Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
9 years experience
Make an appointment
HPV, also known as human papillomavirus, is not a single virus, but a whole group of them. They are transmitted from person to person (usually sexually) and become the cause of papillomas - benign formations. Some of these viruses are oncogenic, that is, they increase the risk of developing malignant tumors, for example, cervical cancer. But HPV is dangerous not only for women, but also for men, as well as for children.
Development and localization
To begin with, it is important to note that there are more than 600 strains of this virus. That is, there is not one diagnosis, one version of the consequences and one version of the manifestations. There are many different situations involving infection.
If the immune system is strong, it can easily cope with the virus on its own and within a few years “displace” it from the body. But at the same time, re-infection or illness with a different strain is also possible.
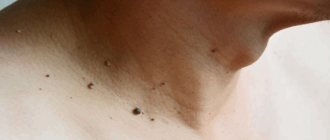
Papillomas and other symptoms of HPV in the form of formations that develop as a result of infection can appear in different places:
- on the skin anywhere;
- in the anogenital area;
- in the oral cavity, bronchi and upper respiratory tract;
- in the rectum, etc.
Formations can grow and form entire groups, or they can gradually dry out and disappear - it all depends on the specific situation.
Is human papillomavirus (HPV) a sexually transmitted disease?
HPV - in more detail stands for “a virus that causes a benign tumor of epithelial origin in the form of a papilla” - papilloma (papilloma: Latin papilla - nipple and Greek -oma - tumor). It is classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD). The concept today has, unfortunately, become much broader, and if earlier we heard about several “terrible”, as it seemed to us, classical diseases of Venus, which are actually treated simply and are detected quickly (syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chancroid), then The list of “new” STDs - insidious, difficult to diagnose, and sometimes difficult to treat and completely incurable (HIV) - is constantly growing.
So, we include the following “new” STDs: chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, gardnerellosis, genital herpes, candidiasis, and human papillomavirus. If growths from papillomavirus have formed in the areas of the genital or perianal organs, then they are called “pointed candylomas,” but in fact they are the same virus, only its different strains (types).
HPV strains
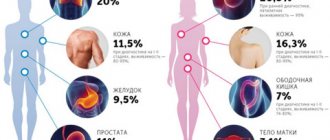
There are strains of the virus that have a high oncogenic potential. They are designated by numbers 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 68, 73 and 82. There are also options with medium (26, 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 53, 58 and 66) and low (6.11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81) oncogenicity. Cervical cancer is most often associated with infection with strains 16 and 18, therefore, when such a virus is detected, maximum monitoring of the patient’s condition is required.
Important clarification! Highly oncogenic viruses detected in the body do not mean that a person will necessarily have cancer. This increases the risk of developing cancer, but is not a 100% determining cause. Moreover, oncology is usually preceded by so-called precancerous conditions. With regular monitoring, doctors have a very high chance of “catching” the disease at an early stage and preventing it from developing into cancer. And cancer itself at the first stage is treated quite successfully. If you have been diagnosed with a virus, do not panic - with proper control, this is not a death sentence for your health and life.
Reasons for formation
The reasons for the formation of such growths include HPV, as mentioned earlier. A huge number of people are carriers of this virus. Having penetrated inside the body, the virus begins to spread, but for a long period of time they may not be reflected. Under the influence of many factors, the virus can form on the skin in the form of papillomas. Such factors include internal infections, consumption of junk food, systematic stressful situations - in general, those factors that cause a weakening of the immune system.
The main criteria that cause the development of the virus and the severity of its symptoms include:
- sexual relationships without contraception, built with different partners,
- bad habits,
- weakened immune system,
- metabolic disorder,
- gastrointestinal disorders,
- failure to follow basic hygiene rules,
- heredity - the virus can be transmitted during pregnancy.
Depending on the location, the patient may need the help of a specialist who can prescribe an effective ointment for papillomas . In a situation where pronounced symptoms are not observed, but a person wants to know for sure whether he can transmit the above-mentioned virus, then he needs to contact our medical specialists: immunologists, dermatovenerologists.
How the virus is transmitted
To properly prevent human papillomavirus, you need to know the routes of infection. There are several transfer methods:
- sexual. Infection is also possible when using a condom - for example, during unprotected oral sex or during kissing;
- from mother to child;
- in domestic conditions, for example, if a person uses an infected person’s towel, razor or toothbrush;
- in public places such as a swimming pool, gym, bathhouse;
- autoinfection. This means that a person can “spread” the virus to other parts of the body himself.
The first route is most common, because the virus does not survive very well in the external environment.
It is also important to understand that the cause of human papillomavirus is weakened immunity - it is under this condition that infection is most likely. The situation is aggravated if the patient already has an STD, has bad habits, and is constantly under stress. Immunodeficiencies and various injuries to the skin and mucous membranes also contribute to the acquisition of the virus.
Women are most often infected. And strains with a high risk of cancer become more dangerous for them.
Who is at risk of getting the papilloma virus?
