Home > Urology > Epidermal cysts
- Treatment of prostatitis
- Pearly penile papules
- Fordyce granules
- Fordyce angiokeratomas
- Epidermal cysts
- Excision of the foreskin
- Short frenuloplasty
- Treatment of hydrocele
- Treatment of varicocele
- Removal of oleogranulomas
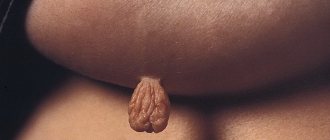
Epidermal cysts are a common type of cyst that can form on the scalp, face, neck, torso and genitals, as well as in areas of frequent friction. It is a flesh-colored tumor-like neoplasm, reaching a size of 5 cm. They are equally common in both men and women.
Cost of epidermal cyst removal
| Cost of laser removal | price, rub. |
| Removal of epidermoid cyst | 5 000 |
Make an appointment for removal of epidermal cysts
- Full name
- Telephone
Epidermal cysts occur due to blockage of the sebaceous glands. Inside the neoplasm there is a capsule, which is gradually filled with sebum, lipids and keratin. Upon palpation, you can feel a dense ball inside; at the initial stage, the cyst does not cause discomfort, except for its unaesthetic appearance.
Treatment of epidermal cyst
Today, there are two types of treatment for this tumor:
- surgery;
- laser coagulation.
Each method has its own advantages, but experts highlight the laser method for removing epidermal cysts.
The laser can most accurately and delicately deal with neoplasms on any part of the body, especially if it concerns the genital organs, because most often in men, epidermal cysts appear in the scrotum area. The main advantages of laser treatment are:
- Bloodlessness;
- No scars or cicatrices;
- Fast procedure;
- Safety;
- Painless;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- No relapses.
What is the danger of an epidermal cyst?
Since the epidermal cyst grows very slowly, many patients are in no hurry to remove it. However, experts recommend not to delay its treatment. Despite the fact that this neoplasm is not malignant, it contains another danger.
The walls of the epidermal cyst are fragile and tear easily; the contents of the capsule enter the dermis, causing inflammation and pain. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Another danger of an epidermal cyst is the possibility of infection; under no circumstances squeeze out the cyst or open it yourself, this can lead to suppuration and hardening of the tissue.
That is why treatment should be entrusted to professionals and modern techniques.
If you are interested in the treatment of epidermal cysts, you can make an appointment with one of the Center’s specialists by calling: +7
Hydrocystoma
Synonyms: eccrine/apocrine hydrocystoma, cystadenoma.
Hydrocystoma is a benign cystic tumor, proliferation of secretory cells of the sweat glands.
Since there is a process of proliferation, the name cystadenoma is considered more appropriate.
There is an opinion that hydrocystoma is a retention cyst of a tightly sealed sweat gland.
Hydrocystomas are divided into two histopathological types: apocrine and eccrine.
Many lesions occur in ectodermal dysplasia, focal hypoplasia of the Goltz skin.
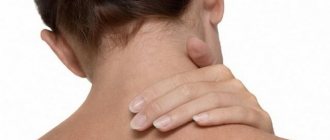
Usually on the face - forehead, cheeks, often grouped at the outer corner of the eye; rare other places.
Hydrocystoma is an intradermal convex elastic nodule; small in size, usually up to 10 mm.
Hydrocystoma varies from transparent to pigmented in shades of blue-blue-black.
Drawing. Translucent cystic formation along the edge of the lower eyelid; Histopathological examination showed hydrocystoma.
While eccrine and apocrine hydrocystomas are similar, the types are distinguished only histologically.
Eccrine type - single-chamber cysts covered with single- and double-layer cuboidal epithelium.
The apocrine type has papillary projections, two rows of cells and secretion by decapitation.
On the outside there is a row of flat myoepithelial cells, on the inside there is a row of tall cylindrical cells.
Secretion occurs through decapitation of columnar cells, round nuclei remain at the base.
Surgeons do not care about the histological type of hydrocystoma; in any case, they perform enucleation.
Drawing. Eccrine hydrocystoma: a round formation containing clear fluid; the cavity is lined by double-layered cubic epithelium without decapitation (2, 3); since the formation is close to the skin, the multilayered flat epidermis is captured in the sample (4).
Drawing. Apocrine hydrocystoma: translucent formation, small in size; papillary growths into the cavity; the wall is lined with two layers of cells - myoepithelial and high cylindrical with decapitation.
On ultrasound, hydrocystoma has a clear oval shape; anechoic, rare fine suspension.
LASER REMOVAL OF PIGMENT STOCKS
After the procedure, the patient must follow the doctor's recommendations. Otherwise, there is a risk of infection or scarring of the tissue (if you wet it or pick off the scab).
The list of mandatory recommendations includes the following:
do not wet the wound or pick off the scab;
avoid situations in which the wound may become wet (visiting a swimming pool, sauna, open water, taking a bath, all water procedures - with caution);
do not apply cosmetics to the wound (for example, foundation or powder for the purpose of masking);
choose clothes in such a way that the fabric does not rub the wound;
In case of purulent discharge, swelling, redness, pain, you should immediately show the wound to a doctor.
The duration of rehabilitation depends on the size of the removed atheroma. The smaller the cyst, the faster the recovery will be. In any case, after laser removal, the healing process will not last long.
Treatment methods
Since the formation takes a long time to develop and is benign, it is not necessary to remove it. The decision to undergo surgical intervention is made for cosmetic reasons or in the event of an unsuccessful pathology location or frequent mechanical damage to a neoplasm protruding above the surface of the skin. This increases the risk of bacterial infection with subsequent transition to purulent processes. In this case, radical treatment in the form of removal is the only way to prevent more serious diseases and complications.
