In a normal state, the lymph nodes do not manifest themselves in any way, and not everyone even knows where they are. But sometimes situations arise when, under the influence of certain factors, these nodes become inflamed, increase in size and cause a lot of suffering to a person. Usually, spinal diseases are not included among the causes of such inflammation, but in rare cases there is a direct connection between them. Let's consider whether there are lymph nodes on the back, why pain occurs and what should be done in such situations?
Lymph nodes on the back
Can't bear your own burden?
Plastic surgery of the anterior abdominal wall for hernias in children
More details
Hernias of the anterior abdominal wall are one of the most common human diseases; they are observed in 2-4% of the total population of the planet. A hernial protrusion is the exit of the peritoneum in the form of a bag with the insides contained in it through any defect of the abdominal wall beyond its limits. There are inguinal and femoral hernias, hernias of the white line of the abdomen and Spigelian line, postoperative ventral hernias, etc.
Symptoms of hernia of the white line of the abdomen in adults
This hernial pathology often causes the appearance of a lump, a bulge with smooth edges in the area somewhat lower than the sternum, but above the patient’s navel. The bulge may be present all the time, regardless of body position (lying, standing, or sitting), or it may only occur when a person coughs, sneezes, or laughs too much. If in some cases patients report a small bulge, the area of the hernia can increase in the absence of any medical attention to the size of a quail, or even a chicken egg (or even more). Some people may also develop more than one epigastric hernia (several in a row, in a chain, or two or three far apart). Although it is not typical for an epigastric hernia to present with any symptoms, patients may notice swelling, swelling, redness, or pain along the linea alba or within the hernia itself.
Acute stomach
What condition is called “acute abdomen” and how dangerous is it?
An untreated, large and neglected epigastric hernia can cause severe pain and complications due to strangulation or provocation of intestinal obstruction. Urgent symptoms of an epigastric hernia include:
- heat;
- lack of appetite;
- increased pain or swelling;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- development of bleeding, peritonitis or other problems.
You can live with a hernia. But not for long...
It should be immediately noted that there are no safe hernias. The presence of a “hole” in the so-called “soft skeleton”, which is the abdominal wall, threatens a number of complications. The most dangerous of them is strangulation of the contents of the hernial sac in the ring. If in this case a loop of intestine or another vital organ is pinched, then the time countdown begins in minutes, and the whole situation develops into a matter of “life and death.” A patient with a strangulated hernia must undergo urgent surgery. Moreover, if the strangulated organ is no longer viable, then the scope of the operation can be very traumatic, and the prognosis is unfavorable. Hernias are strangulated in approximately 10-12% of cases, most often umbilical, inguinal and femoral. If the hernia does not have a tendency to strangulate, then in any case, over time, the hernial ring expands and the hernia increases. In some cases, with ventral hernias of the anterior abdominal wall, a significant part of the intestine, the greater omentum, and part of the stomach end up in the sac, and the hernia becomes “giant.” There are cases when the patient literally “carries a giant hernia in his arms,” without being able to reduce it into the abdominal cavity. What kind of quality of life can we talk about in such cases?! Accordingly, the treatment of such hernias is a complex problem. Considering all of the above, it becomes clear that you should get rid of the disease without delaying or waiting for complications.
The main thing is to return everything to its place!
Treatment of hernias of any localization is only surgical. All hernias of the anterior abdominal wall, with the exception of inguinal hernias, are operated on using the “open” method. An incision is made, the hernial sac is isolated and opened, its contents are inserted into the abdominal cavity. Next, proceed to the main stage. The edges of the hernia defect are sutured according to the chosen technique. Adequate implementation of this stage largely determines the prognosis of the operation. Inguinal and femoral hernias have a more complex anatomy. Their treatment requires not only knowledge of the topography of this zone, but also all modern treatment methods.
Belly patch or new techniques
In recent years, techniques have begun to be used to avoid tissue tension. During the operation, special meshes are inserted through the incision in the projection of the hernial ring to hold the exit of the hernial sac through the aponeurosis defect. The meaning of the action is clear: if a child wipes his pants, then the housewife does not sew up the hole, but sews in a patch. The comparison may be curious for such a serious topic, but it conveys the main idea embedded in the methodology. It should be noted that all “open” operations involve, first of all, an incision, the associated pain syndrome, the danger of inflammation of the suture and, finally, rough scars on the skin. Therefore, in hernia surgery, the search for new operations that would combine not only reliability, but also low trauma does not stop.
