Types of fungal infections
Fungal infections can appear at any age. Infants most often encounter this problem - redness and peeling appear. The symptoms are similar to those of an allergic reaction, so therapy is often carried out, which is ineffective.
The clinical picture depends on the type of disease:
- Because Candida thrives in moist and warm environments, it multiplies in the diaper area of babies. This manifests as intense, large-scale redness with scaly edges.
- Oral thrush is characterized by the appearance of a tight, gray-whitish film in the cheeks and throat. This type of disease is also caused by Candida and is most common among infants.
- Ringworm is accompanied by severe itching, the appearance of round bald spots and blackheads. There is excessive hair fragility, which results in bald spots.
- Vaginal (genital) candidiasis also occurs in childhood, although much less frequently. The victims may be babies in the first weeks of life, whose mother gave them Candida at birth. Babies still have their mother's female sex hormones (estrogens) in their bodies. They appear to inhibit the regenerative ability of the mucous membranes, which in turn contributes to the progression of the disease.
Pet-borne dermatophytes should not be underestimated. The head and torso are affected. The main carriers are cats, as well as guinea pigs and rabbits. Accompanied by severe itching, redness and excessive dryness.
Table - Classification of mycosis pathogens
| Pathogen name | Localization area | How it manifests itself |
| Tinea capitis or Microsporum (microsporia or “ringworm”) | Scalp | Ring-shaped, sharply limited red spots appear, in which the hair either breaks or falls out. Sometimes the scalp starts to ooze due to weeping. Small red pustules may appear. |
| Tinea corporis (dermatophytosis) | Torso and upper limbs | It appears as pale red areas with characteristic peeling. In addition, there is unbearable itching. Therefore, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible to avoid spreading the fungus to other parts of the child’s body through scratching. |
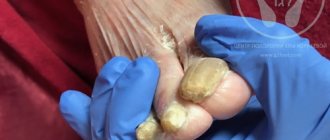
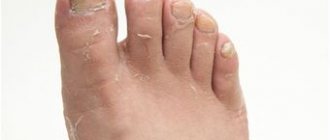
| Tinea pedis (onychomycosis) | Nail plates | The filamentous fungus damages the toes or nails and gives them a characteristic yellowish coloration. The plates with onychomycosis become thick and brittle, with a “loose” structure. With the exception of visual changes, symptoms such as itching do not appear, so onychomycosis is usually diagnosed in the later stages of progression. |
Traditional methods
Wine vinegar has long been the main remedy used against fungal infections.
- The traditional method of treatment is as follows: socks soaked in it are put on the baby at night and taken off in the morning.
- Herbs have an antifungal effect: calamus, celandine, burdock root. Chamomile decoction will relieve itching and inflammation. Apply onion and garlic juice to fungal-affected surfaces.
- An inexpensive way to cure the disease is salt and soda baths. Soda can also be used this way: mix with water to a paste and apply to the nail.
- It has long been customary to lubricate the affected areas with iodine; tea tree oil has a strong antifungal effect.
Advice. Sweets and foods rich in carbohydrates promote the growth of fungal colonies. Traditional healers recommend adding vegetable salads with fresh herbs to your food. Beet and carrot juice are good for fungal diseases.
Reasons for the development of mycosis
Predisposing factors include taking antibiotics, poor hygiene when visiting swimming pools, increased sweating and/or poor immune system protection. In most cases, pathological disorders in the body occur due to a combination of reasons.
Varieties of opportunistic microorganisms that are causative agents of the disease:
- yeast (Candida albicans causes thrush);
- dermatophytes (provokes herpes zoster);
- mold (causative agent of aspergillosis and respiratory tract problems).
The most common is Candida albicans - it is part of the natural microflora, present in 50% of the population. It does not cause problems until it begins to multiply uncontrollably under the influence of certain factors. Most often, Candida passes from mother to baby during childbirth and breastfeeding.
