Moles during pregnancy are not uncommon, which is often associated with global changes in hormonal levels.
The appearance of new nevi or their visual change forces expectant mothers to contact a dermatologist and look for the causes of such phenomena.
What are moles?
Nevi (moles) are small areas of skin that differ in shape and color from the rest of the epidermis.
They are pigmented spots, usually benign.
Nevus is the collective name for circumscribed, benign cutaneous or mucous growths that often originate from melanocytes.
The most common of these are brown nevi of pigment-forming cells (pigmented nevi).
There are congenital moles and acquired ones.
The exact cause of congenital nevi is unknown.
Acquired ones develop against the background of various factors.
Such as a predisposition to formations, hormonal changes (usually during pregnancy), excessive exposure to UV on the skin.
Why do moles appear?
A formation called a nevus grows in a person after he reaches the age of ten. But sometimes parents notice moles on their newborns’ bodies. Therefore, it is impossible to determine the exact period of occurrence of benign growths.
In normal conditions, moles are formed when the skin is exposed to excess ultraviolet radiation. Hormonal imbalances are also a common cause of the formation of growths. In this case, failures do not necessarily have to be observed - simply the activation of certain hormones is enough.
This period is especially acute for teenagers and pregnant women. In the first case, in the period from 11 to 14 years, new nevi form on the skin.
During pregnancy, you can observe the appearance of new formations on the body
For women, there are several moments when moles may appear:
- pregnancy;
- abortion;
- menopause;
- taking oral contraceptives.
Pregnant women especially often experience such changes. An expectant mother should not be afraid of the appearance of moles. The process is considered natural and natural. After all, bearing a child is a time when hormones are in an unstable state. They are necessary for normal growth and development of the fetus. Therefore, the body begins to work in enhanced mode.
Many formations go away on their own after pregnancy. This is observed when hormonal levels are normalized. But even if the nevus remains, you shouldn’t be upset. In its normal state it poses no danger.
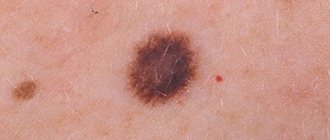
Symptoms of malignancy
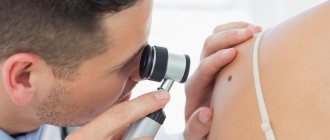
In order not to miss signs of a change in a mole, you need to constantly monitor its condition. You should periodically undergo preventive examinations with a dermatologist or independently examine yourself using a mirror.
Symptoms indicating possible malignancy include:
- change in contours: they become jagged, irregular, blurry;
- a sharp change in volume and shape: a significant increase in size over several months;
- the appearance of new shades: probably an intensification of color (becomes sharply black) or lightening, mottling;
- loss of symmetry of the mole;
- the appearance of a light or red border around the formation;
- hair loss in the area;
- the surface suddenly began to become wet, erosions, pus or bleeding appeared;
- the formation has become dense (rocky);
- the element began to become covered with horny scales.
Are nevi dangerous when carrying a child?
Moles during pregnancy do not pose a danger to the female body. They are benign formations that appear on the skin.
Nevi (the scientific name for growths) can be congenital or acquired. The latter can appear at any time.
There is no need to worry about formations occurring. They are benign tumors, so they cannot harm the body.
Nevi in normal condition are not dangerous
But in some cases, nevi can really cause harm. This doesn't happen often, but it does happen. There may be a process of degeneration of the growth into a malignant one.
This process is triggered by:
- genetic predisposition;
- tissue injury;
- ultraviolet.
Doctors note that moles appear when there is an excessive accumulation of melanocytes. They are cells that synthesize melanin. With excessive localization of cells, nevi are formed.
If moles appear during pregnancy, there is no need to worry. After all, benign formations will not harm the mother and the unborn baby. Then large accumulations of nevi should not be a concern.
Only dangerous formations are removed during pregnancy. In all other cases, the doctor decides to reschedule the operation for the postpartum period.