Epidermal cysts are treated in several ways:
- If the formation is large, it is removed with a scalpel. A scar remains at the site of the incision.
- Laser removal of atheroma is considered the preferred method of choice due to the minimal list of contraindications and excellent results.
- Burning with liquid nitrogen is affordable, but has its drawbacks - inaccuracy of the effect, prolonged healing of the burn.
Important: Do not try to treat epidermal cysts or other skin formations with folk remedies. This is fraught with serious damage and the appearance of a scar at the site of exposure. In addition, without histology it is impossible to accurately determine the nature of the neoplasm, therefore it is impossible to talk about its benign quality. Any unprofessional interventions can cause serious health problems.
Types of cysts
In general, a distinction is made between congenital cysts and acquired cysts.
A congenital cyst appears as a result of pathological formation of tissues and organs during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus. An acquired cyst is a neoplasm that appears as a result of external or internal factors that affect a particular organ or tissue after a person’s birth. Cysts can be true or false. The inner surface of true cysts is lined with epithelium (that is, a layer of cells that are located on the basement membrane and are nourished by nearby tissues). There is no lining inside false cysts.
Also, cysts of internal organs and tissues are classified according to the mechanism of formation. They are retentional, ramolitic, traumatic, tumor, dysontogenetic, parasitic. The advisability of removing cysts is determined by a doctor specializing in the treatment of the organ in which the cyst has formed.
Generally speaking, cysts of internal organs are a “field of activity” for highly qualified surgeons. Our clinic employs just such specialists; we perform removal of cysts of internal organs, as well as soft tissue cysts, including epidermal ones and their varieties - atheromas. Cysts of internal organs are removed by laparoscopy or endoscopically - using a device that avoids large incisions and makes the intervention less traumatic.
ADVANTAGES OF LASER REMOVAL OF atheromas
- Minimal risk of bleeding due to the ability of the laser to coagulate damaged vessels
- Minimal risk of postoperative complications associated with infections - the laser destroys bacteria and microorganisms, thereby creating a sterile environment in the operating area
- Fast recovery - healing occurs approximately twice as fast as after surgical removal
- Ability to remove atheromas of any size
- Subtle (in the case of large atheromas) scarring on the skin or complete absence of scars (in most patients)
Diagnostics
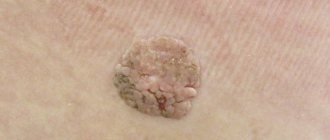
Diagnosis of the disease is based on visual examination, hardware and laboratory tests. Externally, as already mentioned, atheroma looks like a painless bulge on the skin. The capsule is mobile and can move under the skin under mechanical stress. Atheroma can be detected in areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands. A cyst often appears on the face, scalp, behind the ears, and on the back. Education is characterized by slow growth.
In a calm state, a cyst on the body does not cause physical discomfort to patients. However, in the presence of an inflammatory process, the tumor can look quite scary - redness and swelling of nearby tissues, thinning of the skin in the area around the tumor. Touching the subcutaneous lump can be extremely painful. The size, condition of the cyst and its location influence the choice of treatment tactics.
Chalazion
Synonyms: chalazion, hailstone.
A chalazion is a cyst of the sebaceous gland on the upper or lower eyelid, caused by a blocked duct.
A deep chalazion comes from the meibomian gland; superficial chalazion - from the Zeiss gland.
A chalazion is a dense, round tumor, ranging in size from a pinhead to a large pea.
At the maximum volume from a minor injury (rubbing the eye), the secretion comes out into the surrounding tissues.
In the soft tissues of the eyelid, the secretion of the gland (foreign body) causes a lipogranulomatous reaction.
Acute pain, erythema, swelling appears; later a chronic, non-painful nodule forms.
Histology shows many foci of granulomatous inflammation around small lipid spots.
Drawing. On histology, chalazion: foci of lipogranulomatous inflammation around empty spots previously filled with lipids (lipids removed from treatment); the inflammatory infiltrate consists of neutrophils, plasma cells, lymphocytes, epithelioid histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells.
In the first days, the appearance of a chalazion is difficult to distinguish from an infection of the glands of the eyelid - barley.
Styes are internal - meibonian glands, external - glands of Zeiss or Moll near the eyelashes.
Primary meibomian gland cancer initially occurs as a chalazion; prone to metastases.
WHERE DO ATHEROMAS COME FROM?
For one reason or another, the duct of the sebaceous gland becomes clogged, and the resulting sebum ceases to be excreted; it begins to accumulate, stretching the duct - this is how the atheroma grows in size.
Due to damage to the skin, epidermal cells enter the sebaceous gland duct, and right in the duct they produce keratin - a dense mass is obtained that accumulates and does not come out due to excessive viscosity.
Regardless of the mechanism of occurrence, the clinical course of atheroma is the same. Susceptibility to the formation of atheromas is observed with acne. Acne causes clogging of the sebaceous gland ducts.
Ducts also become clogged for the following reasons:
01 metabolic disorders causing changes in the thickness of sebum;
02 mechanical trauma to the sebaceous glands (when acne or pimples are squeezed out);
03 inflammatory processes of hair follicles, causing a slowdown in the release of sebum;
04 hormonal changes;
05 improper use of decorative cosmetics;
06 excessive sweating;
07 genetic diseases
Attempts to squeeze out epidermal cysts are usually unsuccessful, because the contents are located in a capsule in a hard shell and have a fairly large volume. And the viscous, dense consistency of the contents does not allow it to freely exit through the too narrow lumen of the gland duct. Sometimes it is possible to squeeze out part of the contents with the risk of introducing an infection from the outside and “earning” an inflammatory and even purulent process.