Dermatology is a field of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases. The discipline also focuses on hair, nails, and mucous membranes. In therapeutic terms, science is closely related to endocrinology, venereology, rheumatology, allergology, oncology, and neurology. In surgery - with plastic surgery.
The history of dermatology goes back centuries. In ancient Chinese treatises there are descriptions of symptoms and recipes for the treatment of leprosy, scabies, alopecia, acne and other diseases. A number of skin diseases are described in the works of Hippocrates, Celsus, and Avicenna.
Nowadays, dermatology is one of the most rapidly developing branches of medicine. Scientists are methodically developing new ways to maintain healthy skin, hair and nails.
Which dermatologist should I contact?
Within dermatology there are narrow specialties. Namely:
- Dermatovenerologist . Deals with issues of sexually transmitted infections.
- Dermatologist-oncologist . The specialist focuses on benign and malignant skin tumors.
- Trichologist . Works with hair pathologies.
- Dermatocosmetologist . Engaged in cosmetic procedures that have a positive effect on the health and youth of the skin and improve its structure.
The profession of a dermatologist and a cosmetologist is often put on the same level. You can make an appointment with a dermatologist, including for cosmetic purposes. The doctor will provide the most accurate description of the skin condition and determine its type: dry, oily, combination, sensitive. Thanks to this, you will be able to choose the right cosmetics, achieve better results in care, preserving youth and beauty.
However, in most cases, the following gradation is accepted: a dermatologist deals with pathologies, a cosmetologist deals with healthy skin. If you suspect the presence of certain skin diseases, you should contact a dermatologist. A dermatologist will trust only laboratory tests; a cosmetologist’s diagnostic capabilities are limited (as a rule, assessment of the skin condition is carried out more superficially, using hardware methods).
Why are moles dangerous?
Moles, which are scientifically called pigmented nevi, can turn into a malignant tumor - melanoma. Melanoma is truly dangerous, because it can lead to the death of a person within a few months. Of course, not every mole (nevus) will necessarily turn into melanoma, but any of them can theoretically do so. People with fair skin and a large number of nevi are at particular risk. Another “aggravating factor” is heredity; If one of your relatives has or had melanoma, then the person has an increased risk of developing this tumor.
How to reduce the risk of melanoma? Scientists now believe that the main method of prevention is sun protection. Sunburn and sun exposure in general increase the risk of developing melanoma. Accordingly, to reduce it, you need to use products with a high SPF, avoid walking under the scorching sun and sunbathe less often.
In what cases should you consult a dermatologist?
Contrary to popular belief that visiting a doctor is necessary when there is an obvious problem, visiting a dermatologist can also be preventative. A particularly important element of prevention is regular examination and check of the condition of moles, especially in places where they are difficult to check independently (for example, on the back, buttocks). During the visit, the specialist will assess whether the changes to the skin are harmless. If he notices the development of pathologies, he will prescribe a detailed diagnosis.
It's also worth making an appointment with a dermatologist if you have problems such as:
- flaky, dry skin;
- lesions of the skin or nails of unknown origin;
- acne;
- warts;
- increase in the size of moles;
- change in color of moles;
- burning sensation, tingling, swelling of the skin;
- skin itching;
- dandruff;
- excessive sweating, diaper rash;
- pigment changes;
- symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases;
- sores and blisters;
- excessive hair loss;
- skin hypersensitivity;
- the appearance of growths;
- difficult-to-heal wounds;
- unhealthy looking nails.
If deviations affect the genital area, both sexual partners should visit a venereologist-dermatologist, even if one has complaints. Only in this case will the treatment be effective.
Dermatocosmetologist
A skin doctor who combines aspects of aesthetic correction in his practice is called a dermatocosmetologist. His responsibilities include not only treating diseases, but also carrying out a number of procedures:
- Facial massage.
- Masks, wraps, peelings.
- Cleaning (manual, vacuum, laser).
