Cutaneous horn is a common dermatological pathology that can occur at any age. But, as medical statistics show, cutaneous horn is rare in children. Older patients are at risk. The cosmetic defect is diagnosed in men and women with equal frequency. The skin abnormality is particularly common in women over 55 years of age. But at its core, the cutaneous horn is a benign neoplasm from the cells of the upper layer of the epithelium.
This disease is called so because of the similarity of the shape of the emerging formation with the horn of an animal. Moreover, the surface of the growth is dense, with keratinized particles as a coating.
Clinical picture
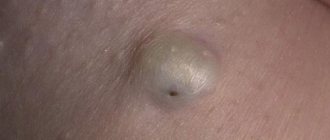
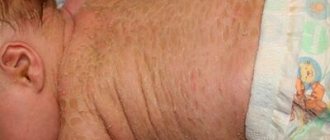
As already mentioned, a new growth appears on the skin, similar in shape to a horn. It has a hard consistency and a rough surface texture. Most often, horny keratoma affects the scalp and neck. Sometimes a cutaneous horn appears on the face. However, these are not the only places of localization. Specialists at the Lasersvit medical center for diagnosing moles are faced with the need to eliminate pathology in various parts of the body. Cutaneous horns are often found on the leg, back, and even on the genitals.
The cylindrical neoplasm has clear boundaries. The color of the growth is dark brown or flesh-colored. The size of the formation varies from a few millimeters to several centimeters. In most patients, keratoma corneum appears in a single copy. But in some patients, our dermatologists diagnosed and removed multiple formations.
As in the diagnosis of other types of tumors, in the case of examining the cutaneous horn, dermatoscopy and histology are used. An integrated approach to making a diagnosis allows you to exclude cancer.
Forecast and prevention of the disease
The prognosis for keratoma keratoma is favorable, and relapses are extremely rare. A benign growth becomes malignant extremely rarely, in 5% of cases.
To avoid the recurrence of an unpleasant disease, dermatologists recommend taking less sunbathing and sticking to proper nutrition. And also take care of personal hygiene, avoid skin trauma, and take immunomodulators. If a skin growth appears, you should see a doctor immediately.
The cutaneous horn causes physical discomfort and is easily injured. If the growth is damaged, there is a possibility of an inflammatory process and the tumor degenerating into a malignant one. Removing the growth in a medical facility does not require preliminary preparation, the rehabilitation period is painless, and the healing process lasts about 7 days. After the operation, the removed growth is sent for histology. This test is ordered to check a patient for cancer cells.
Is cutaneous horn dangerous?
Cutaneous horn in humans, despite its benign nature, is a disease that requires treatment. After all, a tumor has a predisposition to degeneration. Therefore, if such a pathology is detected on the skin, it is recommended to treat it. Well, even in a “calm” state, it is better to remove the growth on the eyelid, lip, nose, since the formation significantly spoils the appearance. A conical growth 1-5 cm long attracts increased attention from others. This causes uncertainty, discomfort, and social withdrawal.
But let's return to the risks of malignant degeneration. This process occurs due to hereditary predispositions to the appearance of tumors. And the first symptom of danger is the appearance around the base of the growth of signs of inflammation and pain when touching the growth. It is better not to wait for such manifestations. Seek medical help if any pathology occurs. In our medical center you will receive qualified and professional care.
Description
Cutaneous horn (xanthelasma or xanthoma) - what is it? Cutaneous horn refers to neoplasms that are keratinized growths on the skin. At an early stage, the growth looks like a smooth yellowish or grayish plaque, which, as it grows, forms a cone-shaped bulge and rises above the skin. Typically, xanthoma forms in folds of skin that form wrinkles.
This neoplasm appears as a result of excessive proliferation of epidermal skin cells. Active and dead cells accumulate and subsequently merge into a single formation of a specific shape. This collection of cells grows in length and does not usually affect healthy tissue. In most cases, the neoplasm is 1–3 centimeters in size, but sometimes growth up to tens of centimeters is observed. The largest record cutaneous horn reached a length of 30 centimeters.
Horny keratoma usually forms in older people, and in most cases in women. In men, this neoplasm is rare, and, as a rule, among those working in harmful and dangerous conditions (drivers, stokers, miners, sailors, industrial workers). The International Classification of Diseases classifies this neoplasm in the section “Other specified epidermal thickenings.” The ICD 10 code is L85.
Medical scientists doubt the independence of this pathology; the pathogenesis of horny keratoma has not been fully studied. Modern dermatology considers the term “cutaneous horn” to be a collective term, since it can be the result of many tumor processes, including as a condition of an optional precancer.
Cutaneous horn is dangerous because in 5% of cases it becomes malignant. The neoplasm degenerates into squamous cell carcinoma of the epidermis. Therefore, if such a formation is detected, it is necessary to undergo a histology analysis.
Keratoma keratoma occurs extremely rarely in children. This neoplasm is formed in a child due to various damage to the skin or infections that have entered the skin. One of the reasons for the appearance of such pathology in adolescents is considered to be changes in hormonal levels. Horny keratoma can arise from hormonal imbalance and changes in the body. Such processes occur both in adolescence and old age, or during pregnancy.
