Fungal diseases of the skin of the feet and nails in children often cause panic among young parents who are faced with a similar problem for the first time.
By missing the first symptomatic manifestations of the disease, you can allow the active development of the pathology, which is why the disease will remain with the child for the rest of his life.
To prevent complications and undesirable consequences, experts recommend preventing fungus , and in case of infection, prescribe effective treatment.
general description
Mycosis of the feet is a dermatological disease caused by dermatophytes, molds or yeasts. The pathology has a number of characteristic signs that cause significant discomfort to the small patient, and in the absence of proper treatment can be complicated by severe skin lesions or bacterial infection.
Unlike adults, children are more susceptible to mycosis, since their immunity is not sufficiently developed, and the skin on the legs is too thin and delicate, which allows fungi to easily penetrate the body and multiply.
Important!
According to many doctors, children's skin is ideal for the rapid proliferation of fungi that love a warm and humid environment. In addition, newborns can also become infected if the woman did not have time to get rid of thrush at the time of birth.
Classification of candidiasis
Candidiasis can be acute or chronic.
According to the clinical course: According to the clinical course:
- pseudomembranous.
- atrophic.
- hypertrophic.
- erosive-ulcerative3.
By location:
- Stomatitis is a disease of the oral mucosa.
- Cheilitis is a lesion of the lips, with the lips being dry and covered with cracks. All lips, as well as just the corners of the lips (jams) can be affected.
- Gingivitis – the gums are affected and tend to bleed when brushed.
- Glossitis is a disease of the tongue.
Forms
Before you begin to treat the fungus, it is important to determine its form. There are 4 varieties - they differ from each other in the localization of the fungus and the depth of tissue damage.
Interdigital
With the interdigital or intertriginous form of mycosis, the skin between the toes begins to peel off and become covered with cracks. At the same time, the skin becomes red, dry and thickened , and the nails become brittle. The child may complain of constant itching and burning.
"Athlete's foot"
The skin becomes rough and covered with a powdery coating, the nails lose their natural color, are shaped like a bird's beak and acquire a yellowish or brown tint. Scaly circles form on the foot, which is accompanied by itching.
Vesicular
Small blisters containing pathogenic exudate form on the skin. When scratched, the bubbles burst and the liquid spreads over healthy areas. The danger of the disease lies in the possibility of a secondary infection, which is why the disease can become chronic, affecting the lower leg and knee.
Mixed
At the initial stage, the fungus is not identified, hiding between the fingers, but over time, the patient experiences deformation of the nail plate, a rash and swelling appear.
Candidiasis (thrush) in children
The following forms of thrush are distinguished:
- Thrush of the mucous membranes (oral cavity, tongue, gums, pharynx, tonsils, trachea, larynx, red border of the lips, corners of the mouth, teeth, vagina, vulva).
- Thrush of the skin and its appendages.
- Thrush is visceral, systemic.
- Allergic manifestations of thrush in children.
Candida infection most often manifests itself as thrush . It most often affects newborns, infants and preschoolers. The main symptom is curdled white deposits on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, gums, and palate. The overlays are initially located pointwise and then merged. Easy to remove. If treatment is not carried out in time, the overlays become denser and become grayish-dirty in color, they are increasingly difficult to remove, and the mucous membrane bleeds after removing the overlays. The general condition is not significantly disturbed if the children in the first days of life are not sick with anything else.
If the infection affects the mucous membrane of the tongue, then not only fungal overlays appear, but also areas without papillae. Swelling of the tongue, focal hyperemia and striations with furrows are recorded. The tongue becomes more sensitive to spicy and hot foods. Patients may complain of a burning sensation and dry mouth. It is difficult for infants to suckle milk, which is why they have difficulty eating.
Candidiasis tonsillitis , as a rule, appears against the background of candidiasis of the oral mucosa. It manifests itself by the appearance of loose whitish deposits on the surface of the tonsils, which can be removed with a spatula without effort. The tissue of the tonsils is practically unchanged. The child's general condition is almost normal. The temperature is elevated only if candidiasis of the tonsils occurs against the background of ARVI.
When diagnosed, fungal tonsillitis is distinguished from localized diphtheria of the pharynx by the absence of fever, the absence of hyperemia of the tonsils, and the normal size of the regional lymph nodes.
Candidiasis infection of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and tonsils can spread to the mucous membrane of the larynx, trachea, and esophagus. In such cases, symptoms such as hoarseness and difficulty breathing appear.