- Mesotherapy, biorevitalization.
- Applying makeup, tattooing.
- Epilation, etc.
A dermatologist with a focus on cosmetology will provide a more comprehensive correction of acne, post-acne, hair loss and other conditions of a medical and aesthetic nature. Usually we are talking about non-invasive or injection correction.
What to look for when choosing a dermatologist
The experience and reputation of a doctor are key parameters when choosing a specialist. Among the accusations against incompetent doctors, the most often mentioned are:
- very short visiting time;
- no interview, the doctor does not ask questions;
- complete absence or very superficial examination;
- refusal of additional tests and diagnostics;
- prescribing potent drugs without conducting research;
- ignoring the patient’s comments about the effectiveness of prescribed drugs.
Also, be careful when choosing a cosmetologist, make sure that the specialist has the appropriate qualifications and experience. Do not trust fly-by-night salons; it is better to opt for cosmetology in a medical clinic. There are often cases when, after anti-aging procedures by a cosmetologist-esthetician (a specialist without medical education), a person is forced to go to a dermatologist’s office to treat the mistakes of a pseudo-professional. A real cosmetologist is a doctor who can perform a primary skin diagnosis.
In our Clinic, the listed phenomena are absolutely unacceptable. Our employees include experienced specialists (dermatovenereologists and dermatocosmetologists), who are distinguished by their professionalism and sensitivity towards patients. You can count on a comprehensive diagnosis and detailed history taking. All necessary conditions are provided for conducting accurate laboratory tests. The combination of these factors will ensure a quick recovery.
Division by specialization
If the problem occurs in a child, it is usually dealt with by a pediatric dermatologist who specializes in pediatrics and has experience treating children.
A doctor who is actively involved in scientific activities along with providing care to patients may be called a dermatopathologist. If a doctor treats skin and sexually transmitted diseases, then such a doctor is called a dermatovenerologist .
Some diseases at this level of medical development cannot always be completely cured, but with the right approach, an experienced specialist can help achieve long-term and sustainable remission.
How to prepare for your appointment
No special complex preparation is required before visiting a dermatologist. However, there are a few important rules. Namely:
- For skin problems . Hygiene is necessary, but without shower gels and soaps. If you apply any ointments, gels or other products to the affected area, you should stop using them 2-3 days before your appointment.
- For problems with nails . 3-4 days before the visit, you cannot cut your nails; the biomaterial may be useful for laboratory research. Clear or colored varnish must not be used. Avoid using antifungals and other topical products.
- For problems with facial skin . Do not use creams, wash your face without special products. Women need to come without makeup - you need to get rid of makeup at least 2 hours before your appointment.
- For problems with the scalp . Do not use hair styling products or other cosmetics. Do not wash your hair 1-2 days in advance - this will give a clearer clinical picture.
You must take with you a medical card with the results of general clinical tests (if any). It is important to remember as many details as possible about the problem that worries you (when the malaise appeared, in which cases exacerbations and periods of remission are observed, etc.).
How is the first appointment and diagnosis carried out?
The appointment begins with a conversation, during which the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints and asks questions to obtain all the necessary information. The next step is a physical examination. A dermatologist examines the skin, hair, and nails to evaluate possible causes of problems. However, he always keeps in mind that the source of warning signs does not necessarily have to be dermatological diseases. There are often cases when skin defects serve as symptoms of internal diseases and abnormalities (hypothyroidism, hormonal changes, cancer, sexually transmitted diseases, etc.).
Typically, the examination includes studies such as:
- Palpation . The doctor assesses the degree of skin elasticity, pain, and temperature.
- Scraping . Using a special microscope glass or a blunt scalpel, the dermatologist scrapes the skin. This is necessary to find out whether there are peelings and how tightly the scales adhere to the skin.
- Diascopy . The method involves pressing on the affected area. Thanks to the skin reaction, you can evaluate the nature of the spots (pigmented, vascular, etc.).