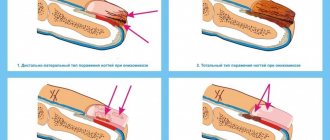
Etiology and pathogenesis of onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is caused by three main classes of fungi: dermatophytes, yeasts, and nondermatophytic molds.
Dermatophytes are the most common cause of the disease. Two main pathogens are responsible for 90% of all cases of onychomycosis: Trichophyton rubrum (70%) and Trichophyton mentagrophytes (20%). Onychomycosis, caused by non-dermatophytic mold fungi of the genera Fusarium and Aspergillus, as well as Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, is an anamorphic (asexual) representative of the genus Ascomycota, is gradually spreading throughout the world. Today they are responsible for 10% of cases of the disease. As for candidal onychomycosis, it is caused by Candida albicans and is quite rare.
In distal lateral subungual onychomycosis, Trichophyton rubrum is usually detected. Proximal subungual onychomycosis is typical in immunocompromised patients . The same type of onychomycosis, but with periungual inflammation, is caused by non-dermatophytic molds. White superficial onychomycosis of the nails is caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and its deeper forms are caused by non-dermatophytic molds. Candida nail infection is often observed in premature infants, immunocompromised patients, and individuals with chronic mucosal candidiasis.
Risk factors for developing onychomycosis:
- family history;
- elderly age;
- warm and humid climate;
- weakened body;
- nail injury;
- regular fitness classes;
- immunosuppression (drug, HIV, etc.);
- visiting public swimming pools, baths and saunas;
- tight shoes.
Repeated microtrauma of the nails in tight and uncomfortable shoes provokes onycholysis (detachment of the nail from the soft tissues of the finger) and other degenerative conditions that contribute to the penetration of fungi into the nails.
Symptoms of fungal infections
The nature and severity of pathological changes depend on the virulence (pathogenicity) and type of pathogen, as well as on the reactivity of the body, the area of localization and the area of the lesion. Signs of the disease cannot be identified independently. When primary symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor rather than begin self-medication.
The main symptoms of fungus in children:
- Body and scalp. Accompanied by redness, peeling and baldness (hair is broken off at a height of 4-5 mm), as well as the appearance of grayish-white scales.
- Feet, hands and interdigital space. Toenail fungus in children is characterized by excessive dryness, redness, moderate weeping and peeling. There are also bubbles and cracks that itch unbearably.
- Mucous membranes of the oral cavity and genitals. Thrush or candidiasis is accompanied by the appearance of a white, cheesy coating. Extensive superficial ulcerations and vesicular rashes are accompanied by burning and itching.
None of the known fungal diseases develops lasting immunity, so repeated infections are not excluded. That is why parents should know what fungus looks like in children and consult a doctor when the first symptoms appear.
Proper nutrition
The antifungal diet is aimed at reducing or completely eliminating from the diet foods that the pathogen “likes.” The child’s nutrition should be based on the following products:
- vegetables, mainly root vegetables: potatoes, carrots, onions, garlic;
- fermented milk products: kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese;
- chicken eggs;
- fruits: unsweetened apples, cranberries, lingonberries, sea buckthorn, grapefruits;
- yeast-free bread, sugar-free baked goods;
- legumes, such as beans;
- seeds, nuts;
- all types of unsweetened tea.
Junk and heavy foods should be avoided during treatment. Additionally, it is recommended to take multivitamin complexes to strengthen the immune system. Such an approach to combating onychomycosis will allow you to recover from the disease much faster.
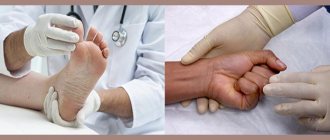
Diagnosis of mycosis
To make a diagnosis, an examination is carried out by a dermatologist or mycologist. The first step is a microscopic examination of the scales of the epidermis, hair and nails.
Laboratory testing allows you to determine the presence of spores or hyphae, which is necessary to clarify the type of pathogen and make an accurate diagnosis. The dermatologist also performs an examination under a Wood's lamp. This approach allows us to determine the type of disease and differentiate it from dermatitis.
