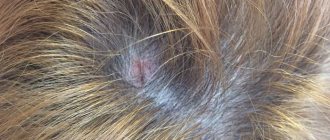
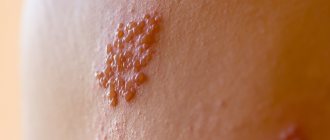
Types of pemphigus
People distinguish between true pemphigus (pemphigus) and other blisters on the skin. The true one is of the following types:
- ordinary, or vulgar - occurs most often. Externally intact and undamaged skin becomes covered with blisters with serous fluid inside, which burst easily and quickly and heal. Localization - the mouth area and the mucous membrane of the lips, as well as the nasolabial triangle. At first glance, harmless bubbles appear more and more often, each time occupying a larger area throughout the body. When they burst, they leave pink eczema in this place. The child should begin receiving adequate therapy between 6 months and 2 years. Otherwise, there is a danger of death;
- vegetative - the course of the disease differs from the usual type only in the consequences on the skin. In this case, instead of eczema, vegetation papillomas of a grayish tint remain. These papillomas are growing;
- leaf-shaped - got its name due to the visual appearance of the crusts formed after the bursting of bubbles. A distinctive feature of this species is the rapid development of pathology. In this case, the count is not in months, but in days. In this case, the skin peels off in whole pieces shaped like leaves;
- erythematous - is a complication after leaf-shaped and has no striking differences from the previous form of pathology;
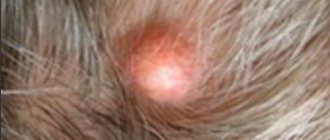
- seborrheic - originates in the hair on the head and face. Small bubbles quickly become a yellowish crust. The progression of the pathology is slow, affecting the back, abdomen and limbs. After peeling off the crust, weeping eczema remains.
There are other types of pemphigus that are not related to pemphigus:
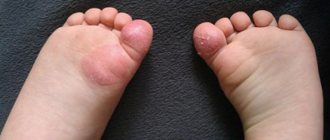
- infectious viral pemphigus in children - develops under the influence of viruses: Coxsackie, enterovirus 71. In this case, the latter option may have the nature of an epidemic. It has specific localization sites - feet and palms, butt and genitals;
- congenital syphilis - occurs when there is intrauterine infection with syphilis. It appears within a couple of days after birth. The blisters burst quickly and leave behind weeping pink eczema.
Untrue types of pathology in medicine refer to the symptoms of pemphigus in children. This course of the disease allows for faster and more correct treatment of pemphigus in children, aimed at eliminating the root cause. The most difficult thing in this pathology is establishing the true cause of the disease.
A rare but severe type of true pemphigus is the paratumor type. It has the most striking symptoms. It occurs against the background of leukemia and lymphoma, and also appears as a harbinger of the development of a malignant tumor.
Mechanism of bubble formation
Pemphigus is a disease in adults, a photo of which will help in home diagnosis and will force a person to go to the hospital for examination. The pathology primarily affects the oral cavity.
Blisters form, then they burst open and painful ulcers remain in their place. The rash then affects the skin, spreading rapidly. After opening the blisters, weeping or ulcers remain, covered with a crust on top. The risk of infection in open wounds increases.
Causes of occurrence and development
The pathology begins its development after the development of autoimmune antibodies aggressive to desmoglein proteins. These proteins act as an adhesive base used to connect skin cells. In the process of protein destruction, the skin is destroyed. At this point, bacteria from the environment begin to penetrate the skin layers, causing the formation of blisters.
The factors that trigger the pathological process still remain unclear. Some of them are established by science:
- genetic predisposition to autoimmune processes;
- malfunctions of the central nervous system;
- the presence of viruses, infections or other pathogens in the body - a connection has been identified between infection with endogenous bacteria and the appearance of an autoimmune reaction.
Russian official medicine identifies the following reasons causing an inadequate immune response:
- taking medications of the thiol group - strong antibiotics, immunomodulators and others;
- burns;
- herpes virus types 1, 2 and 8;
- tactile contact with pesticides;
- severe stress or nervous overload.
It is almost impossible to establish the true cause of the disease. In fact, in laboratory conditions only the presence of aggressive antibodies is determined.
Prognosis for patients
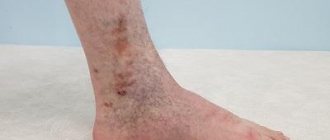
Pemphigoid is a benign skin disease, and therefore in most cases it is not too severe. Moreover, almost any hospital in a large city successfully treats a disease under such a complex name - bullous pemphigoid. In Orenburg, Moscow and any other city you will definitely find a good specialist. The cost of therapy will depend on the place of residence, since the prices for certain medications at different pharmacies vary.
With proper treatment, stable remission can be achieved. From time to time, some patients experience relapses, which, of course, is unpleasant, but not fatal. On the other hand, in the absence of therapy, the site of rash formation can become a gateway for infection, which, accordingly, ends in a more massive inflammatory process, suppuration of wounds, and penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the deeper layers of the skin.
