July 5, 2020
Dry patches on the skin are a common dermatological symptom that can indicate either a temporary failure and disruption of the barrier functions of the epidermis, or a skin disease. It all depends on the size of the spots, the clarity of their boundaries, as well as the duration of their presence on the skin.
The causes of dryness can be divided into two large groups:
- nonspecific - allergic reactions to household chemicals, laundry soap, cosmetic products, dehydration due to cold and wind;
- specific - then the spots become a manifestation of dermatological diseases.
Sometimes a person himself may notice that dry spots appear on his skin after a certain event occurs, for example, after washing clothes by hand. Then the reason is obvious and easy to eliminate. But if dry spots on the skin do not go away, they itch, or flake, you should consult a doctor.
Forms and complications of seborrheic dermatitis
There are pediatric and adult forms of seborrheic dermatitis.
Sometimes the disease is associated with psoriasis (seborrheic psoriasis).
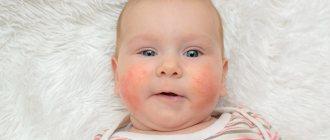
The severity of the disease varies from mild dandruff to severe erythroderma. Dandruff affects the scalp in the hair growth area. In 70% of children, seborrheic dermatitis usually appears by 3 months of age and resolves spontaneously by 6-12 months.
In adults, seborrheic dermatitis begins in adolescence. Predominant in young and elderly people. More often affects men.
What diseases cause itching and flaking of the skin?
There are quite a few diseases accompanied by itching and peeling of the skin of varying degrees of intensity and prevalence:
- allergies to food, medications;
- contact dermatitis;
- seborrhea;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- fungal skin diseases;
- disruption of the sebaceous glands;
- infectious diseases;
- diabetes;
- hormonal disorders;
- thyroid diseases;
- blood diseases;
- parasitic diseases (scabies, demodicosis, etc.).
Causes of the disease
The reasons for the development of the disease are not completely clear. Seborrheic dermatitis is not a disease of the sebaceous glands, although it develops in areas saturated with them.
A significant role in the development of the disease is played by yeast-like fungi of the genus Malassezia (they exist on the skin of most healthy people, but in some they can cause rashes and skin irritation), the composition of lipids on the surface of the skin, as well as the characteristics of the immune response to Malazessia fungi and their metabolic products.
In adults, severe disease is associated with the following conditions:
- oily skin (seborrhea);
- lack of sleep and stress;
- history of seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis in relatives;
- states of immunosuppression (organ transplantation, HIV, lymphoma);
- neurological or psychiatric disease.
The main cause of seborrheic dermatitis in children is increased activity of the sebaceous glands (rapid growth and secretion of sebum), which occurs due to the circulation of maternal hormones in the child’s blood in the first weeks of life. Malacesia is not a leading factor in children, unlike in adults.
What is itchy skin like?
Itching of the skin can be of various types:
- Physiological and pathological itching. In the first case, the skin may itch due to some mechanical or chemical irritants, as well as insect bites. Pathological itching is a sign of a skin disease or other pathological condition, for example, neurological disorders or hormonal imbalance;
- Localized and generalized itching. Itching can be localized in a specific place, for example, under the hair on the head, in the genital area or anus, etc. As a rule, the symptom is paroxysmal in nature, often combined with other pathological manifestations of a particular disease. We are talking about generalized itching when literally the whole body itches. Often the symptom is associated with an allergic reaction or dry skin caused by dysfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- Constant and paroxysmal itching. With constant itching, the symptom persists throughout the day, its intensity may increase at a specific time of day, often in the evening. Paroxysmal itching appears independently or under the influence of certain irritating factors.
Symptoms
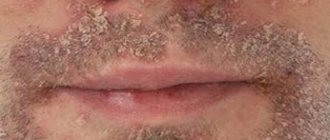
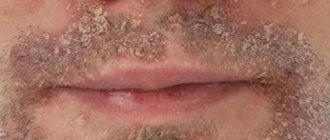
Seborrheic dermatitis is manifested by redness, peeling with “oily” scales with a certain localization of foci.
In children - isolated on the scalp (in the frontal area it is called the “baby cap” or “milk crust”), behind the ears and in the external auditory canal, on the face (in the area of the eyebrows, wings of the nose), on the back of the neck (along the edge of hair growth), in areas of skin friction (in folds), under diapers.
Sometimes seborrheic dermatitis in children is widespread. These are rashes in the form of spots with greasy crusts, merging into larger areas. In some cases it is accompanied by itching.
In adults, seborrheic dermatitis is presented in the scalp area, on the face: in the area of the eyebrows, behind the ears, inside the ears, on the wings of the nose and in the areas of the cheeks adjacent to the nose.
It can manifest itself as separate spots with peeling, total damage to the scalp, damage to the eyelids in the form of blepharitis, damage to the chest wall in the form of individual nodules and spots with crusts on the surface, inflammation of the hair follicles on the skin of the upper half of the body (ostiofolliculitis).
What is keratosis?
Let's start with the fact that cutaneous keratosis is a collective term that refers to a whole group of non-inflammatory diseases associated with impaired keratinization of the skin. Clinically, the process can manifest itself as slight peeling or the formation of thickened horny layers. There are follicular, seborrheic, and actinic keratoses.
Keratosis follicularis is characterized by the formation of horny plugs at the openings of hair follicles.
Seborrheic keratoses are plaque-like or nodular formations with a warty surface, covered with dry, horny masses that are flesh-colored, brown, or black in people over 50 years of age.