Candidiasis of the corners of the mouth (jam) in children occurs in rare cases. It is recognized by cracks in the corners of the mouth and erosion with perifocal infiltration. Usually both corners of the mouth are affected. The disease is distinguished from streptococcal infection - with it the inflammatory reaction is more pronounced.
Candidiasis of the red border of the lips (in the literature referred to as cheilitis) is often combined with candidiasis of the oral mucosa and erosions of the corners of the mouth. The red border of the lips swells and becomes hyperemic. The patient complains of dryness and burning of the lips. The disease lasts a long time.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis is symptomatically manifested by white discharge. The mucous membrane of the genital organs is moderately hyperemic, with loose cheesy deposits of a whitish or grayish tint visible on it. Rarely does it have superficial erosions. Overlays can be found in some cases on the vaginal mucosa and cervix. The external genitalia are very itchy and there is a burning sensation.
Intertriginous candidiasis occurs most often in infants in the area of large skin folds. The skin is hyperemic or eroded, and maceration of the stratum corneum is observed on it.
Smooth skin candidiasis in infants occurs mainly as a result of the spread of intertriginous candidiasis from skin folds. Candidiasis of the scalp is rare in children .
Chronic generalized granulomatous candidiasis is typical for children who are malnourished, suffer from gastrointestinal disorders, and bronchitis. The disease begins with oral thrush, then the process causes glossitis, cheilitis and seizures, which are treated poorly and ineffectively. In many cases, deep dental caries develops. The process subsequently affects the skin on the face and under the hair, and later on the torso, arms and legs. The appearance of hyperemic spots with a bluish tint, with infiltration and superficial peeling is recorded. These epidermal lesions gradually become granulomatous. Papules and tubercles appear, many of which are covered with a yellow-brown crust, under which papillomatous growths form. In almost all cases, the disease affects the nails and nail folds.
Microscopy results show the presence of yeast-like fungi in the urine and feces, and in some cases in the blood. Serological reactions in all sick children are positive.
In recent years, visceral candidiasis most often manifests itself as pulmonary candidiasis, which appears as a result of long-term therapy with antibiotics that were prescribed incorrectly. Pulmonary candidiasis manifests itself with a variety of symptoms. The disease can be acute or take a protracted, chronic nature. Relapses and exacerbations are possible.
Abscessing and cavernous forms of candidiasis pneumonia, pleurisy, which are difficult to distinguish from tuberculosis based on symptoms and radiographs, have been recorded in the literature.
Gastrointestinal candidiasis is distinguished by the fact that the deposits are abundant, sometimes completely fungal, they can cover the entire mucous membrane of the esophagus. Symptoms such as progressive dysphagia and the inability to swallow food are noted. Babies stop reaching for their mother's breasts and vomit. In especially severe cases of the disease, due to the massiveness of the deposits on the esophagus, its lumen may narrow, or even obstruction may occur. Histologically, deep destruction of the esophagus is revealed. In most cases, damage to the esophagus is also accompanied by thrush of the oral mucosa, which provides clues to diagnosticians.
Gastric candidiasis is a rare disease in children. It can only be detected by obtaining histological examination data. On the affected part of the stomach, hyperemia of the mucous membrane and small erosions are noted. Typical overlays, as with thrush, are quite rare.
With intestinal candidiasis, symptoms of enterocolitis or colitis, intestinal colic, and bloating are recorded. The stool is watery and may contain blood. The disease lasts a long time, there are relapses.
Damage to the urinary tract by Candida fungi manifests itself as urethritis, pyelitis, cysts, nephritis.
Generalized candidiasis in children can lead to endocarditis with damage to the heart valves or meningitis and meningoencephalitis, which is typical mainly for infants and preschoolers. With candidiasis meningitis, mild meningeal symptoms and a slight increase in temperature are observed. The disease progresses sluggishly, torpidly, and relapses are possible.
The most severe manifestation of candidal infection is candidal sepsis . This form of the disease occurs mainly in babies from 0 to 6 months. Before the disease, as a rule, there is another serious illness or microbial sepsis, which is complicated by an associated superinfection with the Candida fungus.
Candidiasis can spread through the oral mucosa to the esophagus, intestines or to the larynx, bronchi and lungs and end in sepsis . Also from the oral mucosa, Candida can spread through the blood. The symptoms of candidal sepsis are almost similar to ordinary bacterial sepsis. Diagnosis is made by isolating Candida from the blood of a sick child.