- Dermographism . The method is similar to the previous one. Here, too, pressure is applied to the skin, but the reaction of the blood vessels is assessed. If the white or red mark after mechanical action does not go away for more than 3 minutes, it means that vascular tone is impaired.
During the examination, the doctor may use a dermatoscope - a device with a built-in lamp that increases the field of view similar to a magnifying glass. This allows you to take a closer look at the affected area. To determine the extent of the skin rash, the examination can be carried out in a dark room under oblique rays of light (transillumination).
Sometimes the doctor can make a conclusion at this stage, but in most cases additional diagnostics will be required. To do this, material can be collected - scraping the skin and nails. The manipulation is absolutely safe and painless.
Tasks of a dermatovenerologist at a medical examination for a health certificate
When passing a medical examination to obtain a medical record, one of the required specialists is a dermatologist, and in most cases, a dermatovenerologist. The main and main tasks of a dermatovenerologist:
- identify sexually transmitted infectious pathologies that give a characteristic symptomatic picture on the skin (today this includes gonorrhea and syphilis);
- identify skin infectious pathologies that have a high degree of contagiousness (infectiousness) - pediculosis and scabies (a type of acariasis).
Treatment methods and follow-up features
Treatment of dermatological diseases depends on the form of the disease. Sometimes oral medications are needed, sometimes topical medications, often in the form of ointments, gels, creams, lotions, shampoos. A dermatologist may prescribe antibiotics (for syphilis, gonorrhea, or acne) or antiviral drugs (for herpes). In case of allergies, contact with the allergen is limited, for burns, topical ointments and creams are used, in case of mycoses, topical medications or oral treatment are used (in advanced cases).
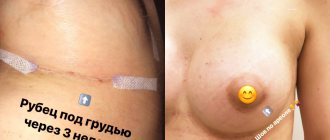
Sometimes therapeutic procedures such as laser mole removal, electrocoagulation, cryosurgery, light therapy, scar removal using dermabrasion, etc. are necessary. The treatment plan depends on the type of problem and is selected on an individual basis.
Additional diagnostic methods
Diagnosis is usually based on laboratory tests. Sometimes it is necessary to do a general and biochemical blood test, microbiological culture, take hormonal tests, and analyze stool and urine. Allergy tests are often prescribed, including PCR techniques, serological blood tests, and others.
If during research it turns out that the problem is directly or indirectly related to disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems, the dermatologist will write out referrals to the appropriate specialists. For example, to an endocrinologist, oncologist, allergist, etc.
What diseases does a dermatologist treat?
The area of expertise of a dermatologist covers a wide range of diseases. Among them:
- skin allergies;
- atopic dermatitis;
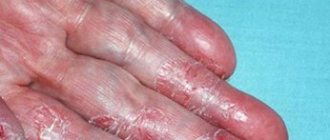
- mycoses of the skin and nails;
- papillomas;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- alopecia;
- melanoma;
- herpes;
- chloasma;
- acarodermatitis;
- erythema;
- eczema;
- folliculitis;
- pityriasis rosea;
- acne;
- rosacea;
- vitiligo;
- hidradenitis;
- punctate keratolysis;
- erysipelas;
- pediculosis;
- psoriasis, etc.
Remember that the sooner the disease is diagnosed and treatment is started, the sooner recovery will occur. You should not delay your visit to the doctor to prevent severe forms of illness.
Oncologist
Another complication is the question of which doctor treats skin cancer. If any tumor is suspected, dermatologists seek advice from oncologists. It is these specialists who have sufficient competence to diagnose and treat neoplasms (especially malignant ones).
Among traditional studies, the oncologist performs a biopsy (taking a piece of skin) and sends the tissue for histological analysis. Benign formations undergo routine removal, while malignant ones require specific therapy and long-term observation.
A diagnosis of a benign or malignant tumor cannot be made without consulting an oncologist. Treatment of atypical conditions is also within his competence.