Symptoms and signs
The early stages of the disease have virtually no dangerous signs. The child’s health remains normal, and skin changes have not yet appeared. The condition worsens as the area of the affected skin gradually increases.
The bubbles themselves have a number of distinctive features - lethargy, easy to open, sagging skin under the liquid inside the bubble. Primary rashes are always localized in the mouth and mucous membranes of the lips. There are no painful sensations. Opened blisters form skin crusts or wet eczema, which take a long time to heal.
Gradually the affected area increases. Infection with bacteria leads to the appearance of suppuration and foci of inflammation, in place of which eczema and large erosions subsequently appear. Another distinctive feature is the lack of healing of the skin at the site of the blister rupture. Gradually, the erosions expand and unite into a single lesion.
All forms of pemphigus have a wave-like manifestation of symptoms. In the absence of a timely response, intoxication syndrome begins - nausea and headaches. Ultimately, the death of the little patient inevitably occurs. Viral pemphigus in children has symptoms similar to the true disease, and there is a pronounced viral infection.
When to see a doctor
Baby rash appears frequently and rarely poses a real threat to the child's life. Basically it becomes a reactive feature to allergens and infections. It is important for parents to know which rashes pose a mortal danger to the child. If signs of such a rash appear, you should seek help from a dermatologist.
The pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) has been guarding children's health for many years. You can make an appointment with a dermatovenerologist by phone. The clinic has a convenient location, a two-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station, as well as the possibility of placement in a hospital for examination and treatment.
Dispensary observation
Treatment for pemphigus should begin as soon as the first symptoms appear. All patients are advised to undergo clinical observation and take systematic medications. Timely therapy reduces the risk of disease progression and allows you to bring it under control.
Diagnosis, treatment and observation are carried out around the clock in a hospital setting. By monitoring the patient’s condition, the dermatologist assesses the dynamics of the pathology and adjusts the therapy.
Prevention and prognosis
Medicine has not proposed any specific measures to prevent pemphigus due to the fact that the true causes of its occurrence have not been established. A set of preventive measures is aimed at strengthening the health of a little person:
- formation of strong immunity;
- hardening and walking in the fresh air from the moment of birth;
- proper nutrition;
- avoidance of excessive use of drugs and medications.
Forecasts depend on the speed of contacting a doctor - for symptoms of pemphigus in children, treatment should begin as early as possible. Therefore, you should not self-medicate under any circumstances. In order not to miss the appearance of signs of pathology, it is necessary to examine any skin problems with a dermatologist.
The prognosis of true pemphigus is a priori conditionally unfavorable. Even with adequate and timely treatment, the likelihood of death cannot be eliminated. Any form of pathology is considered chronic.
At the same time, the introduction of hormonal drugs into therapy made it possible to reduce the mortality rate from 65% to 7%. The disease requires constant maintenance therapy. Otherwise, 91% of cases experience acute exacerbations and sudden progression, and consequently an increase in the likelihood of death.
Forecast
The prognosis for acantholytic pemphigus is conditionally unfavorable. On the one hand, in the absence of effective treatment, there is a high probability of complications and death.
On the other hand, patients with pemphigus are forced to take glucocorticosteroids for a long time, and sometimes for life, which is fraught with the development of side effects. But hasty refusal of drugs leads to immediate relapse of the disease. Glucocorticosteroids do not eliminate the cause of the disease, but inhibit the pathological process and prevent its progression.
Diagnostics
This pathology is rare, and pediatricians, as a rule, cannot determine it accurately. Therefore, the primary stage of diagnosis is the distinction between pemphigus and other dermatological diseases that are accompanied by rashes of blisters and blisters.
Differential diagnosis is carried out using a special method - Nikolsky's test. The essence of the test is to rub the skin near the bubble and on a distant area of the skin, as well as pressing the fingertip on the bubble. A positive result is considered to be the presence of signs of skin separation:
- spreading of serous fluid into adjacent layers of skin when pressed;
- slight peeling of the skin in the form of a ribbon when you gently pull the skin over the bubble - similar to a sunburn;
- friction on a healthy area shows the mixing of the upper layers of the epidermis.
One of the most informative diagnostic methods is a blood test for the presence of aggressive antibodies to the desmoglein protein. If these antibodies are present, a diagnosis of pemphigus is made.
Additionally, the following may be assigned:
- cytological studies of serous fluid samples from the bottom of the erosion or from the bladder;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- chest x-ray;
- consultations with related doctors - nephrologist, cardiologist, infectious disease specialist.
Preventive measures
There are no specific measures to prevent the development of pathology. The higher the level of immune protection, the less chance of dermatological diseases.
Important:
- control the nature of chronic diseases;
- strengthen immunity;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- Healthy food.
Measures to prevent pemphigus in newborns:
- change your underwear more often;
- Caring for newborns with pustular skin lesions is prohibited;
- Take regular care of your child’s skin;
- strengthen the immune system of weakened children;
- daily wet cleaning and ventilation of the room are required.
