Make an appointment by phone +7,,
Make an appointment online
A furuncle that occurs in the ear is an inflammation of the hair follicle. An abscess is usually caused by the proliferation of Staphylococcus aureus and causes extremely unpleasant sensations.
The location of the boil can be different: behind the ears or in the ears, in the auricle, on the lobe or inside the ear canal. The most dangerous is considered to be a formation formed in the area of the ear canal. Do not underestimate furunculosis. This is a disease that can have dangerous consequences. If it is not treated in time, serious complications may develop in the form of inflammation of the eardrum and even problems with the membranes of the brain. The most effective method of treatment in such cases is opening the boil of the ear canal.
Causes of a boil in the ear
The reason for the formation of a boil (popularly known as a boil in the ear) is infection by bacteria of the hair follicle of the outer ear and the sebaceous glands located next to it. Most often, inflammation is caused by staphylococci. Other causes of boils are as follows:
- Constant microtrauma to the skin of the external auditory canal (especially when cleaning with chopsticks).
- Prolonged contact with water.
- Constantly wearing headphones (vacuum), hearing aids (not the right size).
- The presence of dermatoses with itchy skin, which lead to scratching of the ear.
- Immunodeficiency conditions, hypovitaminosis, concomitant endocrinological and oncological diseases.
- Frequent stressful situations.
- Concomitant pathologies of the ear - otitis, labyrinthitis, tubo-otitis of various etiologies.
Also, the cause of a boil can be irregular adherence to personal hygiene rules or complete disregard for them.
Clinical picture
The main symptom of the occurrence and development of a boil in the external auditory canal is pain, which can radiate to the eye, neck, teeth, or spread diffusely throughout the head.
It intensifies when talking or chewing, because the head of the mandibular joint is displaced (moved). Pain in the ear intensifies when pressing on the tragus and pulling the auricle upward or backward. In the ear canal you can see a raised area of hyperemic (reddened) skin, which has a rounded shape and narrows its lumen. In some (but rather rare) cases, several boils form at once. It is very difficult to insert the ear funnel into the external auditory canal with severe swelling and inflammation. Infiltration of the skin of the ear canal often extends around the auricle, as well as into the soft tissue of the mastoid process. There is an increase and thickening of regional lymph nodes. When palpated, severe pain is noted. If the boil is located on the front or lower wall of the external auditory canal, then the inflammatory process can spread to the parotid salivary gland, which will lead to its inflammation. Body temperature depends on how severe the intoxication is. In some cases, there is a sharp increase in temperature and chills. When the boil of the external auditory canal matures, it can open on its own. Then the pain decreases, and the patient’s general condition improves significantly. But with such a combination of events, there is a possibility of relapses in the development of the boil.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
What are the symptoms of a boil?
Patients in the initial stages of the pathology complain of burning and itching. Then a pain syndrome occurs, the intensity of which gradually increases. Symptoms of a boil in the ear include bursting, throbbing pain that can radiate to the back of the head, temple, jaw, and sometimes to the neck. In some cases, the symptom manifests itself as diffuse cranialgia. When you press on the tragus, the pain intensifies (as with chewing and swallowing). Palpation on the earlobe is not painful.
Be sure to read:
Causes of boils on the body and proven methods of treating them
Patients complain of severe weakness, increased body temperature to 38 degrees, lack of appetite, inability to carry out any activity, and sleep disturbances. There is also a slight decrease in hearing on the affected side, and an increase in lymph nodes in the neck.
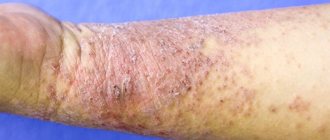
Photo of a boil in the ear.
On average, a week after the onset of symptoms, pus leaks from the boil. As soon as this process begins, patients immediately notice an improvement in their general condition, and pain is also significantly reduced.
Stages of maturation
There are several stages of formation and maturation of the boil. The first begins with itching and complaints from the patient himself about slight discomfort in the affected area. The remaining steps are as follows:
- The appearance of hyperemia and increasing swelling in the tragus area is the infiltrative stage.
