Ringworm is a general name for a group of skin diseases that manifest as characteristic rashes that can be localized in different parts of the body.
Infections differ in pathogen, clinical manifestations, severity and treatment tactics. One of the fairly common types of lichen is Zhiber's pink lichen.
Zhiber's pityriasis rosea is an acute inflammatory dermatosis of unknown etiology that develops against a background of weakened immunity, for example, after an acute respiratory viral infection or influenza. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in adolescents and young adults, while it is rare in children and the elderly.
Doctors do not have a clear opinion about the causes of pityriasis rosea, but most dermatologists are inclined to believe that the causative agent of the infection is herpes virus types 6 and 7. The herpes virus remains in a latent state in the human body for a long time, but when the protective forces are weakened, it begins to actively develop and affects the upper layers of the skin with the formation of symptoms of pityriasis rosea.
What does pityriasis rosea look like?
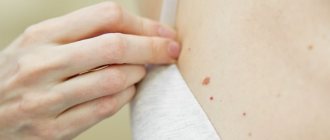
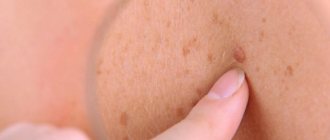
The main symptom of lichen Zhiber is the appearance of a characteristic pink rash. First, a bright, slightly convex plaque with a diameter of 2 to 5 cm is formed on the body, the center of which may peel off slightly and differ in color from the edges. This is the so-called “maternal plaque”, next to which, after 5-10 days, small pink spots (up to 2 cm in diameter) appear along the skin tension lines (Langer’s lines).
“Daughter” rashes do not appear simultaneously, but throughout the entire illness. The rash is bright pink, peeling in the center. But after 4-5 weeks it begins to lose pigmentation, the plaques peel off without the formation of scar tissue or scars.
A number of patients may have atypical pityriasis rosea, in which the maternal plaque is absent and the body is covered with small pink spots.
Dermatologists also distinguish the following types of atypical Zhiber disease:
- urticarial - instead of pink plaques, blisters appear on the skin;
- vesicular - rashes consist of small blisters filled with clear or cloudy liquid;
- papular - cavity-free formations appear protruding above the surface of the skin.
The rash is most often localized on the torso, less often on the neck, face and limbs.
Publications in the media
Pityriasis rosea is an acute dermatosis characterized by abundant, finely scaly pink spots on the trunk, neck and proximal extremities, most often occurring in the autumn-winter period. One of the most common skin diseases; usually resolves spontaneously. Risk factors: infectious diseases, prolonged hypothermia. Frequency. 5% of patients who consulted a dermatologist. It is observed mainly in middle-aged women, rarely in children and the elderly.
Clinical picture • The process begins with a primary maternal plaque, which is much larger in size (2–6 cm) than subsequent rashes, and is often located on the trunk, in the area of the collarbone and shoulder blades. After 7–10 days, sometimes later, many spotted or macular-urticarial elements appear, up to 1–2 cm in diameter, pale pink or slightly brownish in color with pronounced pityriasis-like peeling. The long axes of the spots are located along Langer's lines, indicating the direction of maximum extensibility of the skin • The rashes are localized in the axillary and groin areas, on the inner surface of the thighs and the flexor surface of the forearms. In adults, the skin of the face, scalp, hands and feet, and mucous membranes are usually not affected • Itching is mild or absent altogether • Along with typical manifestations, there are other types of pityriasis rosea •• Urticarial form •• Vesicular form •• Papular form •• Lichen annulare bordered Vidal or pityriasis rosea giant is a rare variant of pityriasis rosea, characterized by single large rashes (up to 8 cm in diameter) of red or pink color with small pityriasis-like peeling along the periphery in the form of a ring, as well as a long course; may occur independently or together with typical rashes.
Test methods • Blood test: slight leukocytosis and eosinophilia • Serological test to rule out syphilis • Skin biopsy: inflammation with cytolytic degeneration of keratinocytes adjacent to Langerhans cells. Differential diagnosis • Toxidermia • Trichophytosis • Syphilitic roseola • Psoriasis • Parapsoriasis • Eczema • Lichen planus • Dermatomycosis of the trunk.
TREATMENT General recommendations • Avoid water treatments, hypothermia • Maintain good hygiene to prevent the development of secondary infection • Diet with limited pickles, spices, marinades, concentrated broths • Insolation • Drug therapy is symptomatic only.