Actinic keratosis appears on exposed areas of the skin, initially appearing as bumpy, rough skin that eventually develops into rough, scaly patches ranging in color from normal skin tone to reddish brown. They are often limited in size and vary in size.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in adults and children
Seborrheic dermatitis may resolve without treatment. But it often occurs in waves, with remissions and exacerbations.
Several repeated courses of therapy or ongoing maintenance therapy may be required until the symptoms go away completely. After some time, exacerbation may occur again.
You should consult a doctor if repeating the usual regimens of care and relieving acute symptoms does not help, as well as if there are signs of a secondary infection.
The basis of therapy is the use of medicinal shampoos, creams and lotions.
For children, it is recommended to use special children's shampoos; before washing, you can apply oil or cream to help soften the crusts.
In children, it is important to stop itching, since scratching can cause secondary infection of the scabs.
Features of the treatment method
When selecting external skin care products, choose products containing the following ingredients that reduce skin inflammation:
- Keratolytics: salicylic, lactic acid, urea, propylene glycol.
- Topical antifungal agents: shampoos and creams containing ketoconazole (ciclopirox).
- Products with selenium disulfide or zinc pyrithione.
- Local low-strength corticosteroids can only be used as prescribed by a doctor to relieve the acute phase of the disease, except for the facial skin.
- In case of resistant forms, patients may be offered oral antifungal drugs.
- In severe cases, isotretinoin or phototherapy may be considered.
How is seborrheic dermatitis treated at the Rassvet clinic?
We evaluate the patient's skin type, severity and location of the rash.
The diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis is based on the clinical picture. The detection of Malacesia has no diagnostic value, since this is a normal microflora of human skin.
A dermatologist evaluates the condition and makes a differential diagnosis with psoriasis, rosacea (on the face), pityriasis versicolor (on the body), and atopic eczema in children. At first, we usually recommend shampoo and only if the selection of permanent skin care products fails, do we move on to active drug therapy.
My face looks like an orange peel: what should I do?
When “orange peel” appears, the question is how to remove unpleasant symptoms.
Many people try to disguise them using foundation. In fact, this tactic is highly undesirable, as it can lead to clogged pores and make the problem even worse.
If the skin on your face has become like an orange peel, you need to undergo a series of restorative cosmetic procedures as soon as possible. In this case, atraumatic facial cleansing, peeling and laser exposure are most effective.
Atraumatic facial cleansing
This procedure is a combination of soft dry cleaning and mechanical action. It allows you to eliminate acne, oily shine, inflammation, and activates regeneration processes.
Atraumatic facial cleansing has many advantages:
- visible result after the first session;
- no risk of skin damage;
- the ability to treat only problem areas.
The first stage of the procedure involves sequential application of masks with glycolic acid to the skin. However, since such an effect does not eliminate all impurities, it is combined with manual peeling.
At the end of the procedure, a mask is applied to help moisturize the skin and tighten pores. In total, the session lasts about half an hour.
Peelings
Peels allow you to get rid of enlarged pores, increased oiliness or excessive dryness of the skin, inflammatory processes and many other problems.
It is no coincidence that they are one of the most popular cosmetic procedures.
There are chemical, mechanical and hardware peels. The first are based on the influence of chemicals (usually acids), the second are based on manual application of drugs with active ingredients, and the third can be carried out using a laser or ultrasound.
Depending on the degree of impact, the following types of peeling are distinguished:
- surface;
- median;
- deep.
Maximum penetration into the skin layers allows for the most pronounced effect, but is accompanied by increased skin trauma. That is why such procedures should be carried out exclusively in the salon.
Laser
The effect of the laser also allows you to quickly eliminate the effect of orange peel on the face. This procedure is in great demand because it acts against a number of cosmetic defects:
- hyperpigmentation;
- wrinkles;
- striae;
- enlarged pores;
- acne and post-acne;
- rosacea;
- scars.
A positive result is noticeable after the first visit to the clinic, but usually experts recommend at least 2-3 sessions.
At Nomosclinic, this procedure is carried out using a reliable Italian Synchro Play DEKA device equipped with a cooling system. The cosmetologist can regulate the depth of its effect, ensuring a pronounced result without unwanted side effects.
More about procedures
Jessner Peel
Laser rejuvenation
Atraumatic cleaning
What are destructive (ablative) methods?
All skin tumors must be examined by a dermatologist before removal due to the risk of skin cancer. Treatment performed in a timely manner will help prevent the development of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) or squamous cell carcinoma of the skin (SCC).
- Cryosurgery using liquid nitrogen is the most common method for treating keratoses, but is not suitable for hyperkeratotic lesions. Liquid nitrogen is sprayed directly onto the affected areas of the skin using a cryodestructor or applied using the “reed” method (application with a cotton swab on a wooden stick). Cryosurgery is easily performed on an outpatient basis, shows excellent cosmetic results and is well tolerated.
- Radio wave, electro- and diathermo-laser destruction.
- Photodynamic therapy involves the application of a photosensitizing agent, methyl aminolevulinate, and then exposure to light of a specific wavelength, which leads to tissue necrosis. Photodynamic therapy is well tolerated and has excellent cosmetic results.
- Surgical removal . The surface of the skin is cleaned with a special instrument (curette).
- Chemical peeling:
- Jessner's solution (resorcinol, lactic and salicylic acids in ethanol);
- trichloroacetic acid solution 35%.
- Dermabrasion . The affected areas of skin are removed using a fast-moving abrasive brush.
- Phototherapy (IPL) and fractional photothermolysis - coagulation of keratosis elements using light energy. Suitable for the initial manifestations of actinic keratosis.