Author:
- Shachnev Konstantin Nikolaevich
otorhinolaryngologist
4.00 (Votes: 4)
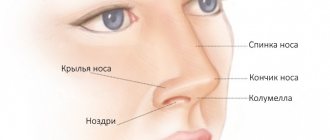
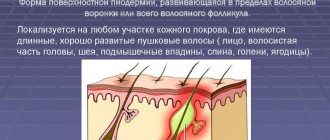
A furuncle is an acute inflammation of the hair follicle (bulb) together with the sebaceous gland, adjacent areas of the skin and subcutaneous fat. The initial sections of the nose, called the vestibule of the nose, have a large number of hair follicles, and therefore it is there that boils most often develop. They are less common in the area of the tip of the nose, wings and slope of the nose, and nasolabial fold.
Stages of development
The first stage in the development of the disease is a traumatic injury to the skin and nasal mucosa (such as an abrasion, scratch or cut), through which the infection penetrates deep into the tissue. The causative agent of the disease is usually pathogenic staphylococci and streptococci. The infectious agent then spreads along the hair root into the follicle. This process is accompanied by local inflammation and the formation of a painful infiltrate. This stage of the boil is called the infiltration stage. After this, necrosis develops and a necrotic core is formed. The surrounding tissues undergo melting and transform into purulent masses, after which they begin to accumulate under the layer of epidermis surrounding the mouth of the follicle, which is why a subcutaneous abscess develops. This stage of the boil is called the abscess stage.
Causes and course of the disease
The cause of a carbuncle or boil of the nose is staphylococcus. Due to the prevalence of carriage, Streptococcus aureus plays a dominant role. The cause of a boil can also be streptococci (beta - hemolytic streptococcus of group A). Groups of streptococci such as viridans and non-hemolytic cause this disease much less frequently. The development of the disease is significantly influenced by a decrease in human immunity. This helps to increase the number of boil recurrences. The following diseases have an adverse effect on the course of the disease, increase the frequency of relapses and affect the prognosis:
- hypovitaminosis;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- diabetes.
The penetration of infection into the area of the external nose and the vestibule of the nasal cavity is facilitated by:
- violation of skin integrity due to microtraumas;
- skin pollution;
- the influence of such production factors as cement and coal dust, fuels and lubricants;
- overheating or hypothermia, which significantly reduce the anti-infective resistance of the skin.
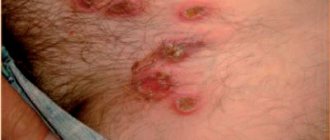
Two or three boils may merge together to form a carbuncle. In this case, an increase in local inflammation is observed. The hair follicle is surrounded by an inflamed infiltrate (accumulation of fluid in the tissues of cellular elements mixed with lymph and blood). The process of thrombosis begins in small venous vessels. An increase in infiltrate can cause the spread of thrombosis into the vessels of the skull, which can lead to the development of severe intracranial complications or sepsis.
Possible complications of a nasal boil
A nasal boil is not at all as harmless a disease as boils in other locations. The fact is that it is located in the nasolabial triangle (otherwise it is called the “triangle of death”). Its peculiarity and danger as a source of inflammation lies in its extremely developed blood supply: there are many vessels of the venous and arterial network located here. In addition, these veins do not have the valves inherent in the veins of other areas, and therefore formed blood clots, bacteria and their toxins can spread along the venous pathways into the orbit and venous sinuses of the brain. This can cause phlegmon of the nasolabial, buccal area and orbit, thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus and other serious complications - meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess. Less common is the generalization of infection – sepsis. The most common local complications are sinusitis, sinusitis and nasal septum abscesses.
