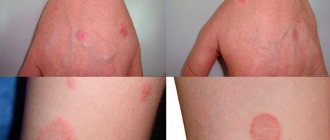
Hives are an allergic disease that appears as spots or red, intensely itchy plaques on the skin. Prevalence depends on age and environmental conditions, as well as comorbidities. The most common allergic dermatosis is recurrent urticaria.
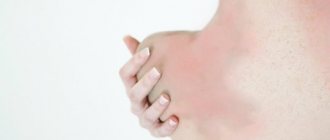
The swelling and itching caused by hives can be severe. The feature that distinguishes this disease from others is red spots on the surface of the skin. They have irregular edges and small bubbles. Typically, hives are caused by allergies. When an allergen enters the body, histamine is released into the bloodstream and causes: swelling, redness and itching.
Types of urticaria
There are two forms of the disease: acute and chronic. Acute urticaria is often caused by food allergies, insect bites, medications, or exposure to an allergen. It lasts, as a rule, up to 1.5 months.
Chronic urticaria lasts more than 6 weeks. It can begin when the immune system attacks the body's tissues, thereby causing an autoimmune reaction. Antibodies (proteins that normally fight bacteria and viruses) cause the release of histamine, which leads to lesions on the skin.
The rash can be localized or appear anywhere on the body, from the neck to the knees. Rarely does the allergy affect the arms, legs and face, unlike angioedema. Characterized by the appearance of rashes and spots on the skin. There is also swelling in the eyelids, lips and larynx.
Angioedema urticaria is a medical emergency because it can cause breathing problems and suffocation.
It is believed that 30 to 50% of cases with chronic urticaria have an autoimmune cause. The reason why autoimmune urticaria develops is unknown, even though it often occurs along with other autoimmune diseases such as:
- rheumatoid arthritis – the immune system attacks the joints;
- lupus – the immune system attacks the joints and skin.
In rare cases, chronic hives can also be caused by other infections (eg Helicobacter), hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), hepatitis B or C (liver infections), intestinal parasites.
Table - Types of urticaria in children
| Name | Peculiarities |
| Immune (IgE-dependent - food, drug, helminth; complement components - anaphylotoxins C3a and C5a; complement-induced - hereditary or acquired deficiency of the C-1q inactivator) | Characterized by skin damage and itching. Quincke's edema, urticarial type of vasculitis and anaphylactoid urticarial reaction are possible. |
| Non-immune (based on a pseudo-allergic reaction) | There is no true reaction of interaction between antibody and antigen with the formation of an immune complex. Ig-E does not increase. Occurs due to consumption of foods that contain vasoactive amines. |
| Pigmented | Accompanied by an increase in the number of mast cells. Often found on the upper and lower extremities or trunk. May damage internal organs and be accompanied by systemic mastocytosis. |
| Vascular urticaria or vasculitis | It is characterized by several lesions that have an unusual shape and disappear after a few days. Other symptoms of urticaria vasculitis include fever, joint and muscle discomfort, abdominal pain and headache. |
Possible complications and their consequences
Urticaria, despite its apparent harmlessness, can lead to serious consequences, primarily to Quincke's edema. Its characteristic initial symptoms, in addition to the swelling itself, are difficulty breathing and paroxysmal cough with whistling (bronchospasms). Swelling of the internal mucous membranes is dangerous due to disruption of the housing and communal services, the first signs of which are a gag reflex and stool disturbance. From the nervous system, severe cases of urticaria are dangerous due to damage to the meninges, which can be fatal in the absence of medical assistance.
Causes of urticaria
As soon as the hypothalamus registers an increase in body temperature in the brain, it sends an impulse to neurons that activate the sweat glands. Neurons release acetylcholine, which stimulates the release of histamine and heparin from mast cells in the skin (mast cell degranulation). This degranulation results in a diffuse release of histamine near the sweat glands. Histamine activates an inflammatory response in surrounding tissues and causes itching and redness. When you sweat (which is difficult for people with cholinergic urticaria), the skin reaction stops.
Chronic stress and nervousness can trigger an attack of psychosomatic urticaria. When constantly anxious, the body releases higher amounts of cortisol and adrenaline (stress hormones). But when the body is constantly in a state of tension and hormones continue to be released into the bloodstream, hormonal imbalance occurs. Adrenaline and cortisol combine with mast cells in the skin to produce histamine. Elevated levels of cortisol in the body cause allergic skin reactions such as hives and may even slow down healing.
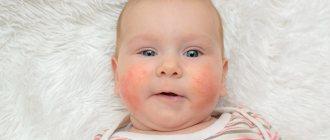
Urticaria is usually a consequence of an allergic reaction in children when the body is exposed to the following allergens:
- pollen of flowering plants;
- house dust (dust mites);
- pet hair;
- some preservatives;
- Food.
Hives can also occur when a child wears clothes that are too tight and made from irritating materials such as polyester. It can also be caused by infections caused by bacteria, viruses or other microorganisms.