Drug therapy • For an inflammatory reaction and itching - topically: ointments with menthol (0.25–1%) • For very severe itching - prednisolone 10 mg 4 times a day orally until the itching disappears (if discontinued, the dose is reduced gradually) • Antihistamines • Anti-inflammatory drugs (salicylates, indomethacin) • Calcium pantothenate. Complications • With irrational therapy, the development of eczema is possible • Secondary infection. Forecast. Recovery is usually within 4–6 weeks. Very rarely, rashes persist for more than 3 months and, as a rule, are due to irrational therapy. Synonyms • Tinea rosacea Giberta • Giberta disease • Roseola exfoliating
ICD-10 • L42 Pityriasis rosea [Gibera]
How is Zhiber's pityriasis rosea transmitted?
Zhiber's pityriasis rosea is not contagious - it is impossible to catch it from a sick person, even with close household contact: using shared dishes or towels. Therefore, patients do not need to quarantine or limit social contacts; they can continue to lead their normal lives during therapy.
Most dermatologists are inclined to believe that Zhiber's pityriasis rosea is caused by the herpes virus, which is present in the human body in a latent form.
Activation of the pathogen occurs against the background of decreased immunity, which can be caused by:
- hypothermia;
- recent injuries, surgeries and infections;
- overwork and stress;
- long-term exposure to adverse factors: for example, toxins at work;
- bad ecology;
- alcohol abuse;
- chronic diseases: diabetes, heart failure;
- hormonal fluctuations: for example, pregnancy in women;
- sudden climate change;
- smoking;
- unbalanced diet.
Most often, the virus is activated in the spring and autumn, during the season of influenza and ARVI epidemics. Vitamin deficiency, uncontrolled use of medications, and a course of antibiotics can contribute to the development of Zhiber's disease.
Do pityriasis rosea need to be treated?
Many patients mistakenly consider Zhiber's disease to be a harmless dermatosis that does not require therapy or contact a dermatologist. Despite the fact that the disease is prone to self-healing, improper treatment or its absence can lead to a long course of infection (up to six months or more) and various complications.
If a rash is detected on the body, it is recommended to make an appointment with a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist as soon as possible.
This is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis: pityriasis rosea can easily be confused with such dangerous diseases as:
- seborrheic eczema;
- psoriasis;
- parapsoriasis;
- mycosis of smooth skin.
For diagnosis, in addition to a general examination, a dermatologist prescribes a number of tests:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- skin scraping;
- serological study.
Based on the results, appropriate treatment is prescribed. The dermatologist develops a treatment regimen taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, the course of the disease, and the symptoms present. This allows you to select the most effective drugs that bring significant relief from the first use.
What you need to know about diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of pityriasis rosea is based on taking the patient's medical history. To confirm or refute and analyze complex cases, a number of laboratory tests are prescribed. They include clinical examination of blood and urine. It is necessary to exclude syphilis and mycosis, therefore serological and microscopic studies are additionally carried out. If these methods do not provide enough information to verify the diagnosis, the patient is referred for a biopsy (biopsy histology).
Treatment for pityriasis rosea is not always required. The disease is prone to voluntary self-healing within 5 weeks. However, dermatosis should not be considered harmless. First of all, antipruritic therapy is required. For this purpose, topical glucocorticosteroid drugs and antihistamines are used externally. Ointments, gels, pastes cannot be used without a dermatologist's prescription. Otherwise, the rash may increase the extent of skin damage, covering new areas. Antibiotics and antiviral drugs may be prescribed depending on the indications. Ultraviolet therapy has a good effect.
Why does pityriasis rosea recur?
Viral infections tend to recur. Lack of treatment for pityriasis rosea leads to the fact that the pathogen is not eliminated, and after some time (usually 4-6 weeks) it goes back into a latent form until a new weakening of the immune system. Because of this, many patients experience symptoms of Gibert's disease after each seasonal cold or severe stress.
The first manifestations of the disease are:
- formation of a large pink “mother plaque”
- mild itching of the skin;
- a feeling of tightness of the skin in the area of the rash.
Subsequently, “daughter” spots appear that do not go away within several months unless you consult a dermatologist. In some cases, patients may experience other signs of a viral infection: a slight increase in body temperature, weakness, and decreased performance.
To recover, it is necessary not only to eliminate the symptoms of pityriasis rosea, but to get rid of the cause that caused the disease, and also to destroy the pathogen. This requires complex therapy under the supervision of an experienced dermatologist.