Treating cutaneous horn at home
There are a dozen folk recipes that tell how to remove skin tumors. But you should not smear the skin with aggressive substances so that the horn falls off. Do not pull the growth or drip acid or alkali onto it. These tips carry health risks. Even if it is possible to remove the formation from the surface of the skin, the surrounding tissue can be seriously damaged. Also, the growth may not be completely removed, which will lead to relapse. And most importantly, it is impossible to conduct tissue histology at home. Therefore, it will be impossible to prevent the risks of degeneration at an early stage.
Causes
Modern medicine has still not fully elucidated the etiology of cutaneous horn. Most often, such neoplasms form in older people. The reason for this is age-related metabolic disorders, which leads to abnormal proliferation of epidermal cells. In the presence of harmful factors, this disease can occur even in infants.
Scientists believe that several processes serve as prerequisites for the development of cutaneous horn:
- acceleration of mitotic division of skin cells;
- acceleration of migration to the surface of skin cells with excess keratin;
- acceleration of physiological death of skin cells;
- accumulation of keratinized skin cells, which leads to growth in length.
Some internal factors are considered to be the causes of keratoma keratoma:
- genetic predisposition;
- obesity;
- hypovitaminosis (lack of vitamins in the body);
- digestive disorders;
- a history of cancer;
- hormonal imbalance;
- disruption of intracellular metabolism in the body;
- alcoholism and drug addiction;
- disorders in the body's immune system;
- nervous overstrain.
Possible external causes of the appearance of a cutaneous horn are:
- excessive insolation (long-term exposure to solar radiation);
- skin infections (for example, cutaneus larva migrans - a rare disease transmitted to humans from cats and dogs);
- damage to the skin;
- viruses (human papillomavirus, feline viral leukemia, etc.);
- failure to maintain personal hygiene;
- aggressive environment (contact with acids and alkalis);
- poor circulation from wearing tight clothes.
In addition, many diseases can cause the formation of horny keratoma:
- warts;
- papillomas;
- keratoacanthoma - a benign tumor of the hair follicles;
- actinic keratoma (keratosis) – benign skin formation;
- leukoplakia – a disease of the mucous membranes that causes keratinization;
- fibroma is a benign tumor of fibrous connective tissue;
- angiokeratoma is a dermatosis characterized by single or multiple benign vascular formations;
- Bowen's disease is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma;
- fungal diseases;
- seborrhea;
- psoriasis;
- long-term dermatitis and allergic rash of various etiologies;
- lupus erythematosus and tuberculosis (in rare cases).
Many of the above factors serve as a stimulus for the appearance of hyperkeratosis - abnormal growth of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Cutaneous horn is one of the histological signs of hyperkeratosis. In many cases, this disease is accompanied by other skin pathologies: acanthosis, keratoacanthoma, papillomatosis.
Would you like to receive an estimate for treatment?
*Only upon receipt of data on the patient’s disease, a representative of the clinic will be able to calculate an accurate estimate for treatment.
How to cure cutaneous horn?
For several decades, cutaneous horn removal was carried out only surgically. This method is quite effective. But after excision of the formation with a scalpel, scars and cicatrices almost always remain on the skin. This is a problem for patients whose cutaneous horn appears on open areas of the skin - on the face, on the neck, on the arms.
A modern alternative to surgery is laser removal of the skin horn. Laser therapy, especially in the early stages of pathology, has proven itself to be an effective and efficient way to completely, completely remove skin abnormalities.
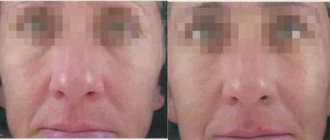
The laser beam acts precisely and at the desired depth, so neighboring tissues are not damaged. The treatment is painless and long-term rehabilitation is not required. Since trauma to the skin is minimal, there are no scars or scars left on its surface. You can verify this by looking at photos of the skin of our patients before and after microsurgery.
It is important that there is no bleeding or inflammation at the site of micro-operation. After all, the laser beam cauterizes capillaries and tissues, preventing infection. The safety and painlessness of laser technologies allows them to be used not only in the treatment of skin pathologies in adults, but also in children. The method has only a few limitations. You can find out more about them at an appointment with a dermatologist at the Lasersvit Medical Center for Mole Diagnostics.
Laser therapy for keratoma
Laser surgery for skin horns is also based on heating the cells. It can be performed without anesthesia, especially in the case of small growths. Under the influence of a special length of light beam, tissues are heated and destroyed. The advantage of such removal is that when the laser beam hits healthy skin, it does not cause any harm - it is simply not sensitive to their influence. This significantly increases the accuracy and efficiency of the impact. The procedure is considered the most gentle one known today. The blood vessels attached to the skin horn and feeding it are carefully sealed. This eliminates the need to suture the wound, subsequent bleeding, infection and other complications. Laser removal cannot be performed on dark skin.
Reviews
Alexander. My father developed a cutaneous horn on his temple and grew quite large. They removed it with a laser at the clinic, very carefully and painlessly. 2 years have passed and so far everything is fine.
Natalia. An incomprehensible growth formed on my mother’s eyebrow. It turned out to be a cutaneous horn. At the medical center it was removed using liquid nitrogen. Mom has already fully recovered.
Tatiana. A lump grew near my ear. I thought it was a wart. When I went to the doctor, they said it was keratoma keratoma. When asked how to treat, they suggested removing it with a laser. I'm happy with the result, I recommend it to everyone.