Causes
Dermatologists identify a number of external and internal factors that can provoke the development of a pathological process due to the penetration of a fungal infection into the child’s body. These include:
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- close contact with an infected patient;
- wearing shoes that are not yours or made from synthetic materials;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- skin damage in the form of scratches, abrasions, or calluses;
- visiting public playrooms without slippers or socks;
- vascular pathologies of the lower extremities;
- long stay in a humid environment;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- hereditary predisposition;
- poor diet and lack of vitamins;
- changes in hormonal levels.
Important!
The development of the disease is also caused by frequent stress, so parents need to monitor the emotional state of the baby.
Why do children get nail fungus?
Onychomycosis is considered an age-related infection and is more common in older people.
In childhood, the risks of its development are minimal due to:
- rapid growth of the nail plate;
- small surface area;
- absence of chronic diseases leading to malnutrition and blood supply to the extremities;
- coordinated work of local protective mechanisms.
Fungus in a child under 2 years of age is rare, but sometimes it occurs even in newborns. In infants, its appearance on the hands provokes a “predilection” to keep their fingers in the mouth during teething. Warmth and moisture create favorable conditions for the growth of a fungal colony on a thin, soft nail plate.
Most often, nail fungus is found in children aged 3 years and older. This is due to visiting kindergartens and clubs, where pupils are in close contact with each other and can transmit the infection. The risk group includes premature babies, babies with Down syndrome, decreased activity of the immune system (immunodeficiency). Due to poor health, such children have a much higher risk of developing onychomycosis.
In 70–80% of cases, the infection is transmitted from parents or relatives who are in close contact with the baby.
The following also contribute to infection:
- walking barefoot in swimming pools, public showers, locker rooms, water parks;
- trying on someone else's shoes, socks, tights;
- wearing shoes made of non-natural materials that do not allow air to pass through, causing excessive sweating;
- wounds, cuts, abrasions on the skin through which fungal spores easily penetrate the skin;
- improper nail care;
- frequent contact with soil, for example, among children living in rural areas;
- excess amount of sweets in the diet.
As in adults, children develop nail fungus on their hands much less frequently than on their toes.
Signs and symptoms of the disease
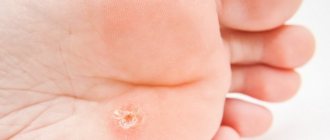
Any form of mycosis of the feet in children is characterized by the following:
- severe itching and burning in the affected area;
- swelling and redness of the skin;
- focal increase in temperature;
- peeling and small scales;
- thickening and roughening of the skin;
- sores, cracks, or blisters between the fingers;
- unhealthy shade and roughness of the nail plate;
- unpleasant smell.
Important!
If one or more symptoms of mycosis are detected, you should immediately consult a dermatologist.
What is foot fungus
Foot fungus is a form of mycosis in which the causative agent of the pathology affects the epidermis of the foot, and in the absence of qualified and timely therapy, spreads to the nails, as well as to other parts of the body. The occurrence of pathology is provoked by infection of the epidermis with various types of fungus.
When certain conditions are created, pathogens can parasitize inside the body, as well as on the skin and nail plates. As a result of the activity of these harmful microorganisms, local and systemic pathologies arise.
The disease is characterized by a structural change in the epidermis. The symptoms of the disease depend on the type of fungus. Common symptoms are itching of the epidermis, peeling, and keratinization of the skin.
At the first signs of foot fungus, it is recommended to consult a specialist. Timely and correct therapy will help get rid of the pathology in a short period.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
To successfully treat the fungus, the patient needs to consult a doctor - he will conduct a visual examination, carefully examining the lesions. Laboratory tests will help determine the type of pathogen.
- Bakposev - the collected biological material is placed in a nutrient medium. If the scraping contains pathogenic microorganisms and growing fungal colonies, the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed.
- Enzyme immunoassay - blood is taken from the patient’s vein to detect antibodies to a specific pathogen.
- Microscopy – the sample taken is processed with special preparations and examined under a microscope.
- Polymerase chain reaction - allows you to determine the type of fungus by identifying the DNA of the pathogen. To conduct the study, a scraping from the affected area is required.
How to treat?
The treatment regimen and choice of medications depend on the form of the disease diagnosed by the doctor. To prescribe the correct treatment, the dermatologist takes into account the test results , the body weight and age of the child, as well as possible contraindications and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Drug treatment
Depending on the form and stage of the disease, a small patient may be prescribed systemic medications in tablet form and the use of antifungal ointments that can eliminate the unpleasant manifestations of the pathology.
Systemic drugs
The most popular systemic drugs intended to treat fungus are:
- Terbinafine - the drug belongs to the group of allylamines that destroy fungi at the genetic level. The medication gets rid of pathogens and accelerates skin regeneration.