Clinical picture
Most patients do not have severe symptoms of the disease; in some cases they complain of mild or severe itching. The problem occurs in emotional people or patients with skin allergies that react inadequately to external stimuli.
The first sign of pathology is the formation of a “mother spot” - a large pink area of dermis with pronounced peeling. After the scales are torn off, the spot acquires a brown tint and clear boundaries. It does not exceed 2-5 cm in diameter. Initially, a single focus of pityriasis rosea is registered, later several additional ones appear on the body.
Secondary spotting forms a few days after the appearance of the mother spot. Changes are recorded on the arms and legs, back, and abdomen. Secondary rashes have a similar shape, with a reddish or pinkish tint. They rarely occur in the neck or face. The appearance of the first spots requires immediate consultation with a doctor and treatment prescribed by a specialist.
Is it possible to cure pityriasis rosea permanently?
Many patients, faced with a recurrent disease, are interested in whether it is possible to get rid of pityriasis rosea forever? It is possible if you consult a dermatologist. The doctor will not only select highly effective medications to eliminate rashes and itching, but will also develop preventive recommendations to prevent relapse.
Typically, the treatment regimen for pityriasis rosea includes the use of the following medications:
- local ointments with corticosteroids: act simultaneously on several levels - relieve skin tightness, promote rapid healing of the rash;
- antihistamines – eliminate itching;
- immunomodulators - activate natural defense mechanisms to combat pathogens.
Additionally, a dermatologist may prescribe treatment of rashes with antiseptic solutions to prevent secondary infection by bacteria, as well as emollient ointments for severe peeling.
Following medical recommendations will allow you to quickly recover and forget about Zhiber’s disease forever.
How to cure pityriasis rosea during pregnancy?
Hormonal changes that occur in the body of a pregnant woman often provoke the development of various diseases, including pityriasis rosea. The disease is not dangerous for the fetus, but requires close attention, since it indicates a weakened immune system of the expectant mother and can cause significant discomfort.
The main rule that a pregnant woman should follow when treating pityriasis rosea is not to use any medications or ointments without first consulting a doctor. “Folk methods” can be no less dangerous for the fetus. Any impact on the body is allowed only after agreement with a dermatologist. The complex of drugs is selected by a specialist and may include ointments, vitamin preparations, and antiseptics.
It is also important for patients to follow the following recommendations:
- refuse to visit the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool. Instead of a bath, you should take a shower without using a hard washcloth or rubbing with a towel;
- choose spacious linen made from natural fabrics. Synthetic materials interfere with the natural breathing of the skin, increase sweating, which leads to worsening the symptoms of pityriasis rosea and the appearance of new rashes;
- exclude foods that cause allergies from the diet: eggs, red berries and fruits, chocolate. It is also recommended to reduce the amount of fried, flour, smoked foods and replace them with boiled vegetables;
- Do not use cosmetics on damaged areas of the skin.
By following the doctor’s recommendations, the girl will quickly restore her health without negative effects during pregnancy.
Why do skin diseases worsen during pregnancy?
Pregnancy is a special period in a woman’s life. During gestation, hormonal levels change and the immune system weakens significantly. Therefore, lichen occurs in pregnant women, allergies appear, and chronic diseases worsen. Additional provocateurs of dermatosis:
- contact with an infected person or animal;
- acute allergic reactions;
- moral and physical tension;
- sleep deficiency;
- stress;
- avitaminosis;
- colds;
- hypothermia.
There are several types of lichen in pregnant women. Each type has specific symptoms and degree of danger for the fetus and the expectant mother. Most types of skin diseases during pregnancy are harmless and only spoil the appearance. But there are also dangerous types of dermatosis that can negatively affect pregnancy.
What does pityriasis rosea look like when it goes away?
With proper treatment, pityriasis rosea goes away without the formation of scars. After exfoliation of the plaques, clean skin remains in their place, sometimes a lighter shade, but over time this defect disappears. However, in patients with atypical forms of Gibert's disease, the formation of difficult-to-heal ulcers is possible.
Self-medication and lack of qualified medical care increases the risk of complications:
- secondary infection of the rash with bacterial flora;
- the appearance of suppuration and ulcers;
- the formation of areas of hyperpigmentation after recovery.
To prevent such a development of the disease, at the first symptoms of pityriasis rosea, it is recommended to make an appointment with a dermatologist.
After recovery, the doctor will develop recommendations to prevent relapses.