Papillomas and condylomas can appear, disappear and appear again, because they are manifestations of a viral infection, and their presence depends on the state of the body’s defenses at the moment, that is, immunity. Infection is most likely among smokers and alcoholics, and among those who are indiscriminate in sexual relations.
Women who use oral contraceptives (COCs) for a long time are also at risk of contracting the virus. The carrier of the virus can be both old and young. It is enough for your body to experience internal stress of various origins: you have had the flu or ARVI, gastrointestinal problems have worsened, your body cannot cope with long-term medication use - and here you have a weakened immune system, and with it the papillomavirus.
It is enough to be in close contact or live next to a person carrying the virus, take a swim in a “dirty” pool or shower in a public bath, or just walk along the beach - and if your immune system fails, the virus will invade your life. The papillomavirus “loves” heat and high humidity, when your skin is not protected by clothing. He immediately finds refuge on your heated skin.
Signs
If HPV does not manifest itself in formations (warts, papillomas and condylomas), then without special tests the patient usually does not know that he is infected. In this case, the symptoms of the human papillomavirus are precisely the neoplasms - they can be accompanied by itching and discomfort.
If formations appear in the genital area, they can also manifest as painful and unpleasant sensations during or after sexual intercourse.
Are you experiencing symptoms of human papillomavirus?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Are papilloma and condyloma the same thing?
Genital condylomas in the perineal area are sometimes single, and sometimes look like growths that resemble cauliflower in appearance. Sometimes these formations cause itching, irritation when touched, and sometimes they bleed. SM-Clinic doctors are often approached by patients who, having seen enough advertising, have been treated for years with “one pill” for supposed “exacerbations” of candidiasis (thrush). Upon examination, it turns out that the smear in such patients is normal, and the often recurring itching is actually caused by condylomas.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus includes a doctor’s examination, enzyme-linked immunosorbent test, PCR diagnostics, as well as special tests to determine the oncogenicity of the strain. Women undergo a Pap test, that is, a cytological examination, for which a smear is taken from the vagina. A colposcopy is required - a thorough examination of the cervix using a special device.
Warts
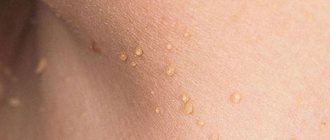
Warts are the most common manifestation of human papillomavirus infection on the skin.
These are rounded formations with clear boundaries and a rough surface. Their size usually does not exceed 10 mm.
The human papillomavirus causes the following types of warts:
- Ordinary or vulgar. They occur most often. They protrude above the skin in the form of dense formations of gray-yellow color with a keratinized rough surface. Formed on the back of the hands, on the fingers, between the fingers. Tend to merge with each other;
- Flat or youthful. They usually occur in children and adolescents. These are flat formations of flesh-colored or pale brown color, slightly rising above the level of the skin. They usually appear on the face, neck, shoulders, hands in groups of several;
- Plantar. They form on the plantar part of the foot in places of greatest pressure: on the heels, under the pads of the toes. Unlike other warts, their growth is directed inward. In appearance, they resemble calluses, but have a rough rather than smooth surface and destroy the skin pattern. Plantar warts are painful when pressed and cause pain when walking;
- Thread-like. These are soft to the touch oblong-shaped growths on a stalk up to 4 mm long. Their color ranges from flesh to dark brown. They form on the neck, skin of the eyelids, armpits, groin area, under the mammary glands.
Treatment
Treatment of HPV does not imply the presence of any specific program that would completely destroy the pathogen. But patients are prescribed therapy that helps strengthen the immune system and self-heal. The assignments come down to several points:
- taking special medications. These are vitamins, antiviral medications and immunomodulators;
- removal of tumors. For this purpose, cryodestruction, laser, and electrocoagulation are used. Removal is possible using the classical surgical method;
- all kinds of strengthening of the immune system. A healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, giving up promiscuity - all this helps maintain immunity.
There are now vaccines for some types of HPV that are optimally used at 11-12 years of age (but can be used up to 26 years of age). Patients over 12 years of age are prescribed the vaccine if the doctor sees indications for this. The vaccine is not able to destroy the virus, but it can protect against other dangerous strains.
How are papillomas treated?
Complex therapy for HPV includes removal of existing tumors by surgical methods, destruction of the causative agent of the disease and increasing the body's protective abilities.
Surgical methods
Popular methods of surgical treatment of papillomas include:
- Electrocoagulation (electrodestruction). It is considered one of the “delicate” methods for removing pedunculated polyps. The growth tissue is excised with an electric knife, and the damaged vessels are “sealed” due to the thermal effects of the current. Wounds after electrocoagulation heal quickly without forming rough scars. This method is often used in cases where special care is needed - if papillomas are located on the face, eyelids, and in the corners of the eyes.
- Cryodestruction. The procedure for destroying selective areas of tissue with cold is minimally invasive, eliminates the risk of infection, and does not require anesthesia. Cryodestruction is carried out by applying liquid nitrogen to the affected area. The formation of ice crystals in papilloma cells causes irreversible damage.
