The term folliculitis means inflammation of the hair follicle.
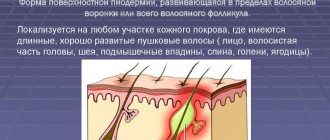
It can occur in any area of the skin covered with hairs (except for the soles and feet).
Folliculitis can be classified as a less serious purulent skin infection.
The etiology of the development of inflammation is varied; the causes may be fungal, viral, or parasitic.
But usually the infection is caused by microorganisms belonging to the group of staphylococci.
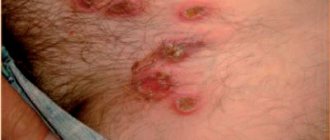
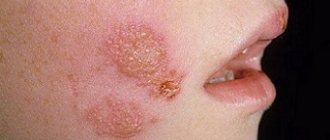
The disease manifests itself in the formation of rash elements (pustula), from the center of which hair grows.
As the pustules progress, they break open, forming small ulcerative lesions followed by scarring.
Residents of hot countries are more susceptible to inflammation of the hair follicles.
Where the climate is conducive to the favorable development of infectious diseases.
A high incidence is observed in people living in unsanitary conditions.
The pathology begins with staphylococcal impetigo.
It is characterized by superficial inflammation of the mouth of the hair follicle.
Manifests itself as an erythematous rash, blisters.
The blisters contain yellowish exudate; after they rupture, a crust forms in place of the blisters.
If staphylococci infect a primary non-infectious inflammation of the skin, they speak of secondary impetiginization.
As the process spreads and affects the deeper layers of the dermis, folliculitis develops.
According to the international classification of diseases (ICD 10), folliculitis is coded L73.8
Folliculitis: causes of inflammation
The causative agents of the pathology are predominantly Staphylococcus.
They belong to the order of gram-positive bacteria.
Less common is folliculitis, the occurrence of which requires other infectious agents: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, treponema, gonococcus.
The reasons are:
- fungal infection of the skin: candidiasis, Malassezia, Microsporum
- viral infections: herpes, chickenpox
- parasitic pathogens: acariases, mites
The risk of infection increases with various injuries, burns, chronic venous ulcers and other skin disorders.
People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to the disease.
general information
The pathology is widespread among residents of countries with high humidity and air temperature. Such climatic conditions contribute to the spread of infectious lesions of the hair follicles. The risk group is represented by socially disadvantaged segments of the population: a person’s failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene leads to the active reproduction of pathogens on the skin.
Often the causes of folliculitis are superficial inflammation of the follicles - ostiofolliculitis. The spread of infection to the lower parts of the follicle leads to the formation of purulent pustules.
What causes inflammation?
The infectious agent penetrates into the cavity of the hair follicle through microscopic damage, provoking an inflammatory reaction.
The likelihood of a pathological process is several times greater in patients with skin disease.
Such as eczema, dermatosis, various types of dermatitis.
The weakening of the barrier function of the skin contributes to the development of the infectious process.
The presence of diabetes mellitus in the patient is identified as provoking factors.
Diabetes is accompanied by a violation of the protective function of the immune system.
Elevated blood sugar levels and its presence in the urine cause frequent bacterial infections.
This is due to the ability of some types of pathogenic microorganisms to draw energy from glucose (simply, to feed on it).
The second provoking factor is acute immunodeficiency conditions: HIV, AIDS.
Long-term use of corticosteroids weakens the immune response and causes general immunosuppression.
The main result of a compromised immune system is the body's inability to fight infections.
Reasons for the development of pathology
In 70% of cases, inflammation of the hair follicles develops under the influence of staphylococci and streptococci. Somewhat less frequently, the causes of the disease are pseudomonas, pathogens of syphilis and gonorrhea, or Candida fungi. Molluscum contagiosum and herpes zoster viruses are less common causes of folliculitis. About 10% of clinically recorded cases of inflammation of the hair follicles occur due to the activity of parasitic mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis.