Prevention
To prevent nail fungus, it is necessary to teach the child to follow the rules of hygiene from an early age. They provide the following points:
- availability of personal care products: towel, washcloth, etc.;
- daily washing of feet before bed, after which the skin must be wiped dry;
- wearing personal footwear appropriate to the size of the feet;
- regularly change socks, which should be purchased from natural fabric.
Children should also receive a balanced, high-quality diet with a limit on light carbohydrates. Strengthen the immune system through physical exercise and prevention of viral diseases.
Treatment of fungal infections
Thrush is treated with antifungal agents that are applied to the skin or mucous membranes. Systemic therapy is also prescribed. If you treat only the symptoms, a relapse will soon occur. The cause of the disease should be combated by strengthening the body’s protective functions.
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is necessary only in case of severe disease and in the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Treatment of fungal infections in children has the following approach:
- prescribing monotherapy or a combination of systemic and external antimycotic agents;
- the use of immunostimulants, glucocorticoids and antihistamines.
To increase the effectiveness of drug therapy, multivitamin complexes and physiotherapeutic procedures (DMV, therapy, darsonvalization, magnetic therapy, medicinal electrophoresis) are prescribed. Treatment should be carried out 2-3 times a day. The hair is shaved and the crusts are carefully removed.
When localized on the feet and hands, it is recommended to use special pastes, creams and ointments based on clotrimazole, neftifine or terbinafine. If a bacterial infection occurs, it becomes necessary to use antibiotics. For protracted and severe fungus of the nails, face and body skin, and hair in a child, antimycotic drugs containing fluconazole, itraconazole or griseofulvin are indicated.
For onychomycosis, it is necessary to use the drug until the nail grows completely. If drug treatment is ineffective, then surgical removal of the nail plates is performed.
To permanently defeat an infectious disease, you need to use the right medications and adhere to a certain diet. Self-medication in this case can lead to the development of serious complications.
Foods that should be excluded from the diet:
- Sugar, in any variety - honey, cane sugar, dextrose, fruit, malt and beet sugar, maple syrup, etc.
- Refined carbohydrates - white bread, buns, cakes or cookies, light noodles, white rice, etc.
- Products containing yeast.
When treating fungal infections in children, it is recommended to keep the affected area dry by frequently changing underwear or diapers. After showering and bathing, it is advisable to pat your skin well with a soft terry towel.
How to avoid recurrence of fungus
If the baby has already encountered onychomycosis, then the likelihood of relapse of the disease increases. Very often, an infection occurs due to the child’s failure to comply with individual hygiene rules.
Older children should be taught to use only their personal belongings. If microtrauma of the skin or nail occurs, it must be immediately treated with an antiseptic.
Constantly strengthening the immune system is the key to health. Includes a balanced diet, prolonged exposure to fresh air, and physical exercise.
Memo to parents
The resistance of the fungal infection is quite high, so the drug fight against it drags on for many months. The disease actively develops, eventually affecting the child’s nails. Parents should not ignore these changes, citing lack of time and funds. The problem goes deep inside, and a mild form of onychomycosis sooner or later affects the overall functioning of the body, in particular, its immune system.
It is easy to identify nail fungus by its appearance - every attentive mother will notice changes in the color and structure of the plates. From this moment, treatment should begin under the supervision of a specialist and preventive measures.
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations and take an integrated approach to the problem, your child’s nail fungus is gradually eliminated. Therapy can be carried out both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital, depending on the degree of onychomycosis. In any case, it is necessary due to many health-related factors.
What does Dr. Komarovsky say?
A well-known pediatrician believes that systemic medications - tablets and capsules for oral administration - should be prescribed in exceptional cases. Such antimycotics put a serious burden on the child’s liver and kidneys, exposing him to unnecessary risk in the form of complications with these organs.
Komarovsky insists that systemic drugs should be prescribed to children only if local remedies - ointments and varnishes - have not had the desired effect and the disease is progressing. That is, in extreme cases. The specialist also dissuades parents from self-medication and choosing traditional medicine recipes as the main therapy.