Symptoms
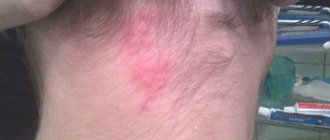
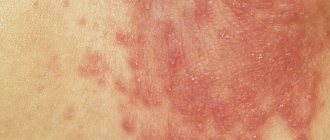
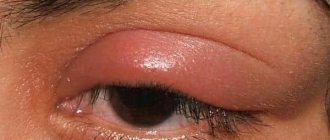
You can determine lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis yourself only if the superficial lymph nodes are affected - in the neck, armpits or groin. The main signs are the formation of visible tubercles under the skin, dense, painful and mobile to the touch. Their appearance is usually accompanied by fever, general malaise, redness and swelling of adjacent tissues. Sometimes additional problems with breathing, tachycardia, the appearance of a rash in the area of the lump, and skin itching are observed.
Hernia “in a hammock”
Since 1992, “closed” methods of surgical treatment of inguinal hernias, the so-called “laparoscopic hernioplasty,” began to be used in our country. Operations are performed without an incision. Through small punctures, long thin instruments are used to sew the mesh into the abdominal wall in the projection of the hernia defect. At the same time, the principle of “no tissue tension” is maintained. The mesh covers the entire groin area, including the medial, lateral fossa and femoral canal - i.e. all “weak” places of possible release of other hernias of the inguinal localization. Laparoscopic operations currently meet all the necessary requirements for a surgical procedure: low trauma, safety, reliability, high cosmetic effect, short rehabilitation time. All this, of course, provided that the method is in the hands of a high-class professional and not an amateur.
Diagnostic methods
The main task of diagnosis for enlarged lymph nodes is to identify the real cause among many possible ones. An initial examination and history taking are ineffective here; the doctor can only confirm the presence of changes in the superficial nodes. Therefore, the patient needs to undergo a detailed examination.
Table. Diagnostic methods for enlarged lymph nodes
| Type of study | What does it show |
| Blood analysis | The level of red blood cells, lymphocytes, ESR, as well as the presence/absence of viral and bacterial infections are determined. |
| Provides a three-dimensional image of the affected area, which allows you to clarify the size of deep lymph nodes, identify neoplasms, and also determine whether there are pathologies of the spine. |
| Gives a more accurate result compared to fluoroscopy. Layer-by-layer images help to identify the slightest structural changes both in the lymph nodes themselves and in adjacent tissues and the spinal column. |
| Allows you to determine the location of lymph nodes, their size, number, structure. |
In some cases, when these studies do not reveal the exact cause, the patient undergoes a lymph node biopsy.
…We have been treating hernias for 9 years. Invaluable experience of professionals
The surgical department of the Center for Endosurgery and Lithotripsy has been actively working to improve surgical methods for treating abdominal wall hernias for 9 years. Along with traditional methods, preference is given to new “closed” hernioplasty techniques.
The work is mainly carried out in three directions:
- Surgical treatment of giant ventral hernias of the anterior abdominal wall
Work in this area includes:
- Determination of indications for choosing a surgical method (with or without prolene mesh);
Preparing patients for the upcoming operation;
- Improving methods of pain relief during surgery;
- Cosmetic aspects of giant hernia surgery;
- Prevention of cardiopulmonary complications in the early postoperative period
- Laparoscopic methods for treating inguinal hernias
This direction is a priority. Suffice it to say that the first laparoscopic hernioplasty in Russia was performed in our department. Currently, CELT surgeons have the greatest experience in performing these operations in our country. Long-term results are being analyzed. It can already be said that in terms of the number of complications and recurrences of hernias, laparoscopic hernioplasty has a number of undeniable advantages over traditional operations. In our department, patients after laparoscopic hernioplasty get out of bed in the evening of the day of surgery and most of them are discharged from the hospital the very next day after the intervention.
Work is carried out in the following directions:
- Expansion of indications for laparoscopic hernioplasty;
Improving surgical techniques to reduce its invasiveness;
- Features of the postoperative period;
- Laparoscopic technique for the treatment of “giant” inguinal-scrotal hernias;
- The possibility of performing simultaneous (simultaneous) laparoscopic operations for combined diseases of the abdominal organs requiring surgery;
- Study of long-term treatment results.
- A new way to treat giant inguinal hernias
Laparoscopic techniques have a number of limitations. In particular, throughout the world the presence of a large inguinoscrotal hernia is a contraindication to laparoscopic surgery. Traditional methods give a high percentage of recurrence of these hernias in the long term. The surgical department of the clinic developed an original method for treating this pathology. The essence of the method is that part of the operation is performed through a small, 3-4 centimeter incision in the groin area. In this case, the hernial sac is isolated and the external inguinal ring is sutured. The second stage is endoscopic. Through punctures using laparoscopic technology, a mesh is installed to cover the hernia defect from the inside. In this combination method, combining elements of “open” and “closed” techniques, it is possible to operate on fairly large hernias with minimal losses for the patient. Patients are discharged from the hospital 2-3 days after surgery. To date, we have not found a single relapse of the disease. Our method of combined laparoscopic hernioplasty was presented at a surgical congress in Italy in 1998 and aroused keen interest among foreign colleagues. First of all, they have not seen such huge, neglected hernias in their countries for a long time and, of course, the new technique, in their opinion, has opened up new opportunities in the surgery of complex defects of the anterior abdominal wall.