In some cases, a mandatory consultation with a doctor is necessary. This is important when the mole:
- increases;
- itches;
- changed color;
- bleeding.
For any altered conditions, it is important to conduct a full examination of the formation. This will require consultation with a dermatologist or oncologist.
Indications and contraindications for mole removal
Mole removal has aesthetic and medical indications. It’s definitely worth removing a mole if it:
- located on the face and creates a pronounced cosmetic defect
- exposed to frequent injury (razor, clothing, hand)
- is located in an open area of the body and is regularly exposed to insolation (ultraviolet exposure)
- intensively increases, changes shape, color (histology is required)
- crusted over
- hurts, itches
Even if a nevus looks normal, it may undergo malignant processes that are invisible to the naked eye. Absolutely all of them are prone to degeneration into a malignant tumor. According to statistics, skin melanoma accounts for 10% of all diagnosed cancers. Therefore, before removing a nevus, specialists must examine the type of cells of which it consists.
Do not put off your preventive examination until later, at the ABC Clinic, we will examine you and give the necessary recommendations for the prevention of dysplasia and malignancy.
Removal of benign nevi is contraindicated in cases of increased sensitivity to solar radiation (photodermatosis), which is diagnosed in 10% of people. Relative (temporary) contraindications include taking tetracycline drugs and local inflammatory processes.
Increase in the size of nevi
There is no need to worry if moles appear during pregnancy. After all, the process is normal and does not require any special measures. But you need to pay attention to the formations that undergo changes when carrying a child. A woman should be wary if:
- changes in shade;
- increase in size;
- the appearance of pain syndrome;
- detection of itching and burning;
- transformation of flat formations into hanging ones.
The nature of the changes should be determined by the doctor during the examination.
Any changes should prompt the woman to visit a doctor. It’s better not to panic in advance, because new properties are often caused by increased hormone levels.
Many women do not know who to contact with a problem when a mole has enlarged. First of all, it is necessary to notify the obstetrician-gynecologist who is observing the woman. You can also contact a dermatologist or oncologist yourself.
The doctor must examine the formation. Based on it, you can determine the type and nature of the mole.
Preventive measures
To prevent an emerging mole from becoming dangerous and posing a threat, you need to remember basic preventive measures.
- A woman needs to hide her mole. The nevus must be hidden from exposure to ultraviolet rays. At the same time, you need to avoid excessive natural tanning and refuse to visit the solarium.
- An enlarged mole must be protected from injury. It is important to ensure that it does not rub against clothing or become damaged.
- If the nevus enlarges, you should avoid scratching it.
- It is forbidden to squeeze out liquid in a mole.
If you follow simple measures, you will be able to avoid further growth of the nevus. Also, these rules will help prevent its transformation into a malignant formation.
A pregnant woman needs to protect herself from negative influences
Is it possible to remove moles during pregnancy?
You can also read:What does a mole on the neck mean?
In normal conditions, a doctor may recommend that a person get rid of a nevus. But during pregnancy, women rarely have moles removed.
An indication for removal may be the danger of formation. At the same time, the doctor assesses the risks of developing melanoma and the consequences of maintaining the mole for the mother and fetus.
If there are no serious concerns, removal will not occur. Doctors recommend doing this later, when the woman gives birth. The doctor can give recommendations regarding the care of formations in order to prevent complications.
Examination before mole removal
All patients undergo a dermoscopic examination before removal of nevi. The essence of dermatoscopy is to repeatedly enlarge the area under study, down to the cellular level. The doctor determines what cells the neoplasm consists of and whether there is dysplasia. As a rule, no tests are required before removal. However, if a large area of skin is affected or the mole has signs of malignancy, in addition to the histological analysis of the nevus itself, you will need to submit the following:
- clinical blood and urine test
- blood chemistry
- blood for infections, clotting
- blood group and Rh factor
- and undergo fluorography
Myths about moles during pregnancy
The appearance of moles during pregnancy is a common occurrence. Therefore, women begin to come up with various legends regarding nevi. Many of them have no real confirmation.