Some medications, such as ibuprofen, can cause hives in children as a side effect. Also, such a reaction can occur if the child has an individual intolerance to one or another substance included in the medicine. Most often these are antibacterial and non-steroidal drugs.
If children are suddenly exposed to large temperature fluctuations, hives may result. Likewise, prolonged exposure to the sun or cold can cause a similar skin reaction. In rare cases, urticaria can develop due to diseases such as leukemia and lymphoma. This happens because the immune system is weakened.
Hives in children can also be caused by insect bites, which can lead to significant swelling. If it's a mosquito or spider bite, sensitive skin may respond by releasing histamine, which causes hives. Contact with various viruses or bacteria can cause a diffuse rash. Reddened plaques can be observed throughout the body.
Symptoms of urticaria
Hives appear as red spots, swelling and blisters. The main symptoms are itching and burning sensation on the skin. Symptoms may progress and spread to other areas of the body.
Additional symptoms of urticaria in children include:
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- discomfort in the joints.
The spots can be as small as a dot or the size of a coin. Typically, spots appear and disappear within a few hours. However, chronic hives can last for more than 6 weeks.
Diagnosis of urticaria in children
A preliminary diagnosis is made by the doctor after an initial examination of the skin.
The doctor knows exactly what urticaria looks like in a child, so he will not confuse it with manifestations of other diseases. For allergies, the following tests are prescribed:
- general blood test to exclude immune and inflammatory processes;
- allergy tests to identify the allergen.
In some situations, a biochemical blood test and examination for helminthic and parasitic diseases are performed. If necessary, a thyroid examination is prescribed to identify hyper- and hypothyroidism.
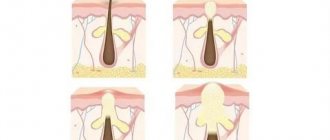
The mechanism of occurrence of urticaria (pathogenesis)
The human body contains mast cells or mast cells, which are specific elements of connective tissue. They are the central element in the development of urticaria, activators of inflammation. When an allergen enters the body for the first time and in small doses, the child does not experience any external manifestations or reactions, but sensitization occurs, which can be represented as the first acquaintance with the allergen, resulting in the production of histamine. It is this substance that causes redness, swelling and other inflammatory factors. It gradually accumulates in mast cells, and when its amount reaches a critical threshold, the cell membrane is destroyed with the release of histamine into the bloodstream and a subsequent cascade of pathological changes in the body.
Treatment of urticaria
Pharmaceutical drugs used to treat urticaria should be taken as recommended by your doctor. The best treatment for this condition is to know and avoid trigger factors. The hives will probably go away on their own. But at the same time, medical supervision is a prerequisite to exclude the development of complications.
Treatment for urticaria in children includes:
- taking antihistamines to reduce the rash;
- eliminating foods that cause hives;
- prescribing diuretics to eliminate severe edema;
- using antipruritic ointments to relieve the condition.
- in some situations, hormones are used (topically and by injection).
You need to keep a diary about what the child does and eats. This approach allows us to identify predisposing factors and eliminate them.
Gradually, one can narrow down the real causes and respond accordingly.
With such a complication as Quincke's edema, coughing attacks appear and breathing becomes difficult. In this case, urticaria in children requires emergency care.
Young children often experience swelling of the gastrointestinal mucosa, which is accompanied by vomiting. In severe cases, damage to the nervous system and brain occurs. Such conditions are dangerous to health and life, so delaying a visit to the doctor is unacceptable.
Most children switched to a hypoallergenic diet recover quickly and recover even without medication.
How long does it take to cure hives?
Within 4-6 weeks, acute urticaria resolves in almost all patients with this diagnosis.
However, sometimes the acute form can become chronic, and then the disease becomes incurable, with periods of exacerbation and complete remission with the absence of symptoms, which alternate with each other. To deal with this allergic reaction as quickly as possible, it is recommended:
- Immediately consult a doctor at the clinic or call an ambulance.
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet for several months.
- Follow all doctor's orders and recommendations regarding treatment. Do not stop taking allergy medications at the first signs of improvement, but complete the full course.
- Be sure to have modern antihistamines recommended by an allergist in your home medicine cabinet.
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist
Forecast and prevention of urticaria
Hives usually go away over time. However, it is impossible to predict how long this problem will persist. In many cases, the disease can be controlled by avoiding trigger substances and taking antihistamines.
Prevention methods include diet control and avoidance of contact with volatile and food allergens. You should wear loose clothing made from natural fabrics and not cause stress in your child. It is unacceptable to neglect chronic diseases.
Before treating hives in a child, you should consult your doctor. Contact a pediatrician or allergist at the RebenOK clinic in Moscow. We employ specialists with extensive practical experience. Thanks to modern equipment, it is possible to quickly diagnose and, based on the results obtained, prescribe effective therapy.