If you notice any rashes on the skin, the formation of pustules and blisters, immediately contact a dermatologist.
Treatment
How to treat pemphigus in a child? The main drugs today are hormones from the group of glucosteroids. In this case, systemic therapy is carried out without age restrictions.
Treatment of pemphigus has several main directions:
- preventing the appearance of new blisters and erosions;
- healing of affected areas of the skin.
Glucosteroids are administered in increased dosages. Due to this technique, the intensity of the formation of new foci decreases and the restoration process begins in existing erosions. This process takes about 2 weeks. Subsequently, the patient is transferred to maintenance hormonal therapy. The drug does not change, but the dosage is significantly reduced.
Viral pemphigus in children treatment is aimed at suppressing the virus. Pemphigus vulgaris requires the administration of a larger volume of drugs than foliaceus. The transition to maintenance therapy is carried out gradually. Moreover, the vast majority of patients are forced to take daily injections of maintenance doses of glucosteroid drugs throughout their lives.
Children should take hormonal medications simultaneously with calcium and vitamin D. The effectiveness of treatment increases due to the use of immunosuppressive drugs from the first days of treatment. These drugs have a depressing effect on the activity of the body's immune system.
Early stages of treatment often involve the use of procedures aimed at clearing the blood of aggressive antibodies. Such procedures include hemodialysis and plasmapheresis. The skin must be treated with antiseptics and special ointments to reduce the risk of infection.
Treatment of pathology is daily and lifelong. Sometimes there may be breaks between relapses of the disease.
Baby care
The diagnosis of pemphigus requires special, attentive and daily care for the child. The organization of a baby’s life directly affects his life expectancy. The initial stage of treatment takes place within the walls of the hospital. After discharge, the child should receive all necessary medications in the prescribed volume and time of administration. Parents must learn how to give injections, because the daily services of a hired nurse will negatively affect the family budget.
Every day your child needs to treat blisters and eczema on the skin. Processing is carried out using aniline dyes. This group of agents has the widest spectrum of action on various microbes, including staphylococcus. Erosion and crusts formed are treated with corticosteroid-based ointments.
The presence of infectious signs in the form of pus, inflammation, swelling means the start of using antibiotic ointments. Large affected areas require the use of sterile dressings to help avoid further injury. Dressings are changed at least 2 times a day. For small affected areas, the relevance of bandages is associated with the child’s high motor activity.
The appearance of pain requires taking painkillers and consulting a specialist. The presence of damaged areas in the oral cavity is associated with mandatory rinsing of the mouth with antiseptic agents. A useful and effective means of care is taking baths with antiseptic agents. It is mandatory to take vitamin and mineral complexes consisting of vitamin E, calcium, magnesium and folic acid.
The diet also requires enrichment with vitamins and minerals. Meals are provided on a fractional and frequent basis, at least 6 times a day. This diet plan is especially important when the esophagus and mucous membranes in the mouth are affected. Diet therapy is based on the complete exclusion of salt and increasing the amount of protein. Registration at a dispensary and systematic visits to a dermatologist are required - at least twice a year and urgently in case of relapse. The use of immunosuppressive therapy imposes restrictions on vaccinations.
Some similar diseases
It is worth noting that bullous pemphigoid belongs to the group of so-called blistering dermatoses. These ailments differ from true pemphigus because they are not accompanied by acantholysis. The group of skin lesions includes several other ailments, the clinical picture of which is quite similar:
- Benign non-acantholytic pemphigus, in which the disease affects exclusively the mucous membrane of the mouth, without causing a rash in other areas. The disease is also characterized by a benign course. By the way, it was first described in 1959.
- Cicatricial pemphigoid is a rather dangerous disease that affects the mucous membrane of the eyes and conjunctiva, causing its atrophy. Rashes on the body are possible, but are observed relatively rarely. The main risk group is women over 50 years of age, although sometimes the disease is also registered among male patients.
Complications
Pemphigus has an unpredictable course, often becoming chronic and resistant to therapy. Pemphigus vulgaris sometimes leads to the development of a secondary infection: encephalitis, meningitis, pneumonia, damage to the heart and joints. Dermatosis of newborns is dangerous due to the possibility of sepsis.
Local complications are non-healing suppurating erosions and ulcers, chronic infections of the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract.
The disease, which occurs in a severe form, requires the use of potent medications. Due to the need for long-term hormone therapy, the following problems arise:
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- diabetes;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestines;
- arterial hypertension;
- osteoporosis;
- mental disorders;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Routes of transmission
This type of viral disease can be contracted in almost any public place.
The most common methods of infection with viral pemphigus are:
- Airborne droplets - most often when visiting public places such as kindergartens and schools;
- Through contact with household items that have previously been touched by an infected person.
Thus, it should be noted that short-term contact of a healthy child with an infected person can cause infection with viral pemphigus.
Children especially often become infected with viral pemphigus in the absence of necessary food processing and failure to wash their hands after visiting the street.