They usually include a number of activities to strengthen the immune system:
- regular intake of vitamin complexes in the autumn-spring period;
- proper rest, especially during times of increased intellectual, physical or psycho-emotional stress (exams, important projects, other stress);
- rejection of bad habits;
- moderate physical activity;
- maintaining a balanced diet, with limited consumption of allergenic foods, as well as smoked, fatty, flour foods.
Following these tips allows you to maintain immunity, which suppresses the herpes virus and prevents the recurrence of pityriasis rosea.
Diagnosis of the disease
Determining the correct diagnosis is sometimes difficult due to the absence of a pathogen. The disease can be confused with other lichen and toxicoderma.
The examination is a visual inspection. A qualified dermatovenerologist will take into account the characteristic placement of spots on the body, their appearance, shape, and based on this will make a diagnosis.
Tests that may also be prescribed:
- general urine and blood tests;
- microprecipitation reaction (diagnosis of syphilis);
- scraping from affected areas.
After diagnosis, the specialist will determine how to treat pityriasis rosea and will advise the patient in detail regarding lifestyle.
Make an appointment
Why can't you scratch pityriasis rosea?
Zhiber's pityriasis rosea can occur without symptoms, including without skin irritation. But some patients suffer from itching in the area of the rash. As with other dermatoses, you should not scratch the site of infection.
Violation of this rule leads to:
- damage to the top layer of skin and the appearance of scratches;
- the risk of introducing bacterial flora into the plaque, which will cause inflammation and suppuration of the tissue;
- increase in the area of rashes.
To cope with itching and skin irritation, seek help from a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist. The doctor will select corticosteroid ointments to relieve inflammation and antihistamines to relieve itching and burning.
Ringworm in humans: types, symptoms
27.01.2021
Ringworm is a skin disease characterized by the appearance of patches that peel off. May occur at different ages. Most often it occurs in young people. The disease occurs in autumn and spring. Can be transmitted from a sick person or animal.
Causes:
- stress;
- reduced immunity ;
- hypothermia;
- heredity;
- overwork.
Symptoms: the disease begins with a single plaque. But it can increase to two or three pieces. The plaques can be from 3 to 5 cm in diameter. Within about a week, the rashes acquire a more characteristic type. There are more and more of them. They appear on the stomach and back and are accompanied by severe itching. If you have lichen on the scalp, your hair will fall out. The duration of the disease lasts from 1 to 2 months, after which they disappear on their own.
At risk are:
- Small children;
- pregnant women;
- people with weakened immune systems ;
- people who do not observe personal hygiene rules;
- those who have pets.
What can cause the disease?
Microscopic fungi can cause the disease; they live on the skin and fur of animals. In soil and on human skin.
Types of lichen
- Ringworm most often affects children . It is very easy to get sick from it, just touching the patient is enough. Appears on the face , neck , shoulders and head. Characterized by round, red and pink spots.
- Pityriasis versicolor or multicolored lichen - appears due to excessive sweating of the body, which leads to changes in the chemical composition of sweat. Excessive and prolonged exposure to the sun, use of fatty creams. The spots are located on the surface of the entire body, excluding the head and limbs. The first days the spots are greenish in color, but over time they become light brown.
- Shingles the nerve, appearing where the nerve passes. Most often in adults, but can also affect children. Occurs due to stress and hypothermia of the body. First, reddish bubbles filled with liquid appear. After a few days, the blisters burst and crusts appear in their place.
- Lichen planus is a chronic disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes. Appears between the ages of 35 and 65 years. The cause is unknown. But most often it occurs in people with diabetes and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Men get sick less than women. The patient's nails crumble, and red and purple nodules appear on the skin. On the skin of the abdomen , legs and chest .
- Solar lichen is characterized by the appearance of white spots on the skin of various shapes. There may not always be itching and burning. Inflammation occurs in winter. The spots reach a diameter of 4 cm.
- Squamous lichen - has a chronic form. Skin throughout the body may be affected. It may or may not be transmitted through casual contact.
- Ringworm ( eczema ) can be transmitted through household contact. It looks like a red spot that appears on the hands and face . Then bubbles appear, which then burst and release serous fluid. When they dry out, they become crusty.
Diagnostics
Examination by a dermatologist . They do an iodine test, and then wipe it with alcohol. Scraping Blood and urine analysis .
What complications can there be?