- Nimzoral - changes the composition of fungal cell membranes and stops their growth. The drug has a number of contraindications, so before you start taking it you need to make sure that they are absent.
For topical use
At the initial stage of the disease, you can get rid of the fungus using ointments and creams for external use. Showed themselves well in the treatment of mycosis:
- Exoderil is a cream that has a powerful bactericidal and fungicidal effect. The product quickly eliminates the symptoms of the disease and is used at any stage of mycosis.
- Miconazole is an anti-inflammatory drug that destroys fungal pathogens by suppressing the synthesis of ergosterol in the cell membrane.
- Clotrimazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal ointment. The active components of the drug disrupt the synthesis of cell membranes, as a result of which fungal cells are destroyed.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are sometimes used to treat children from fungal diseases:
- electrophoresis - exposure to constant electrical impulses to provide a local therapeutic effect;
- Darsonvalization is a technique of applying high-frequency pulsed currents to the affected areas of the skin;
- pulsed magnetic therapy – the use of pulsed magnetic fields of varying frequencies and intensities.
Folk remedies
Using proven folk remedies as additional therapy, you can speed up the healing process and get rid of discomfort. However, before using alternative treatments, you should consult a dermatologist.
Ointments
Homemade garlic ointment will help eliminate the fungus. To do this, mix garlic with butter in a 1:1 ratio and apply the product to the skin for 30–40 minutes. The ointment should be used with caution, as it is considered quite aggressive.
Compresses, rubbing, lotions
Compresses and lotions with herbal decoctions are ideal for treating complex forms of the disease . To prepare the medicine, you need to mix 1 tbsp. l. dried flowers of calendula, verbena and oak bark.
Pour 500 ml of water into a container with dry ingredients and cook for 20 minutes over medium heat. Cool the resulting liquid, strain and apply lotions 2-3 times a day.
Treatment with soda
Baking soda is an affordable and safe product for children that copes with fungus no worse than pharmaceutical drugs. To eliminate the symptoms of mycosis and improve the condition of the skin, it is enough to combine 1 tbsp. l. soda with a small amount of water until you get a paste. The mixture should be applied to the affected areas in a thick layer for 10 minutes, then rinsed with warm water and wipe your feet dry.
Toe baths
Dissolve 3 tbsp in 3 liters of warm water. l. baking soda and salt. Immerse your feet in the liquid and keep them in the medicinal solution for at least 15 minutes. After the specified time has passed, rinse your feet well with clean water and dry them.
Consequences of lack of treatment
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease, lack of treatment or untimely initiation of therapy threatens the young patient with such negative consequences as:
- disruption of the regeneration process of the epidermis;
- lymphostasis and suppuration in case of bacterial infection;
- formation of large calluses;
- loss of the nail plate;
- allergic reaction of the skin and mucous membranes;
- exacerbation of existing dermatological diseases.
Important!
The prolonged course of the disease leads to the spread of the fungus to the nails, hands and skin of the entire body.
Causes of fungal infection
A healthy nail is able to resist the penetration of pathogenic fungi. Infection occurs through contact with a carrier, using shared hygiene items, or visiting public places, especially with high humidity. Factors that weaken local and general protective forces are the following:
- past infectious diseases: mononucleosis, tonsillitis, herpes, etc.;
- long-term antibacterial therapy;
- injuries to the nail plate and periungual folds, including ingrown nails;
- flat feet;
- corns and calluses are entry points for infection;
- increased sweating;
- previous operations;
- lack of vitamins and minerals, poor diet.
Fungus in the child’s immediate family and/or people living with him is the main cause of the disease.
Prevention
To avoid the penetration of a fungal infection into the child’s body, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Strengthen the baby's immunity by hardening, choosing healthy foods and taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Always dress your child according to the weather, avoiding hypothermia or overheating.
- Avoid items made from synthetic fabrics and wear socks and shoes made from natural materials.
- Make sure that the child does not wear someone else’s shoes, but wears slippers in public places.
- Take care of the skin of your feet and nails using personal hygiene items.
- Periodically take baths with soda solution and after the procedure lubricate the skin with moisturizer.
- Regularly treat insoles with disinfectants and dry them well.
Fungal infection of the skin of the foot is a common disease among young children that requires timely treatment. With the right choice of medications, the pathology will have a favorable outcome, so if you notice the first symptoms of mycosis, you should consult a dermatologist.
The doctor will carry out diagnostic measures and prescribe effective therapy aimed at eliminating unpleasant manifestations and suppressing the mechanisms of disease development.