- Laser removal . The technique is based on ablation (evaporation) of tissue with a light pulse. This is an effective and safe method for removing skin tumors, allowing you to work in the most delicate areas - on the face, lips, tongue, eyelids. Coagulation of small vessels, which occurs during the “burning” process, prevents the development of bleeding. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
- Radio wave surgery is a non-contact method of destroying tumors using high-frequency radio waves. The procedure is performed using the Surgitron device. It is bloodless and painless, does not leave scars and eliminates relapses, since radio waves have a sterilizing effect.
Important! Do not try to cut or pick out the growth yourself - such actions can lead to suppuration or malignant degeneration of the tumor, and the virus becomes more active when the papilloma is damaged.
Therapy methods
Therapy for papillomavirus is aimed at inhibiting HPV activity and increasing immunity. The most frequently used antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs in medical practice are Acyclovir, Isoprinosine, Viferon, Condimin, Panavir, Aldora and Bonafton ointments. They cause the death of a significant part of the virus, and reduce the risk of re-growth of papillomas after their removal.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone.
Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it Please note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Questions and answers
How to get rid of the human papillomavirus forever?
It is impossible to get rid of it 100% using certain medical programs. But the virus can disappear from the body on its own, which does not eliminate the risk of re-infection.
How dangerous is the human papillomavirus?
The human papillomavirus is dangerous because some of its strains contribute to the development of cancer - in particular, cervical cancer.
If a virus is detected, will there definitely be cancer?
No, there is no absolute dependence in this case. We are talking about increasing risks, but this does not mean that cancer will definitely develop - people who have been diagnosed with the virus need to undergo regular examinations with doctors, and then the probable disease
Papillomatosis in the throat
There is also papillomatosis of the respiratory tract, when the tissue lining the nasopharynx begins to grow from the nose to the lungs, also often affecting the larynx. This is also one of the types of disease caused by the papilloma virus; the formations in this case are considered benign. SM-Clinic doctors are good at diagnosing this type of HPV and successfully treating it, while the disease is not always recognized by local or ENT doctors, who at best shrug their shoulders and prescribe rinses.
Methods for removing papillomas
In our medical center, before removing a tumor, a dermatologist examines it and, if necessary, performs dermatoscopy in order to differentiate the type of papilloma and select the optimal method of removal.
It is possible to get rid of papillomas in our clinic without surgery using the destruction of formations using a laser, radio knife and plasma. Removal of papillomas with a laser, especially removal of papillomas on the face, is not carried out so often due to the high traumatic nature of the method and the possibility of hypopigmentation and scarring. Preference is given to radio wave destruction, as well as diathermocoagulation. These methods are highly effective and low traumatic.
- The radio wave method is one of the most effective and least traumatic ways to remove almost all types of papillomas. It is performed on the Surgitron DF-120 device (Ellman International Inc, USA). Removal of the tumor occurs due to local evaporation of cells under the influence of heat generated in the tissues in response to the penetration of radio frequency waves. The cells evaporate and the tissues move apart as if cut with a scalpel. In addition, instant coagulation of blood vessels occurs in the treatment area, so there is no bleeding and no damage to surrounding healthy tissue. In this aspect, laser removal of papillomas is significantly inferior to the radio wave method.
- Diathermocoagulation using the Plasmaskin device (Ultramed, Russia) is a non-contact effect on the affected tissue with a plasma beam. The high temperature of the plasma (up to 2000-2500 C) is combined with the bactericidal effect of an air flow containing a high concentration of ozone and has a virus-destructive effect, destroying HPV DNA, which prevents its spread.
The use of radio wave energy on the SURGITRON DF-120 device (Ellman International, Inc., USA) is the method of choice for removing most forms of papillomas, regardless of their location (face/body), and here’s why:
- Radical - no relapses;
- Rapid epithelization - healing;
- Atraumatic - no complications, no marks or scars remain on the skin;
- Painless - anesthesia is required only in cases of large tumor sizes.
- Complete safety of procedures.
During the destruction of papillomas, anesthesia is usually used. Application anesthesia with the application of lidocaine cream can be used, or infiltration anesthesia, when the site of papilloma localization is injected with an anesthetic solution (Ultracaine). The choice of pain relief method is determined by the size and location of the papilloma.
If the patient has no contraindications, removal of papillomas in Moscow in our clinic can be carried out on the day of treatment, immediately after an appointment and examination by our specialist. In this case, no additional tests are required.
In order to prevent relapses after removing a large number of tumors, our experts recommend taking immunomodulatory drugs. Immunomodulatory therapy is selected individually.
Indications for removal
The only way to treat already “formed” papillomas is to remove them. Indications for removal of tumors primarily include:
- Aesthetic problems. Papillomas are skin growths that are perceived as an aesthetic defect, especially when they are localized in open areas of the face and body.
- Papillomas can be constantly injured, cling to clothes, combs, etc. and due to this, quickly spread throughout the skin, soreness, inflammation, cracks and even bleeding may appear in the area of the tumors.
- Considering that some types of papillomaviruses have a high risk of oncogenicity, large papillomas (more than 6-10 mm) may be prone to degeneration, so timely removal of such tumors will prevent a serious illness in the patient.