- Deterioration of vision
- Hearing impairment
- Nerve damage
- Inflammation of the heart muscle
Treatment
to treat lichen on your own . Different forms of lichen are treated differently. It is necessary to disinfect all things used by the patient. Wash your hands after contact with an infected person. On average, treatment takes 1-3 weeks, but if the disease is not advanced. It is necessary to limit water procedures. Do not apply cosmetics. Ointments, immunostimulating and antihistamines, multivitamins, antidepressants , and sedatives are prescribed.
Diet : exclude the consumption of alcohol, tea, coffee, eggs, chocolate, citrus fruits, canned and smoked foods.
Prevention
To prevent a disease such as lichen , you must adhere to a healthy lifestyle and eat well. Treat in a timely manner . And do not self-medicate.
Published in Dermatology Premium Clinic
Can pityriasis rosea be smeared with iodine or brilliant green?
Iodine and brilliant green are one of the most accessible and widely known antiseptic drugs for treating scratches and other superficial wounds. Many patients who are faced with pityriasis rosea “out of habit” use these remedies to treat the rash. But this approach does not give results.
The virus that causes pityriasis rosea is concentrated in the deep layers of the skin - iodine and brilliant green will not be able to eliminate the cause of the infection. In addition, both products dry out the skin greatly and can lead to additional chemical burns. As a result, the patient will only worsen the symptoms and delay recovery. Iodine and brilliant green should not be used to treat Gibert's disease.
Contraindications
Patients with pityriasis rosea, depending on the degree of the disease, may be contraindicated for prolonged water procedures - hot baths, showers. This is due to the fact that the spots are predisposed to swelling, and water can provoke swelling. If water is regularly exposed, damaged tissue may respond poorly to treatment.
However, it is impossible to completely abandon the treatment of inflammation - bacterial microflora will cause a deterioration in the condition of damaged tissues. In this case, a quick rinse in cool or slightly warm water is recommended.
The patient must avoid skin irritation so as not to provoke an exacerbation of the disease. Irritants include:
- rough linen, wool or synthetic clothing;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- cosmetic and medicinal preparations with tar and sulfur;
- hypothermia.
The disease can be complicated if the diet contains:
- citrus;
- smoked meats;
- dairy products;
- marinade, hot seasonings and sauces;
- fish, seafood;
- carbonated drinks;
- dried fruits.
Only a doctor can give precise nutritional recommendations.
If you notice symptoms of pityriasis rosea, immediately consult a dermatovenerologist.
Other articles by the author
- Pyoderma
- Herpes zoster
- Pityriasis rosea
- Shingles
Is it possible to treat pityriasis rosea with celandine?
Another popular “folk recipe” for treating lichen is using celandine. However, the juice of this plant (as well as a decoction from it) is also not able to penetrate into the deep layers of the skin, that is, it will not be able to cope with the causative agent of the disease.
Also, celandine does not help speed up the healing of the skin, but can lead to additional damage and inflammation. It should be remembered that the juice of this plant is poisonous, can cause burns, worsen general health and cause a number of side effects. Therefore, the use of celandine not only will not alleviate the patient’s condition, but may also aggravate it, increasing the risk of complications.
Is it possible to apply zinc ointment to pityriasis rosea?
Zinc ointment is a popular antiseptic with a softening effect. This remedy is indeed prescribed for the treatment of certain skin diseases, in particular eczema. But it is indicated for use in the treatment of rashes that produce exudate (that is, weeping ulcers), since it has a pronounced drying effect.
In the case of pityriasis rosea, there is no exudate; moreover, the plaque often flakes off and causes a feeling of tightness. The use of zinc ointment can intensify this unpleasant symptom. To improve the condition of the skin, you can use local preparations with a pronounced moisturizing effect. They often contain natural vegetable oils, as well as antiseptic components. But a dermatologist should select medications.
Can pityriasis rosea be treated with salicylic acid?
Salicylic acid, like salicylic alcohol, is another popular antiseptic. It disinfects the skin and fights a wide range of bacteria, viruses and fungi. But in the case of pink lichen, its use is ineffective: the virus is located in the deep layers of the skin.
Antiseptic agents in the treatment of Gibert's disease are used only to prevent the risk of secondary infection of the rash with bacterial flora, and not to combat the pathogen itself. But it is not recommended to use salicylic acid and alcohol for this purpose either: both substances dry and irritate the skin and increase peeling. The effect of using the product will be the opposite: the rash will take longer to heal, and after healing, marks with disturbed pigmentation may remain.