Causes of the disease
Children's skin has its own characteristics that predispose to the appearance of seborrhea. Seborrheic dermatitis in infants occurs due to the large size of the sebaceous glands and increased secretion of sebum. Also, the occurrence of seborrheic dermatitis in infants is associated with high levels of maternal hormones in the child’s body.
Manifestations of the disease
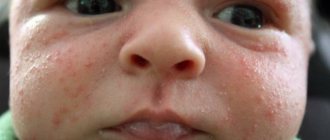
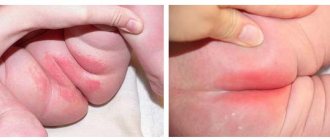
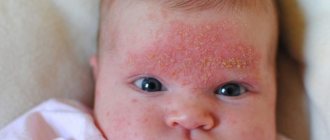
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face of a baby most often affects the forehead, and on the body it manifests itself as inflammation of the folds in the neck, armpits, and groin areas. But the most common manifestation of seborrheic dermatitis in infants is damage to the scalp with the formation of milky crusts - the so-called “baby cap”.
Course of the disease
Mostly, signs of the disease appear on the scalp about a couple of weeks after birth. Fatty-looking yellow crusts appear on the skin, most often on the scalp and forehead. Redness of the skin and flaking behind the ears and at the border of hair growth may also be noted. The rashes on the body are mainly located in the skin folds in the armpits and groin. A rash appears in these areas, skin irritation and maceration begin.
Seborrheic dermatitis in infants does not always lead to severe discomfort ; its manifestations may be minimal. With significant damage, the baby feels itching and becomes restless. In severe cases of the disease, complete redness and peeling of the entire skin is observed, the child may refuse food, and the body temperature rises. This condition requires emergency hospitalization and hospital treatment.
Complications of the disease
Seborrheic dermatitis in infants can be complicated by infection. This condition can lead to pyoderma. If treated incorrectly or untimely, the process can spread to healthy skin, in some cases affecting the entire body.
Forms of seborrhea
Taking into account the external manifestations of the disease and the specificity of the disorders, three forms of seborrhea of the scalp are distinguished:
- fat;
- dry;
- mixed.
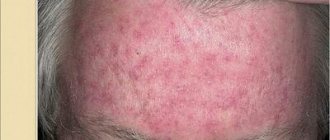
Oily seborrheic dermatitis is observed with excessive production of fatty secretions and is characterized by high oiliness of the dermis and hair, yellowish or red spots on the skin, profuse oily dandruff, thinning and hair loss. Moderate manifestations of the fatty form of the disease are quite common in adolescents and, with proper care, after normalization of hormone levels, do not require special therapeutic effects.
With dry seborrhea, the fatty secretion is produced in insufficient quantities, resulting in a feeling of skin tightness, dryness, severe itching and burning, and dandruff in the form of small dry scales. The hair becomes very thin, becomes dull, brittle and begins to fall out profusely.
The most problematic in terms of treatment is the mixed form of seborrheic dermatitis, in which fatty secretion is secreted in excess in some areas of the dermis, and in deficiency in others.
How is seborrheic dermatitis treated in children?
If seborrheic dermatitis appears in newborns, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor. If seborrheic dermatitis is detected in an infant, treatment is carried out with external means. To loosen the crusts on the head and remove them painlessly, use products based on salicylic acid and oil compresses, which are applied about half an hour before water procedures. To treat seborrheic dermatitis in newborns , you can use drugs with a keratolytic effect. This will help remove excess gland secretion and cleanse the scalp. After softening and removing the crusts, anti-inflammatory agents may be prescribed.
For treatment to be more effective, it is necessary to ensure that the skin is well hydrated and supplied with nutrients in the right quantities. This helps restore and strengthen the water-lipid barrier and restore the proper functioning of the sebaceous glands. Suitable for care are dermatological creams created for children, which contain vegetable oils, sebum-regulating and wound-healing components. If treatment for seborrheic dermatitis in newborns turns out to be ineffective, the following may be included in the therapeutic regimen:
- topical corticosteroids;
- antibiotics and antiseptics;
- antihistamines for severe itching.
What can cause seborrhea of the scalp in children
Seborrhea in newborns is considered a natural physiological process, caused by increased activity of the sebaceous glands. But, if bleeding, redness and itching of the skin occurs or if the disease lasts for a long time (more than 14 months), you should immediately consult a doctor.
Seborrhea of the scalp in children over one year old can be caused by:
- improper nutrition of the mother (if the child is breastfed) or the child;
- unfavorable temperature conditions - if the room is too hot or the child is dressed too warmly;
- allergies to food or hygiene products;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- taking antibiotics or other medications;
- metabolic disorders;
- decreased immunity and hypovitaminosis;
- stress;
- hormonal disorders;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
Preparations with zinc pyrithione
For mild to moderate seborrheic dermatitis on the head in infants, preference may be given to non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs based on zinc pyrithione. For example, Skin-cap shampoo containing activated zinc pyrithione has anti-inflammatory, sebum-regulating, and antimycotic effects. Skin-cap shampoo is prescribed as the main method of treatment to soften crusts and eliminate inflammation; in the future it can be used to prevent relapses of the disease. The activated zinc pyrithione contained in Skin-cap shampoo helps:
- reduce the intensity of inflammation;
- reduce the activity of fungi and bacteria;
- effectively moisturize the skin;
- eliminate peeling, feeling of skin tightness;
- reduce itching.
