - mainly salbutamol, fenoterol, formoterol, terbutaline and inhaled glucocorticosteroids: budesonide and beclomethasone. Oral corticosteroids are not recommended during pregnancy .
In the case of allergic rhinitis , in addition to antihistamines, pregnant women can use nasal corticosteroids, mainly budesonide, and, if necessary, beclomethasone and fluticasone, since there are still no studies confirming their harm during pregnancy .
For atopic dermatitis during pregnancy , topical emollients and antipruritic drugs are recommended. If their use does not bring improvement, general therapy with antihistamines is prescribed.
Home remedies for allergies during pregnancy
In addition to pharmacological agents, pregnant women with allergic rhinitis can use inhalations with sea water or 0.9% saline solution. There are many herbs that help relieve skin and intestinal allergy , but a pregnant woman should consult her doctor .
Published in Allergology Premium Clinic
Tips for intimate hygiene for an expectant mother
Burning and itching in the intimate area during pregnancy can be prevented. Here are 6 simple tips to help reduce your risk of developing infections:
- Take a shower no more than 2 times a day. Water and soap remove natural protection - beneficial microbes.
- Choose intimate hygiene gels containing lactic acid or plant extracts: linden, chamomile, blue lotus, white tea. These natural components have a positive effect on the condition of the most delicate area of our body.
- Dry your body thoroughly after intimate toilet with a cotton towel. Do not share a towel with other family members.
- Wear panties made of 100% cotton, which help your skin breathe and do not create a greenhouse effect, especially in hot weather.
- Use pads filled with cotton extract. They allow oxygen to pass through well, which destroys yeast.
- Replace the bath with a shower. Hot, soapy water can bring dirt into the body and wash away beneficial bacteria. If you really want to soak in the bath, wash yourself in the shower first. Use sea salt instead of foam.
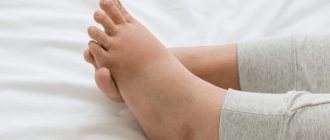
How does thrombophlebitis manifest in pregnant women?
The symptoms of thrombophlebitis in pregnant women do not differ from the symptoms of the disease in everyone else. In the area of the affected vein, there is redness and thickening of the skin, and the surface of the leg may feel hot to the touch. The leg may begin to swell and become painful.
Pain with thrombophlebitis intensifies when walking and subsides at rest. However, sometimes the pain can be very severe, so that the patient will not be able to step on his leg. Often women complain of general poor health.
All this is a consequence of stagnation of blood in the veins and the gradual formation of a blood clot that closes the lumen of the vessel.
Thrombophlebitis during pregnancy: treatment and prevention
As experts note, pregnancy increases all the risks that exist for a particular woman’s body. And this also increases the risk of developing thrombophlebitis. That is why if a pregnant woman already has a diagnosis of varicose veins, she should approach the issue of preventing thrombophlebitis very carefully. That is, constantly wear compression hosiery, prescribed and selected according to the recommendation of a doctor.
If the expectant mother notices the first signs of thrombophlebitis on her legs - redness, thickening in the vein area, then she should immediately consult a specialist. If a woman has a compression stocking or elastic bandage, then before visiting the doctor, you can bandage your leg yourself or put on knitwear. But a vein examination (ultrasound, duplex scanning) should be carried out as soon as possible.
Treatment of thrombophlebitis during pregnancy includes mandatory wearing of compression stockings, which ensures normal blood flow in the vein, as well as taking heparin drugs, which reduce blood viscosity.