- There is an opinion that a new mole on the body of the expectant mother indicates the appearance of the same one in the child. Doctors note that the nature and location of nevi are individual. Therefore, the newborn will not have the same growth. The only true statement is the possibility of a child’s genetic predisposition to formations. Therefore, if the mother has multiple moles, we can assume a similar phenomenon in the baby.
- The second misconception is the fate of moles. Women believe that each nevus carries a certain sign. However, such judgments do not have scientific confirmation. Therefore, only superstitious pregnant women can believe in such legends.
- Women are often mistaken in thinking that they can cause birthmarks to appear in their unborn child. There is an opinion that, when frightened, a woman who grabs a certain part of the body can lead to the appearance of a mole in the baby in this area. Such judgments are absurd. Therefore, doctors recommend not taking these facts into account, excluding reasons for concern.
Moles appear very often during pregnancy. They are associated with hormonal changes in a woman’s body. If they do not create discomfort and remain unchanged, then you should not be afraid of them. You should consult a doctor if the nevus becomes red, grows, or becomes injured. This can lead to serious consequences.
Mole removal methods
The main methods for removing moles and papillomas:
- surgical excision
- laser destruction
- radio wave excision
- electrocoagulation (cauterization)
- cryodestruction (freezing)
The choice of a particular method depends on the indications. Classic surgical removal is indicated for large and medium-sized tumors, as well as for signs of dysplasia. Laser and radio wave removal is used for small and medium-sized nevi. Cryodestruction is relevant for small tumors. Electrocoagulation is rarely used in modern clinical practice, since it is a rather painful and traumatic procedure.
Surgical excision
The surgical method of removing nevi has long been introduced into medical practice; it has not lost its relevance today. With the help of surgical removal of moles and neoplasms of other etiologies, deep-lying elements can be excised. Surgical excision is the best option for removing giant moles. If a histological examination of the removed tumor reveals a malignant process, the skin in the affected area is excised again. The disadvantage of the classical method is the aesthetic defects (scars, scars) that remain after cutting off the tumor. To correct minor aesthetic imperfections, laser resurfacing of scars is used, and when excision of large areas (half the face, the entire abdominal area), skin transplantation can be performed. Rehabilitation depends on the extent of the operation. The smaller the affected area, the faster the recovery period will pass.
Laser destruction
Laser removal of moles and warts is the least traumatic method. When destroying small nevi, the procedure is performed without anesthesia. If medium-sized moles are removed, an anesthetic test is performed and local anesthesia is administered. During the procedure, the doctor projects a laser beam onto the nevus and holds it in this position for 30-60 seconds. After which the treatment area turns white. After 6 hours, redness appears around the treated wound, which disappears the next day. A crust appears in the area of the destroyed neoplasm, which must be protected from damage until it comes off on its own (7-14 days). Tissue regeneration occurs under the crust; if the crust is damaged, a scar will remain at the treatment site. If all rehabilitation rules are followed, the tissues are completely regenerated and no marks will remain on the skin. For quick recovery, we recommend using regenerating ointments. For 6-12 months after removal, the skin in the destruction zone has a pink tint, after which it turns pale and merges with the surrounding tissues.
The laser beam has bactericidal properties—there is no risk of wound infection during the procedure. The processing time for one mole takes no more than 60 seconds. The procedure is painless and there are no scars left after laser destruction.
Radio wave excision
The radio wave excision technique corresponds to the technique of classical cutting of a mole with a scalpel. But unlike the classical method, with radio wave excision there is no blood and the risk of infection entering the bloodstream. The radio knife literally vaporizes the tissue in the affected area. Tissues excised with a radioknife are sent for histology. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, the patient does not feel pain or discomfort. Rehabilitation takes 10-14 days.
Electrocoagulation
Removing moles by electrocoagulation involves evaporating the tissues of the formation using a hot electrocautery (a device in the form of a pen with a thin rod at the end). The procedure is quite painful; local anesthesia is used for pain relief. There is a risk of damage to healthy tissue.