Chickenpox in children is the most common disease after ARVI that parents have to deal with. The disease cannot be called dangerous, since most often it occurs in a mild form, and after recovery a stable immunity is formed. Diagnosing the pathology is not difficult, since the signs are clearly expressed.
Chickenpox - definition
Chickenpox (also known as varicella) is an infectious disease of Chickenpox (Varicella).
It is caused by the varicella zoster virus. By the way, a close relative of the herpes familiar to many. All herpes are contagious, but varicella is the coolest. Chickenpox spreads through airborne droplets, and does so very actively. To catch an infection, sometimes it’s enough to look into the patient’s room for a second.
It always seemed to people that the disease was literally carried through the air, by the wind. Hence the first part of the name - wind. It was named smallpox because of the numerous rashes in the form of fluid-filled vesicles (papules), similar to those that form in smallpox.
Fortunately, chickenpox is not as deadly.
Fenistil
"Fenistil" is a safe antihistamine (antiallergic) drug of a new generation. To reduce the itching of chickenpox, antihistamines are used, this is especially true for children who cannot control themselves and scratch the wounds. It is not advisable to use Fenistil gel for chickenpox, since due to the treatment of large areas of the body it can be toxic to the body. But Fenistil drops for chickenpox are a good way to relieve itching. The number of drops is calculated based on the patient's weight.
Fenistil
GlaxoSmithKline, GSK, UK
The antiallergic effect of Fenistil is associated with competitive blockade of H1-histamine receptors.
Symptomatic treatment of allergic diseases such as: urticaria; allergic rhinitis; food allergies; drug allergy. Elimination of itching from: insect bites; chicken pox; atopic dermatitis. from 237
5.0 1 review
1168
- Like
- Write a review
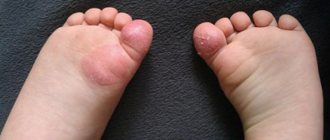
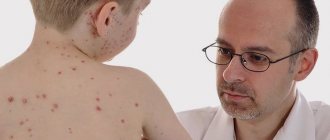
Chickenpox symptoms
Chickenpox usually lasts about ten days. The main symptom of chickenpox is a typical rash. One to two days before the rash appears, the following nonspecific symptoms may occur:
- Fever
- Decreased appetite
- Headache
- Fatigue and general malaise
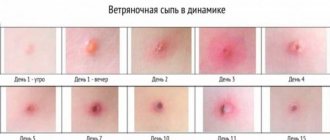
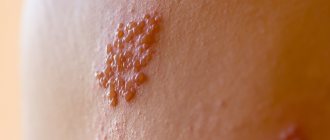
The chickenpox rash goes through three stages of development:
- Pink or red spots and bumps (papules), which appear in spurts, with each new wave of fever, 2-6 shocks per day, for 3-6 days.
- After a few hours, these papules turn into blisters filled with clear liquid (vesicles), they last for a day, after which they burst and the liquid flows out
- After the blisters burst, after a few hours weeping appears - in their place crusts form, which last from several days to several weeks until new tender skin forms under them, after which they fall off.
Fenkarol
Fenkarol is a relatively new anti-allergy drug on the pharmaceutical market, but has already proven its effectiveness and safety. The product is good at relieving itching and inflammation due to chickenpox. Typically, Fenkarol is well tolerated and has no side effects. The only contraindication is pregnancy.
Fenkarol
Olaina Chemical Plant, Latvia
- hay fever;
- acute and chronic urticaria; - angioedema; - allergic rhinitis; — dermatoses (including eczema, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis); — neurodermatitis; - skin itching. from 176
497
- Like
- Write a review
Chickenpox: course of the disease
Chickenpox is characterized by stages, which allows you to assess the course of the disease and navigate the quarantine period.
The incubation period of chickenpox is the time that elapses between the virus entering the body and the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease. It usually lasts 2 weeks, but can range from 10 to 21 days. The incubation period for chickenpox in adults and children is usually the same length.
The prodromal period is the initial stage of chickenpox. It is short (1-2 days), and may be absent altogether. Its characteristic symptoms are poor health, fever, muscle and headaches, and catarrhal phenomena in the nasopharynx. The first symptoms of chickenpox in adults are usually more pronounced than in children.