It is thanks to this combination of effects that Skin-cap shampoo can be used during an exacerbation of seborrheic dermatitis in an infant, then the treatment will be more effective. You can combine the use of Skin-cap shampoo with accompanying medications, including it as part of complex therapy.
Treatment with medications is supplemented by general recommendations for changing diet and caring for the baby. If seborrheic dermatitis is detected on the face of a baby , it is recommended to exclude foods with potential allergens from the diet. You should not put synthetic clothing on your baby so that the skin is not subject to friction and irritation. Parents should pay special attention to the selection of laundry detergents, choosing products without aggressive substances in their composition.
The likelihood of stress for a child needs to be reduced as much as possible, so it is important to maintain a favorable psychological environment in the family.
Features of the treatment of seborrhea of the scalp in children
One of the important factors determining the treatment methods for seborrhea in children is the age of the child. If in infants a slight manifestation of the disease is eliminated exclusively by supportive therapy - regular cleansing of the skin with special means and application of creams, then for the treatment of older children more drastic measures may be required.
In any case, before starting treatment for seborrhea in a child, you need to consult a specialist - a pediatrician, dermatologist or trichologist. Only a doctor can draw up an effective course of therapy that meets all the individual characteristics of the child’s body.
In general, seborrhea in children is treated in the same way as in adults - drug therapy is supplemented by the use of care products, diet and physiotherapeutic procedures. This comprehensive approach allows you to get rid of the disease in a relatively short time and avoid possible complications.
Maintaining personal hygiene
Patients with seborrheic dermatitis are recommended to injure the inflammation as little as possible. Personal hygiene rules include cleansing the skin twice a day using special products with a low pH. To cleanse the skin, it is prohibited to use aggressive agents such as laundry or tar soap.
General recommendations for maintaining personal hygiene:
- the use of washcloths or sponges with hard fibers is excluded;
- For a while, you should avoid cleansing your skin with scrubs and peels containing abrasive particles and aggressive chemical compounds;
- During water procedures, it is recommended to use dechlorinated water; for this purpose, it is recommended to first settle or filter it;
- the duration of water procedures should be reduced to 10-15 minutes;
- when choosing shower products, choose products without dyes and fragrances, with a low pH;
- use towels with soft bristles, and it is better to blot your skin with them rather than rub them;
- to reduce the likelihood of skin injury when combing, try to cut your nails as short as possible;
- Avoid using other people's personal hygiene items.
Causes (etiology) of diabetes in infants:
Unfortunately, at the moment there is no information about the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis, but several risk factors for its development can be identified:
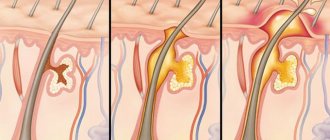
- colonization of the skin by yeast fungi of the genus Malassezia;
- increased secretion of sebaceous secretions (oily skin);
- immunodeficiency conditions (HIV, patients after transplantations, etc.);
- heredity (history of the disease in close relatives);
- unfavorable climate (spring-autumn exacerbations are typical).
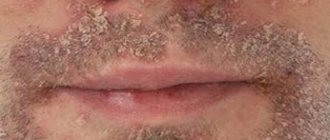
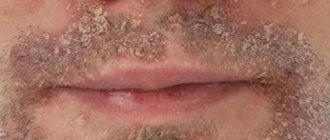
Why is seborrheic dermatitis on the face dangerous?
The localization of seborrheic dermatitis does not have a pronounced effect on the child’s health, however, the abundance of dry crusts on the face can be considered as a cosmetic defect. In addition, inept or overly aggressive fight against them can lead to the exact opposite result. Seborrheic crusts will not only not disappear, but will also cause keratinization of the upper layers of the skin with their subsequent thickening. In other words, the more parents try to get rid of the growths, the more they will spread. It is possible that under unfavorable circumstances, marks on the face from seborrheic dermatitis in newborns will remain for life.
Scalp dermatitis in conditions caused by immunodeficiency
With an active decrease in the protective properties of the immune system, the fungus rapidly multiplies, moving into the pathogenic phase.
Conditions caused by decreased immunity can be primary or secondary.
In the first case, we are talking about the human immunodeficiency virus.
In the second - about a decrease in immunity in acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, diabetes mellitus, and chronic pathologies.
In the case of persistent and prolonged immunodeficiency, dermatitis progresses to a chronic form.
It is extremely difficult to treat effectively.