- The pain gradually increases and becomes throbbing. This indicates the appearance of purulent discharge. Complaints intensify upon palpation.
- After this, the boil begins to increase in size, and the presence of a small white zone is noted in its center. This is an accumulation of pus. The stage is called purulent-necrotic.
- After opening the boil and clearing the pathological discharge, gradual healing of the skin occurs. Usually there is no scar left in the ear area.
With this pathology there is a risk of complications. Patients may experience otitis media, mastoiditis, and inflammation of the mandibular joint. Hearing loss can occur due to a narrowing of the diameter of the ear canal. Sometimes the accumulation of pus can transform into an abscess.
The most severe complications occur when the pathogen penetrates the meninges (meningitis, encephalitis), as well as when the inflammatory process generalizes - sepsis. These pathologies pose a threat to the patient's life.
Symptoms of the disease
If the boil is located deep in the ear, the patient himself cannot notice it. But the following signs may indicate the presence of a purulent formation:
- pain while swallowing;
- painful sensations in the ear, which can spread to the lower jaw and neck;
- itching, noise in the ear;
- ear congestion.
A boil may also be accompanied by swelling of the lymph nodes located in close proximity to it, nausea, headaches, fever, weakness, drowsiness, and hearing loss.
Diagnostics
The ENT specialist collects the patient’s medical history and analyzes his complaints. After this, an external examination of the ear is performed. Then the doctor proceeds with otoscopy, which allows you to accurately determine the presence of a boil. A general blood and urine test is also necessary, and if pus is present, it is cultured. If differential diagnosis is needed, then radiography or computed tomography of the temporal bones is prescribed.
Be sure to read:
What ointments can be used to treat boils
Causes of an abscess
The main cause of an abscess is the entry of staphylococcus into the open area of the ear (wound, damaged epidermis).
The body fights foreign invasion by confining the bacterium to a limited area - a boil. An inflammatory process begins, due to which a necrotic core appears - dead tissue. In addition to it, pus appears - a product of the death of lymphocytes that participated in the fight against infection.
Staphylococcus infection may be associated with:
- improper hygiene of the ear area, in which a cotton swab or other cleaning object scratches the epidermis;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene (when microcracks appear in the epidermis, which has not been cleaned, bacteria penetrate into the tissue);
- vitamin deficiency, in which peeling occurs;
- the passage in the body of a syndrome such as exudative erythema (severe allergic reaction);
- lack of immunity;
- colds or internal inflammatory disease.
The cause of a boil is significant only if it appears as a consequence of general furunculosis and purulent lesions in the middle ear area. Other lesions that cause an abscess are secondary. When treating, the therapist focuses on the abscess and purulent cap.
Please note: The cause of microcracks and wounds in the skin of the ear can be an allergic reaction. In this case, it is necessary to take antiallergic tablets.
Methods for treating a boil in the ear
As soon as symptoms of a boil appear, local antiseptics should be used and the affected area should be treated with boric alcohol . You can also apply compresses for 10-15 minutes several times a day.
As soon as the boil inside the ear has matured, antibacterial ointments (for example, Levomekol, Tetracycline) or Vishnevsky ointment are applied to it, which speed up the process of opening and cleaning from pus. In addition, antiseptics (the same boric acid) can be used. These procedures will promote rapid cleansing of pus and healing of the skin.
Physiotherapy has a good effect - laser therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, magnetotherapy, and exposure to an electric field.
Treatment of a boil in the ear canal
Conservative and surgical methods can be used to treat the disease. In the first case, broad-spectrum antibiotics, medicinal compresses, antibacterial ointments and other drugs are often prescribed. General restorative measures involve the use of multivitamin complexes, immunostimulants, local drops, injections, and autohemotherapy.
As part of surgical treatment, the furuncle of the ear canal is opened with local anesthesia. Especially if the patient’s condition is extremely painful or the formation threatens complications. This method allows you to quickly and effectively get rid of tissue suppuration and necrotic core.