The rash period lasts 3-10 days. Elements of the rash appear in waves, this is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and poor health. 1-2 days pass between “waves” of rashes. There are usually 2-5 of these “waves”, then new elements stop appearing and gradually heal. The next stage begins - healing.
The recovery period begins from the moment when new elements cease to form, and all that appear become covered with crusts.
The period of convalescence (recovery) after chickenpox can last up to 1 year. The varicella-zoster virus causes a serious blow to the human immune system, and the process of its recovery is usually quite long. During this period, the body's resistance to other viral infections, such as ARVI, decreases.
How many days chickenpox lasts depends on the individual characteristics of the disease, the patient’s age, and the state of his immunity. On average, from the moment the first signs of chickenpox appear in a child until the elements of the rash completely heal, 3 weeks pass; in adults it may be longer.
Prevention
{banner_banstat9}
It is almost impossible for a child to avoid infection with chickenpox, since he is constantly in contact with other people. The main method of prevention is strengthening the body’s protective functions and observing hygiene rules.
Important! Vaccination against chickenpox is not included in the list of mandatory vaccines for children; parents can vaccinate with Okavax and Varilrix for a fee - the average cost of the procedure is 2.5–4.5 thousand rubles.
Types of chickenpox (classification of chickenpox).
Chicken pox occurs in typical and atypical forms and in terms of severity is mild, moderate and severe. Chickenpox is also classified according to ICD-10 (with meningitis, encephalitis, pneumonia).
Atypical forms of chickenpox are divided into:
- Hemorrhagic form - a common consequence of this form is bleeding, and this form occurs in people with thrombocytopenia.
- Pustular form - develops when a bacterial agent is attached.
- Gangrenous form - can lead to the development of sepsis and occurs most often in patients with weakened immunity.
- The generalized (visceral) form of chickenpox is characterized by development in patients with immunodeficiency. It is very difficult, the symptoms are more pronounced and often ends in death for the sick person.
- The rudimentary form is found in children who received immunoglobulin during the incubation period. It flows quite easily.
The severity of chickenpox is directly determined by the degree of intoxication syndrome and its criteria, as well as the presence of specific vesicular rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. It should be noted that there are also so-called abortive (very mild) cases of the disease, which occur without the appearance of fever and are characterized by the appearance of single rashes on the skin of the abdomen and back. Such chickenpox is detected in kindergarten during examinations during outbreaks.
To the question “how long does chickenpox last?” It is difficult to answer unequivocally, since the duration of the disease directly depends on the form and course of chickenpox. On average, in the classical (typical) course, the duration of the disease is from 12 to 16 days.
Severity
Depending on the characteristics of its course in children, chickenpox is divided into three forms:
| Mild degree | characterized by isolated rashes, absence of fever and poor health. Herpetic pimples appear in only 2–3 days. |
| Moderate | all the symptoms that traditionally occur with chickenpox in children are present. These include poor sleep, itchy skin, headaches, and a rise in temperature to high levels. Blisters form within 5–7 days. |
| Severe form | Due to high temperature (up to 40°C), the child experiences nausea and vomiting, headache, delirium, and fever. Papules appear on the body from 7 to 10 days. Multiple rashes cover different areas of the body. It can be found in the mouth and on the genitals. |
Diagnosis of chickenpox
The basis for detecting herpes is a virological study - examination of media to detect the pathogen. In case of chickenpox, for diagnosis, liquid from vesicles is used, in which, when stained, accumulations of the pathogen, the Argan corpuscle, are isolated.
Chickenpox is usually distinguished from insect bites. The main difference is the lack of development of elements and bedding, as well as normal body temperature.
Also, the disease should be differentiated from:
- streptoderma - occurs without fever, the rash is different - cloudy, purulent contents, after involution leaving a yellow crust, in its place a red spot forms. The rash is located mainly behind the ears and on the extremities, never on the scalp (a hallmark of chickenpox).
- herpes zoster - the blisters are located strictly along the nerve trunk; they practically never occur on the legs and arms.
- vesicular rickettsiosis - a small scab forms at the site of the tick bite, followed by the formation of an ulcer (a scar forms in its place after healing). Enlargement of regional lymph nodes is typical.
Poksklin
Cooling mousse "Poksklin" for chickenpox has a completely natural base (panthenol, aloe vera, chamomile and lavender). The product cools and reduces scratching, so scars do not form. “Poksklin” relieves inflammation, has an antiseptic effect and accelerates the healing process of wounds.