Pathogens enter the follicles through damaged areas: scratches and abrasions. People suffering from itchy dermatitis and excessive sweating are susceptible to infection. The weakening of the patient's immunity leads to the penetration of infection into the hair follicles. For this reason, dermatologists recommend taking preventive measures for men and women with diagnosed diabetes and chronic infections. The disease often occurs in HIV-infected people and patients taking immunosuppressive drugs.
Symptoms of the disease
The onset of the clinical picture is accompanied by the formation of a small red spot localized around the hair follicle.
After a while, the formation of an abscess filled with pathological secretion is observed.
Later it opens on its own and forms a crust when it dries.
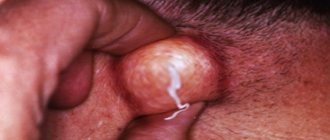
Quite often, the abscess transforms into a boil, which is a complication of folliculitis.
It is strictly forbidden to open a boil yourself.
There is a danger of local spread of bacteria and the formation of an abscess, local cellulitis and even sepsis.
For example, a boil on the head or face can cause purulent meningitis.
Sometimes several boils merge into a large lesion, causing the formation of a carbuncle.
The inflammation is multifocal in nature, the rash can spread to all the hairy parts of the skin.
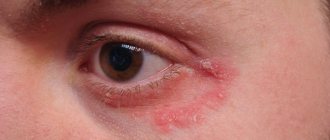
In women, the main localization is in the groin and thigh area, in men - on the face and head.
On palpation, the rashes are painful, have pronounced redness and are accompanied by itching of varying intensity.
The general clinical picture is complemented by:
- burning in the area of the rash
- increased dryness of the epidermis
- formation of scars
Diagnosis is made by physical examination as the lesions are easily recognizable even to the naked eye.
If the doctor has doubts, the specialist prescribes dermatological tests.
Abscessing and undermining Hoffman's perifolliculitis (APFPG) is a rare chronic purulent disease of unknown etiology, manifested by damage to the hair follicles of the scalp, and less commonly, the inguinal, perianal and axillary areas. It is more common in men 18-40 years old. Contrary to the generally accepted opinion about infectious genesis, the deterministic chain of AFPPG begins with the development of occlusion and destruction of pilosebaceous follicles, the formation of keratin in the dermis, to which the body responds with a perifocal granulomatous reaction. The infection theory currently continues to be disputed. Despite this, gram-positive microorganisms are often isolated from pyogenic elements, in particular, hemolytic streptococci, staphylococci and their various strains, which demonstrate resistance to a number of antibiotics. The clinical picture manifests itself very dramatically, which is especially pronounced against the background of immune and endocrine disorders, concomitant and intercurrent chronic diseases. The skin of the scalp is covered with painful, inflammatory, abscessing, yellowish-white, fluctuating and long-persistent nodules, forming tortuous cords, which spontaneously or when squeezed “undermine”. Purulent-hemorrhagic fluid is released from numerous fistulous openings and communicating passages. Ultimately, coarse fibrous connective tissue grows, atrophic or keloid-like scars form, which leads to irreversible scarring alopecia. In addition to inflammatory nodes, non-inflammatory spherical nodes (cysts) of elastic-elastic consistency are also formed. The course of the disease is long, but sometimes the process resolves spontaneously with the formation of scars, including keloids. Infectious agents involved in the development of APPPH produce pyrogenic exotoxins, which sometimes lead to the development of staphylococcal and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, which occurs with severe fever, low blood pressure, diffuse erythematous pharyngolaryngitis, conjunctivitis, signs of functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, etc. History of the use of retinoids in dermatology dates back about 40 years. During this time, about 1,600 retinoids have been synthesized and tested for biological properties, among which there are those that are now firmly established in dermatological practice: the natural metabolite of vitamin A - tretinoin, aromatic retinoids - acitretin, etretinate, the synthetic retinoid isotretinoin and some others. For systemic use, isotretinoin is marketed under the Swiss trade name Roaccutane. It has been scientifically proven that isotretinoin, interacting with nuclear receptors, affects the processes of differentiation of sebaceous gland cells, which