Clinical picture
Within two days from the onset of the disease, compaction, hyperemia (increased blood supply to the tissue), and swelling in the area of the hair follicle appear. Pain also appears, which intensifies with chewing and facial muscle tension. There is a headache, fever, and general weakness. A peripheral blood test shows an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). After 3 or 4 days, the head of the abscess appears, which has a yellowish-white color. In the following days (usually 2-4 days pass), the center of the infiltrate becomes soft and a small amount of pus is released. The necrotic (dead) shaft of the hair follicle is rejected, the cavity of the abscess is cleansed, which is filled with granulations (tissues that develop during the healing of the source of inflammation). Pain sensations decrease, temperature returns to normal, and general condition improves significantly.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
In some cases, abscess formation (limited accumulation of pus in the tissues) of the boil is observed.
Treatment of nasal boil
First of all, it is strictly forbidden to try to treat a nasal boil on your own, much less squeeze it out. Due to the high risk of developing complications with this disease, at the first symptoms you should contact an otolaryngologist.
If the boil is localized small, is in the infiltration stage, and has unexpressed symptoms, outpatient treatment is possible. If the patient applies in a timely manner, the therapeutic program consists of conservative measures: local and general antibacterial therapy, treatment of the boil with antiseptic ointments and solutions, anti-inflammatory and detoxification therapy, etc.
If, at the time of examination, the nasal boil is in an abscessed form, local and general inflammatory signs are pronounced, and there is a risk of complications, then it is necessary to carry out surgical treatment of the nasal boil (opening the boil), and only in a hospital under round-the-clock medical supervision.
Purulent nasal discharge
The appearance of purulent nasal discharge can occur for various reasons. But regardless of them, you need to contact an otolaryngologist, and if this is not possible, then a therapist. We do not recommend trying to get rid of the problem yourself.
The discharge is yellow-green in color and has an unpleasant odor. Additionally, discharge of pus from the nose may be accompanied by headaches, general malaise, chills, itching and pain in the nose.
Causes of purulent nasal discharge
The cause of pus in the nose is considered to be damage to the paranasal sinuses. A blockage occurs, and a mucous secretion accumulates in the sinuses, which can later become inflamed. Additional reasons may be the consequences of injury or the occurrence of an abscess in the nasal cavity.
But the main cause of pus is considered to be diseases of the nasal cavity. To eliminate them, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe treatment and give recommendations. Therapy for adults and children is almost the same. If you consult a doctor in time, the treatment will not be long and surgical intervention will not be required.
At the initial stage of the disease, the pus has a liquid structure and white color. The volume of discharge is small, it can flow down the back wall of the throat. If the viscous structure predominates, this means that the purulent process has entered an advanced stage and urgent treatment is required.
Diseases accompanied by the discharge of pus
To determine the cause and diagnose the disease, it is necessary to consult an otolaryngologist, and at the diagnostic stage it is already possible to distinguish:
- sinusitis;
- nasal polyps;
- nasopharyngitis;
- ozena.
Purulent discharge may be the result of bacterial infections or complications after injury or surgery. Mostly children are susceptible to bacterial infection due to insufficiently strong immunity. In adults, this is rare and occurs only when the immune system is severely weakened and the body is weakened.
Sinusitis
The development of sinusitis is one of the main reasons for the appearance of pus from the nose. With this pathology, inflammation of the maxillary paranasal sinuses is observed. Purulent discharge has a greenish color, sometimes it can turn brown due to inclusions of blood. The development of sinusitis can be triggered by the presence of carious teeth in the upper jaw.
The following symptoms are noted for sinusitis:
- elevated temperature (from 38°C);
- constant headache that cannot be relieved with medications;
- feeling of heaviness in the head;
- loss of smell;
- general weakness and decreased performance;
- sleep problems.
The occurrence and development of sinusitis can occur not only due to diseased teeth. The cause of the occurrence and development of the disease can be an untreated runny nose, injury, decreased immunity and hypothermia.
When you notice the first symptoms of the disease, you should seek medical help and not try to cure yourself. If not treated correctly, the disease can have serious consequences. If you have had sinusitis once, the risk of the disease recurring will be higher than for a person who has not had sinusitis.