Poksklin
PharmaVal AS, Netherlands
Poksklin cooling hydrogel was developed to relieve the symptoms of chickenpox over large areas of the body.
While spreading thick creams and ointments over the body can damage the blisters, the cooling hydrogel is very easy to apply and does not cause friction in sensitive areas when applied to the skin. PoxClean provides an immediate cooling effect, which significantly relieves itching. For this purpose, it can be used as many times as necessary. PoxClean contains the ingredient 2QR, a biologically active antibacterial complex. This component helps your child's natural skin immunity to block harmful bacteria. The antibacterial component in PoxClean is a polysaccharide obtained from the plant extract of Aloe Vera. It creates a barrier on the skin, thereby preventing the penetration and spread of bacteria on the surface of the skin. from 272
5.0 1 review
342
- Like
- Write a review
When to see a doctor?
If you suspect that you or your child has chickenpox, consult your doctor. The doctor will be able to make a diagnosis simply by examining you, studying the elements of the rash and accompanying symptoms. Your doctor may also prescribe medications to reduce the severity of chickenpox and reduce the risk of complications, if necessary. Call the pediatrician in advance and warn that you suspect chickenpox - the doctor will see you in a separate room, without waiting in line, to avoid the risk of infecting other patients.
Also, be sure to tell your doctor if you have any of these complications:
- The rash has spread to one or both eyes.
- The skin around some parts of the rash becomes very red, hot, or painful, indicating a secondary bacterial skin infection.
- The rash is accompanied by dizziness, disorientation, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, tremors (shaking hands), loss of muscle coordination, increasing cough, vomiting, difficulty bending the head forward, or a fever above 39.4 C.
- a history of any immunodeficiency, or age younger than 6 months.
Features of the newborn's body
In babies, the body has many characteristics, since it is still actively developing and adapting to new conditions. Chickenpox in newborns is a rare occurrence. Why?
The child’s own immune system is still weak. But all the necessary antibodies that will cope with pathogens of a variety of diseases come to him through mother's milk. It is known that milk has such a protective function for the first six months, and at approximately 6 months the baby’s body begins to independently fight microbes.
How to treat chickenpox
Chickenpox is a virus. And, like most viruses, there is no specific treatment for it. Helping a sick person comes down to alleviating the main symptoms.
Fever and headache
Remember: paracetamol and nothing else! Popular painkillers and antipyretics based on ibuprofen should not be taken. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of serious skin and soft tissue complications in patients with chickenpox or herpes zoster have been reported to indicate that ibuprofen for chickenpox increases the incidence of complications such as skin infections.
Aspirin is completely contraindicated. In conjunction with the varicella-zoster virus, it has a powerful toxic effect on the liver and brain (the so-called Reye's syndrome).
Itching
To relieve itching, your doctor may recommend an antihistamine. Considering the insidiousness of the virus, under no circumstances prescribe it to yourself!
You can also treat your skin with calamine lotion according to the instructions.
Scratches and wounds
To avoid scratching the skin and causing infection in the wounds:
- Trim your nails as short as possible. If your baby is sick, put on thin protective gloves.
- Wear clean, loose clothing.
- Change your underwear and bed linen more often.
It is not necessary to smear the rashes with brilliant green: brilliant green will not speed up the maturation of the blisters. The color only helps to mark pimples in order to track the moment when new ones stop appearing.
Soreness in the mouth
If there are rashes on the oral mucosa, doctors recommend eating sugar-free popsicles. The cold will help relieve discomfort. Also try not to eat salty and spicy foods.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is not officially recognized by medicine, but has the right to exist.
- Immunity can be supported with a tincture of chamomile flowers, calendula, basil leaves and lemon balm. For the same purpose, you can use a mixture of lemon juice and honey, which should be taken three times a day, 1 tsp.
- To reduce pain and itching on the skin, use a soda solution (1 glass of warm water, 1 teaspoon of soda), which is used to dip the affected areas.
- Baths with chamomile or calendula, celandine remove the manifestations of chickenpox.
- At elevated temperatures and if you have a headache, viburnum drink, sea buckthorn tea, rosehip infusion and cranberry juice help well.
- At home, you can brew chopped parsley leaves and drink 1-4 glasses several times a day.
- Those who do not tolerate the acute period of intoxication well can try fresh celery juice.