leads to a pronounced decrease in their size, suppression of activity and a sharp decrease in sebum excretion rates. Depending on the duration and dose of the drug, the sebostatic effect reaches 90% of the initial level. Isotretinoin also has a moderate immunomodulatory effect and has a mild anti-inflammatory effect. In recent years, there has been a tendency to expand the indications for systemic use of isotretinoin. First of all, attention is drawn to the treatment of APPPG with this drug. We observed 7 patients (men) with APPPH aged from 20 to 25 years. The duration of the disease ranged from 1 year to 3 years. Previous repeated treatment without dynamics. Among the concomitant diseases, the following were registered: chronic gastritis, duodenal ulcer without exacerbation, chronic cholecystitis without exacerbation. Isotretinoin (Roaccutane) was used at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg, which provides a faster therapeutic effect with minimal side effects. The total course dose ranged from 100 to 120 mg/kg (average 110 mg/kg). The duration of taking the drug is from 16 to 24 weeks. According to indications, patients received symptomatic therapy aimed at treating concomitant diseases. All patients underwent general blood and urine tests, biochemical blood tests (bilirubin (total, direct, indirect), glucose, total protein, albumin, globulins, cholesterol, uric acid, urea, creatinine, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase ); Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Among the side effects observed in patients: dry skin and mucous membranes - 5 (68%), cheilitis - 3 (32%). All side effects were dose-dependent and reversible; the drug was not discontinued in any patient. Stable clinical remission was observed for 18 months after treatment. Treatment of APPPG with per os isotretinoin is superior in effectiveness to other methods; the drug firmly occupies a position in the “first line of therapy.” Based on data from other researchers, isotretinoin (Roaccutane) can be used in the treatment of not only abscessive and erosive folliculitis and perifolliculitis of Hoffmann's head, but also other dermatoses, acne, rosacea, folliculitis decalvans, purulent hidradenitis, severe forms of seborrhea, ichthyosis, lichen planus and others dermatoses.
Deep and superficial folliculitis
Ostiofolliculitis or superficial folliculitis is an exudative element of the rash (pustules) measuring 1-2 mm.
It is characterized by a rapid course and the absence of serious complications.
After a few days, the pustule dries out and a crust forms in its place, which falls off on its own, leaving no scars.
Deep (purulent) is accompanied by the formation of a nodule 2-3 mm in size, dark red in color, in the middle of which there is a purulent accumulation.
After 3-4 days, the formation resolves, and an ulcerative lesion appears in its place, leaving scars after healing.
If we are talking about an infectious lesion of the facial area, then acute sycosis is diagnosed.
In addition to the two main ones, a chronic bacterial process is distinguished.
The disease is accompanied by healing and the constant appearance of new elements.
Upon detailed examination, you can see rashes and purulent formations at various stages of development.
The facial area is most often affected by the chronic course of the disease in men who prefer to wear a beard.
Even minor damage to the epidermis, for example, during shaving, can provoke sycosis.
The risks of infection increase in the presence of predisposing factors: immunodeficiency, chronic foci of infection (sore throat, caries, sinusitis).
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist. The doctor examines the patient, during which he performs dermatoscopy. Studying damaged hair follicles using an optical device allows us to determine the depth of penetration of pathogens into the structures of the dermis. Samples from pustules obtained during the examination are subjected to laboratory testing. The study of biomaterials in the laboratory is carried out to identify the causative agent of infection. If signs of gonorrhea or syphilis are detected, the doctor will refer the patient for PCR testing.
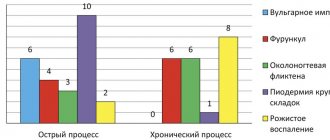
Differential diagnosis allows doctors to exclude drug-induced toxicoderma, pityriasis rosea, streptococcal impetigo, furunculosis and ostiofolliculitis from the patient’s history.
Consequences and complications
In addition to local complications - boils, hidradenitis, lymphadenitis, abscess, carbuncles , folliculitis with weakened immunity, untimely treatment can cause systemic disorders:
- meningitis;
- nephritis;
- pneumonia.