Nasal polyps
Polyps are benign growths and often appear in the nose. But with further growth in the mucous membrane, chronic nasal congestion may occur, a nasal voice may appear, and the sense of smell may decrease. The development of polyps may be accompanied by frequent headaches.
Excessive enlargement of polyps disrupts the proper functioning of the nasal cavity, and the outflow of mucus is disrupted. Inflammatory processes begin to develop in it, which leads to the formation of pus.
The problem cannot be solved with medication; surgery will be required. But even removing polyps does not guarantee that they will not appear again in the future.
Rhinopharyngitis
The disease is accompanied by a simultaneous inflammatory process in the nasal cavity and larynx. The emergence and development of the disease occurs after viral diseases (ARD, ARVI). Symptoms include:
- itching and burning in the nasopharynx;
- disturbances in breathing through the nose;
- change in voice (nasality);
- discharge of mucus and pus from the nose, sometimes the color may turn brown due to the presence of blood;
- swelling of the nasopharynx;
- temperature increase.
To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to carry out complex treatment. If you postpone it, then nasopharyngitis will provoke irreversible changes in the body. In an advanced stage, changes in the tissue of the pharyngeal tonsils may occur, which will require their removal.
Ozena
Ozena is sometimes called atrophic rhinitis. When the disease occurs, damage occurs to the nasal mucosa, accompanied by an unpleasant odor. When the first signs appear, you must consult a doctor and undergo urgent treatment.
Symptoms of the disease:
- purulent nasal discharge, which has a strong and pungent unpleasant rotten odor;
- the sense of smell disappears;
- Dry crusts constantly form in the nasal cavities.
The development of ozena can occur after prolonged chronic rhinitis. This is especially noted in the case when rhinitis was not treated and became chronic. The initial signs are the presence of a large amount of transparent discharge. At first they have a watery structure, but later atrophy of the mucous cavity occurs. After some time, the inflammatory process enters a critical stage, and pus begins to discharge from the nose.
Discharge of pus from the nose can occur due to injury or surgery. The situation is also possible if a bacterial infection has occurred. The appearance of pus indicates that the treatment was carried out incorrectly, or there was non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations in the postoperative period and infection in the operated area.
What you need to know about purulent nasal discharge
If purulent discharge is detected, you should seek medical help and not self-medicate. Timely treatment will have a positive effect, quickly get rid of the problem and avoid complications. If treatment is neglected, the risk of complications increases and surgery may be required. The longer you wait to see a doctor, the more effort and time it will take for a full recovery.
How is the treatment carried out?
There are two methods used to treat nasal discharge of pus. This includes medication and surgery. Drug treatment uses antibiotics to help the body cope with the disease. But they contain components that can affect the intestinal microflora. To level out the effects on the body, probiotics are prescribed to help avoid intestinal problems.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe the use of vasodilators, which help reduce swelling of the mucous membrane and improve the outflow of contents of the paranasal sinuses. Sometimes it is recommended to take painkillers and antipyretics. If the separation of mucus from the nasal cavity is associated with difficulties, then rinsing the nose with an isotonic saline solution is prescribed.
Surgery may be required when polyps are present in the nasal cavity and there is an urgent need to clear pus from the paranasal sinuses. The operation does not require hospitalization and is performed under local anesthesia. After the intervention, the doctor will give recommendations that should be strictly followed to avoid complications.
The postoperative period is accompanied by a mandatory course of antibiotics, which reduces the risk of purulent complications and maintains the body's protective functions.
If you notice purulent nasal discharge, you can call our clinic and make an appointment. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment and give recommendations on further prevention from the development of the disease. If necessary, our doctors will perform an operation and help resolve the problem. After the procedure, the patient can stay in a free hospital for several hours. This will help him recover from the effects of anesthesia, and the doctor will be able to monitor his well-being.