- Skin itching and pain disappear perfectly under the influence of tea tree oil, applied directly to the elements of the rash.
- Blueberries have an excellent antiviral effect in any form.
Traditional methods do not replace qualified medical care and taking medications prescribed by a doctor.
What complications can occur with chickenpox?
The disease is usually mild, but complications may occur, including bacterial infections (eg, bacterial skin lesions, pneumonia) and neurological infections (eg, encephalitis, meningitis, myelitis), which can be fatal.
Secondary bacterial skin infections, which are caused by streptococcus or staphylococcus, are the most common cause of hospitalization and outpatient medical visits. Secondary infection with invasive group A streptococci can cause abscesses and cellulitis.
Pneumonia after chickenpox is usually viral, but can also be bacterial. Secondary bacterial pneumonia is more common in children under 1 year of age. It is characterized by an increase in temperature up to 40⁰C, an increase in pallor and cyanosis of the skin, the appearance of a substernal dry cough and shortness of breath. Patients can take a forced position in bed.
Damage to the central nervous system in chickenpox ranges from aseptic meningitis to encephalitis. Cerebellar involvement followed by cerebellar ataxia is the most common presentation of central nervous system disorders but usually has a positive outcome.
Encephalitis is one of the most dangerous complications of chickenpox (10-20% of cases are fatal). This complication manifests itself as headache, nausea, vomiting, convulsions and often leads to coma. Diffuse brain involvement is more common in adults than in children. Chickenpox meningitis may occur together with encephalitis or independently.
Rare complications of chickenpox include Guillain-Barré syndrome, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhagic and bullous chickenpox, glomerulonephritis, myocarditis, arthritis, orchitis, uveitis, iritis and hepatitis.
Once infected, the virus remains hidden in nerve cells and can be reactivated, causing a secondary infection, herpes zoster. It usually occurs in adults over the age of 50 or with a weakened immune system and is associated with a painful rash that can cause permanent nerve damage.
Chickenpox and pregnancy
A special type of complications from chickenpox can occur in pregnant women. Chickenpox in early pregnancy can lead to a variety of problems in the newborn, including low birth weight and birth defects such as limb abnormalities. A particularly great threat to the child occurs when the mother gets chickenpox a week before giving birth. In this situation, there is a high risk of infection that is life-threatening to the newborn (congenital chickenpox syndrome).
If you are pregnant and have been in contact with someone who has chickenpox, be sure to talk to your doctor about the risks to you and your unborn baby.
Is it worth getting vaccinated?
Doctors began vaccinating children against chickenpox relatively recently. The composition of the vaccine is represented by live but weakened pathogens. The first vaccination is usually given at 12–14 months. The chickenpox vaccine is re-administered after 3 to 5 years. Adolescents and adults who do not have natural immunity are vaccinated twice, with an interval of 1 month or more between injections.
Young children tolerate chickenpox vaccinations well, and pediatricians do not record any adverse reactions. However, if the child is part of a group of frequently ill children, it is necessary to consult with the local pediatrician about the advisability of vaccination. A weakened body may react to vaccination with unpredictable phenomena.
Is it possible to wash yourself if you have chickenpox?
“Is it possible to swim if you have chickenpox?” is an age-old question parents ask their pediatrician. The answer depends on the patient’s well-being. In general, bathing with chickenpox is not only safe, but even beneficial - keeping the skin clean reduces the risk of secondary infection and promotes faster healing. However, at high body temperatures, it is better to refrain from water treatments and limit yourself to treating the rash elements with antiseptics.
If you have chickenpox, you can bathe in a weak solution of potassium permanganate or with herbal decoctions, but it is better to refrain from using cosmetics (shower gels and even soap). It is also undesirable to use washcloths and towels, as they can injure the skin.
Calamine
Calamine topical lotion is based on zinc and calamine oxide. The medicine for chickenpox relieves itching, irritation and inflammation well, and works as an antiseptic. “Calamine” is also as harmless as possible, but is not suitable for those who have individual sensitivity to zinc.
Calamine
The drug Calamine lotion is used in dermatological practice, in the treatment of diseases accompanied by itchy skin.
Therefore, the lotion is prescribed for the complex treatment of chickenpox, eczema, and psoriasis. Used for dermatitis, acne, herpes. Used in the treatment of skin rashes, herpes zoster, urticaria, rubella, etc. from 225
794
- Like
- Write a review