Usually, medications can reduce the severity of the symptoms of the disease.
But they rarely eliminate it completely.
Differential diagnosis of diabetes and other dermatological diseases
Diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis is based on the clinical picture and includes assessment of the nature of the rash (color, shape, and other properties), its location and symmetry. Sometimes it is necessary to use microbiological diagnostics if there is a suspicion of an initially infectious nature of the rash or the addition of a secondary bacterial/fungal infection.
The difficulty in diagnosing seborrheic dermatitis lies in making a correct differential diagnosis with other clinically similar dermatological diseases, because psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, and rosacea (rosacea).
Pathologies of the digestive tract and scalp dermatitis
Normal microflora consists of a certain group of beneficial bacteria.
This is a collection of microorganisms that are mainly found in the large intestine.
This includes primarily bacteria from the groups Enterobacteriaceae (especially Escherichia coli), Enterococcus, Bacillus and Bacteroides.
Under normal conditions they are apathogenic.
But with negative changes, their concentration increases, and dysbiosis develops.
Against the background of bacterial imbalance, pathological changes are observed in the mucous membrane of the digestive organs.
In addition, the synthesis of vitamins necessary for healthy skin is disrupted.
As a result, various reactions from the epidermis are observed: dermatitis, seborrhea, eczema, allergies, etc.
Dry dermatitis of the scalp most often develops against the background of the following gastrointestinal pathologies:
- microbial imbalance of the intestine (dysbacteriosis)
- inflammation of the intestinal mucosa
- inflammatory reaction of the large intestine
- Ulcus Enteritis (duodenal ulcer)
- inflammation of the pancreas
- impaired intestinal motility (defecation disorder)
- conditions associated with helminthiasis.
Features of SKIN-CAP release forms
The cream is quickly absorbed and softens and moisturizes the skin well and does not leave greasy marks on it. It is suitable for facial skin and affected surfaces that require moisturization.
The aerosol can be applied even to the scalp using a special nozzle, which is included in the kit, without touching the hair. It helps eliminate itching and dries out wet rashes.
Seborrhea shampoo effectively7 fights its manifestations on the scalp. Actively helps eliminate dandruff and itching, fights the root cause of the disease - pathogenic microorganisms. Ideal for preventing relapses.
Skin-cap shower gel is a cosmetic product that is indispensable for daily hygiene in cases where seborrhea affects the skin of the chest and back. It cleanses, soothes and moisturizes the skin, helps eliminate inflammation and restores the protective properties of the skin.
Skin care rules
Skin care prone to symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis is primarily focused on normalizing the functions of the sebaceous glands. It is important not only to reduce sebum production, but also to ensure skin hydration.
General care recommendations:
- Try to reduce the use of comedogenic makeup, as it can cause clogged pores.
- Use care products that do not contain alcohol. It irritates the skin, dries it out, causing the sebaceous glands to work more actively.
- For care, choose special cosmetic products designed for seborrheic skin.
Diagnosis of dermatitis
Which doctor should I contact for help, and what tests should I take?
Although identifying dermatitis is not difficult, it is necessary to determine the root cause and triggering factors.
In addition to collecting the patient’s medical history and general examination, you will need to diagnose hormonal levels, as well as study the functioning of the digestive organs.
Laboratory tests are prescribed to exclude endocrine disorders, in particular diabetes mellitus.
Additionally, a stool examination is carried out to determine the presence/absence of dysbacteriosis.
If the dermatologist deciphers the test results and detects pathological changes, the doctor will redirect the patient to specialized specialists.
Most often such doctors are a gastroenterologist and an endocrinologist.
Prevention
By following preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of seborrhea:
- compliance with hygiene measures and hair washing using hypoallergenic, fragrance-free products;
- eating healthy and low-fat foods enriched with vitamins;
- giving up bad habits, including among nursing mothers;
- keeping the premises clean and regularly ventilated;
- walks in the open air;
- clinical examination;
- proper and balanced nutrition in infants, as well as in women during lactation;
- dress according to the season, avoiding excessive sweating;
- avoid stress and overexertion;
- playing sports;
- If necessary, take a course of vitamins 1-2 times a year.
Folk remedies in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children:
- add decoctions of chamomile, string, oak bark to bathing water;
- treat the affected areas with aloe juice diluted with twice the volume of water, which will help relieve inflammation and itching;
- in the morning, treat the skin with a warm (34-36 degrees) herbal infusion: mix equal parts of plantain leaves, chamomile and calendula flowers, herbal mixture (20 grams), brew with boiling water (300 milliliters) and infuse in a thermos;
You should also pay important attention to the baby's nutrition. When breastfeeding, the mother needs to remove butter, full-fat milk and fermented milk products with a high fat content, baked goods, and sweets from her diet. At the same time, you need to drink more, eat low-fat milk, low-fat kefir and cottage cheese.
Formula-fed babies should be fed an adapted infant formula. It is best to purchase a mixture whose packaging is marked “hypoallergenic.”