LDC No. 1 is equipped with modern equipment, and surgical treatment is carried out by experienced doctors in comfortable conditions for patients. Do not try to get rid of a boil yourself if it is located deep in the ear canal. Contact a specialist to prevent complications.
Sign up for ENT, +7, +7, you can also sign up online
Prevention
Preventive measures for the formation of a boil are, first of all, compliance with the rules of personal hygiene and proper cleaning of the ears. You need to pay attention to the condition of the skin in the ear, not to let it crack, peel or dry out.
The second measure necessary for furunculosis is taking a vitamin complex and a correct lifestyle. With poor nutrition, the secretion of toxins through the skin increases, the body more easily catches infections, and the tissues become inflamed. Lack of vitamins leads to cracking of the skin until bloody marks appear. Such phenomena need to be eliminated.
On the street, you need to constantly protect your ears from wind and frostbite, and make sure that there is no pain due to the cool air. Immunity has a significant impact on the patient’s condition and the risk of developing furunculosis. With a low rate, relapses will occur much more often.
Treatment methods for furunculosis
Treatment of a boil can be carried out without the advice of a doctor. You can carry out procedures related to the treatment of growth yourself. But even with home treatment, it is important to remember that therapy must be carried out in strict accordance with the instructions for the drugs. If the patient's condition worsens, professional treatment should be switched to.
If a lump occurs in the ear, at the very beginning of therapy it is necessary to determine what type of treatment the patient needs. There are two options:
- conservative, that is, non-surgical, method;
- surgery of the inflamed area.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment helps those whose condition does not go beyond the norm. A boil in the ear of medium size and with a standard maturation period of 3–5 days does not need to be removed. It should be removed with medication or through procedures.
Before the abscess breaks through, you should take medications aimed at combating pain and inflammation. Conventional analgesics are not suitable: they have too weak an effect. When treating at home, it is recommended to create a mini-first aid kit from the following medications:
- directed against tissue inflammation (Efferalgan or Panadol);
- simple antipyretics in case of fever;
- vitamin complexes for signs of vitamin deficiency.
To relieve pain, it is recommended to do turundas with soothing compounds. After opening the formation and removing the pus, the turundas are soaked in saline solution and inserted into the ear area to dry out the abscess and possible harmful cells that could remain from the pus.
In case of a serious course of the disease, the patient is referred for instrumental treatment. Ultraviolet irradiation, microwave and UHF techniques will help to cope with constant relapses of the boil and overcome a large abscess in the ear.
Antibiotics must be prescribed both internally and externally. Penicillin emulsion is applied to the skin, and other antibiotics are taken orally in tablet form. In extreme cases, two types of injections are prescribed:
- autohematotherapeutic;
- penicillin.
In the first case, the patient’s own blood, taken from a vein, is injected into the muscle tissue.
Surgery
If frequent relapses have been noticed, the boil in the ear has been brewing for more than 5 days or causes severe pain, the therapist prescribes surgical treatment. Under general or local anesthesia, the growth is opened and all contents are removed. After the main procedures, the wound must be treated with alcohol and saline solution.
Surgery can get rid of the abscess in less than an hour. But after surgery, the wound remains open for some time, which is why it can become infected again.
The main symptoms of furunculosis
Symptomatically, inflammation in the ear is similar to many ear diseases. The main sign of the development of an abscess is pain in the ear area. Tears the junction of the auricle and the head. Other symptoms are more specific:
- in the first stages of infection, the skin turns red and purple;
- a whitish growth forms at the location of the wound - a place where pus accumulates;
- inside the formed growth you can see a rod, and also a place where pus will soon burst;
- the patient experiences pain when eating;
- painful sensations intensify when yawning, talking, opening and closing the jaw;
- when touching the area of the ear canal, a sharp unpleasant feeling arises and a desire to urgently remove the hand;
- the lymph nodes located next to the abscess are enlarged;
- insomnia due to pain;
- slight rise in temperature accompanied by chills.
With furunculosis, a complex of symptoms appears. Most often, the inflamed area itches, breaks out, and slowly turns into a mature abscess. Pain and discomfort disappear when development is completed: the abscess bursts, releasing the necrotic core and products of suppuration.