Back diseases and lymphadenitis
Can spinal diseases cause inflammation and enlargement of lymph nodes? There is no direct connection here, but with pathologies of the spinal column, microcirculation in the paravertebral tissues is often disrupted, for example, due to compression of the vessels through which blood and lymph pass. This leads to stagnation of lymph, accumulation of toxins, and the development of inflammation, which causes enlargement of lymph nodes and the appearance of pain.
Damage to the vertebrae and intervertebral discs often causes compression of the lymphatic vessels, which leads to stagnation of lymph and the development of inflammation in the lymph nodes
Such pathologies include, first of all, osteochondrosis, characterized by degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs and vertebrae. Most often, the cervical and lumbar regions are affected, near which there are groups of lymph nodes. With serious tissue damage, the reaction of the lymphatic system is immediately manifested by an increase in nodes, accompanied by inflammation and pain.
Osteochondrosis and inflammation of the lymph nodes
Other pathologies can cause the same reaction:
- Bekhterev's disease;
- spondylitis;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- radiculitis;
- sciatica;
- spinal cancer.
The development of a cancerous tumor in the spine also causes enlargement and inflammation of the lymph nodes
For information: with curvatures (scoliosis, kyphosis), lymphadenitis is usually not observed, unless the disease is complicated by a sharp decrease in immunity and serious disturbances in the functioning of individual organs and systems.
Profitable arithmetic: two operations in one
Cholecystectomy
- Cost: 100,000 - 160,000 rubles.
- Duration: 25-30 minutes
- Hospitalization: 3 days in hospital
More details
We consider performing two or more operations simultaneously for combined surgical diseases as another interesting area of work. There are not so few people suffering from several diseases at once that require surgery. Traditionally, they endure one operation after another, trying to gradually get rid of their ailments. The use of gentle laparoscopic techniques allows you to solve the problem in one step. Our department has accumulated extensive experience when laparoscopic hernioplasty was performed in conjunction with removal of the gallbladder for cholelithiasis, colon resection, gynecological operations, etc. Despite the expansion of the volume, patients tolerate these interventions well, are activated early and are discharged from the hospital in almost the same time frame as after one operation. At the same time, the patient avoids repeated intervention with all the ensuing difficulties and dangers, saving time, effort and money.
Link between swollen lymph nodes and back pain
When the lymphatic system does not cope with its task, the nodes become inflamed, increase in size and cause very painful sensations. At first, the pain is localized around the inflamed node, but then it spreads further and can radiate to other organs and parts of the body, as, for example, pain from a stomach ulcer radiates to the thoracic and lumbar spine. That is, with mediastinal lymphadenopathy it can hurt between the shoulder blades and in the upper back, with damage to the inguinal nodes - in the lower back, coccyx or sacrum, and so on. The same manifestations are caused by lymphadenitis (inflammation) and lymphoma - malignant formations in the tissues and nodes of the lymphatic system.
Pain from inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes radiates to the back of the head and upper back
In this case, the causes of lymphadenopathy may be completely unrelated to pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. As a rule, most often disturbances in the functioning of the lymphatic system are caused by the following factors:
- infection (bacteria, viruses, fungi);
- malignant tumors and their metastases;
- lymph stagnation;
- helminthic infestation.
Important! Radiation therapy and long-term use of medications can provoke malfunctions of the lymph nodes, which negatively affects the immune system. When immunity is weakened, even a mild infection is a serious health threat, and the lymphatic system is the first to suffer.
Hernias “amenable” and hernias “intractable”
All inguinal hernias can be operated on using laparoscopic techniques. These include direct, oblique inguinal and femoral hernias.
Laparoscopic hernioplasty is especially indicated:
- For large inguinal-scrotal hernias;
- For recurrent inguinal hernias;
- Bilateral inguinal hernias;
- When an inguinal hernia is combined with other surgical diseases, if a simultaneous operation is planned.
In the first two cases, traditional operations are accompanied by a large number of relapses. In the other two, open operations are usually performed in stages.
We consider the presence of severe concomitant cardiovascular diseases in the patient as relative contraindications to laparoscopic hernioplasty. These operations are also not indicated during late pregnancy.
When choosing treatment, choose a surgeon!
It can be said that in the Department of Surgery of the Center for Endosurgery and Lithotripsy, almost all modern methods of treating hernias of the anterior abdominal wall of any location and anatomical structure are widely used. In addition, I would like to note that the team of surgeons has been working in the same composition for more than 10 years, which undoubtedly affects the coherence of the work and the quality of the operations performed.
Patients who have undergone hernioplasty in our department are carefully monitored by our specialists for several years, being, so to speak, under “guaranteed service.” This approach allows us to constantly improve and improve the quality of surgical treatment.