Complications of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis is not life-threatening. The disease must be treated because it causes aesthetic discomfort and sometimes pain to the patient. If you neglect the disease and do not adhere to hygiene standards, folliculitis will spread to other parts of the skin with hair. Abscess folliculitis can lead to the following complications:
- Scarring of the affected skin.
- Carbuncles.
- Boils.
- Abscesses.
In advanced and severe cases, the patient’s life is at risk, since with reduced immunity, pneumonia, meningitis and other disorders develop.
- Read - how to treat oil folliculitis
Share this article:
Diet for folliculitis
Diet for facial demodicosis
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 30 days
- Timing: during exacerbation/permanently
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles per week
To prevent skin problems, the development and complications of infectious and inflammatory processes, it is necessary not only to monitor the hygiene and integrity of the skin, but also to take care of a healthy diet that will support the immune system, the normal functioning of all organs and systems, and also normalize sugar levels and other indicators in blood. The diet includes several aspects:
- exclusion from the diet of white refined sugar and foods/drinks containing it;
- avoidance of too spicy and salty dishes;
- limiting the consumption of flour, confectionery, sausage, smoked, canned products;
- enriching the menu with cottage cheese, low-fat cheese, beef, seafood, green vegetables and herbs.
Symptomatic signs of the disease
The disease begins in the scalp, affecting the back of the head and the crown. The disease is characterized by the appearance of dense nodules located deep in the skin.
The disease is accompanied by an acute course, often the patient complains of pain, a burning sensation and itching at the site of the disease, weakness and malaise.
At the initial stage, the formations are small, but later they grow and soften. The affected area becomes hyperemic. The nodules tend to merge, which leads to the formation of abscessed Hoffmann folliculitis.
Risk factors
Folliculitis is a purulent disease that affects the hair follicles. The disease has a racial basis and can be inherited, as a result of which it occurs more often in African Americans.
The risk group also includes people who:
- have increased oily skin and, as a result, frequent blockage of the sebaceous glands;
- do not observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- often injure the skin by scratching after insect bites, scratches, abrasions;
- work in difficult working conditions;
- have complications after poor-quality cosmetic procedures.
The disease affects men and adolescents aged 15 to 35 years.
Hair follicles - definition
What are hair follicles? These are the channels from which hair grows. Hair and fat glands protect the skin from damage (lipid coating) and ensure its gas and heat exchange.
When the follicle is damaged, for example, by aggressive cosmetics or during depilation, microbes enter the base of the follicle and multiply there. The body begins to defend itself against bacteria, and this is how inflammation occurs. Those. folliculitis is an inflammatory reaction to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria or substances dangerous to the body.
Folliculitis
Treatment
Therapy for abscessing and undermining folliculitis should be comprehensive and consist not only of local effects, but also of strengthening the body’s immune forces.
Which doctor should I contact?
The disease must be treated by a dermatologist and infectious disease specialist. If related problems are detected, the patient is referred to specialists.
Drug therapy
The main principle of action in the treatment of folliculitis is the fight against the staphylococcal pathogen and the elimination of blockage of the sebaceous glands.
After bacterial sensitivity testing to antibiotics, the doctor determines the course of the most effective antibiotic therapy. Often these are sulfonamides and other drugs that have a wide spectrum of action.
How to cure folliculitis
Folliculitis should be treated
under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Therapy is based on the use of topical antibiotics in the form of ointments. In case of serious changes, general antibiotic therapy is recommended. Medicines for folliculitis are available with a doctor's prescription. You can also use urea creams for irritated skin, which will soften and moisturize the epidermis.
Herbs such as chamomile and sage are also effective against folliculitis.
What can you use at home for folliculitis?
Home treatment for folliculitis is primarily about hygiene and infection prevention measures.
To wash your body, use gentle lotions
that contain only natural ingredients.
Underwear should be airy and clothing should not be too tight
. To avoid inflammation of the hair follicles on the legs after depilation, it is necessary to disinfect shaving accessories or use disposable razors.