Author
Sadrtdinov Alik Gadelyanovich
otorhinolaryngologist (ENT)
Candidate of Medical Sciences
25 years of experience
+7
Discharge from otitis media
Discharge from the ear can also be attributed to otitis media. Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear and the most common infection in children. This is usually the result of a cold or flu and most often occurs during the cold season, so along with otitis media, the baby may also have signs of a respiratory infection - fever, cough, sore throat, nausea.
Diagnosing otitis media is not difficult: severe pain in the ear, especially at night, insomnia, anxiety, crying... fluid may leak from the ear. Depending on the cause and complexity of the condition, the discharge can be mucous or purulent.
Often acute otitis media goes away on its own. The use of analgesics to relieve pain is recommended. The doctor will also prescribe ear drops.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is based on an analysis of the patient’s complaints (pain in the vestibule of the nose) and data revealed during examination (the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate).
The facial area has a highly developed network of anastomoses (connections) between deep and superficial vessels, so the development of septicemia (blood poisoning with toxins) and (or) septicopyemia (a form of sepsis with purulent metastases in the internal organs) is possible.
A sign of a complicated course of this disease is the occurrence of phlebitis (inflammation of the walls) of the facial veins. In this case, redness and thickening along the vessel, swelling of the lower and upper eyelids, forehead, chills, and increased temperature are observed.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Discharge from external otitis
Discharge is one of the leading symptoms of otitis externa. They are white or yellow in color with an unpleasant odor. The discharge is accompanied by ear pain and redness. The ear canal may also become swollen. Sometimes the swelling is so severe that the ear canal becomes blocked and no longer transmits sound.
Itching is more common with fungal infections than ear pain. There is also a feeling of swelling in the ears. An Aspergillus infection causes a gray, black, or yellow discharge surrounded by a loose substance. Candidiasis does not cause such changes. It is characterized by a thick, creamy, white discharge.
To treat bacterial inflammation, drops containing acid and corticosteroids are prescribed. Sometimes it is necessary to use local antibiotics, less often their systemic form, tablets are prescribed. Before starting treatment, the doctor must clean the ear, remove dirt and pus. Hearing is usually restored after cleaning the ear canal.
Painkillers will relieve pain. They will especially help you in the first 24 to 48 hours before the inflammation begins to subside.
Even with a fungal infection, the ear canal is thoroughly cleaned and antifungal drops are prescribed. Repeated cleaning may also be required. According to some experts, a mixture of alcohol and white vinegar is especially effective for fungal diseases: alcohol helps dry out the ear canal, and vinegar restores the acidic environment. Let us remind you that the proliferation of fungi occurs as a result of a violation of the acid-base balance.
For both bacterial and fungal infections, it is important to keep the ear dry until the infection clears up.
Is wax in the ear normal or pathological?
Purulent, mucous, or other discharge may appear in the ear. As for the organ of hearing, another secret is added to this list - the mass of sulfur. The latter is the most common form of ear discharge.
Wax is formed in the external auditory canal. The latter extends from the visible part of the ear to the middle ear. The skin in this area contains certain glands that produce sulfur. After leaving the glands, the wax slowly moves to the visible part of the ear and either on its own or leaves the ear during washing.
The ear glands constantly produce wax, so there is always enough wax in the ear canal.
Earwax performs several important functions.
- It moisturizes the skin of the ear canal, preventing the ear from drying out.
- Contains chemicals that destroy harmful microbes and protect us from infection.
- Sulfur is a kind of shield erected between the outside world and the internal structures of the ear. When dust, dirt and other unwanted particles enter the ear, wax absorbs them and prevents them from penetrating deep into the ear. So her disappearance cannot bring anything good. Therefore, it is a mistake to inexorably fight sulfur - you cannot get rid of it, and there is no need for this.
Regular washing is enough to keep your ear clean. You can also clean the outer ear with a towel to remove wax. But under no circumstances use cotton swabs or other long objects - the hearing aid and membrane are very soft and easily damaged.
In addition, pressure can cause wax to penetrate deeper into the ear. Be careful: While wax is designed to prevent harmful particles from getting deep into the ear, you'll be doing the opposite if you're extra active.