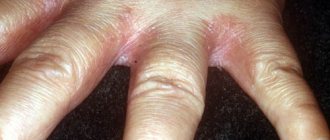
Causes of peeling skin in children
Children quickly react to factors in the space around them. In addition to dry air and the adaptation period after birth, there are a number of other reasons for the appearance of peeling:
- improper care and hygiene violations;
- reaction to dry air or cold;
- allergic reaction to hygiene products, food;
- clothing made of synthetic materials;
- congenital diseases;
- lack of vitamins A and E.
Each of these reasons is widespread, but they are not always immediately excluded as a provoking factor. Dry air can be humidified. The optimal indicator for an infant is 50-60%. If necessary, it is recommended to change shampoos, soaps and bathing gels to hypoallergenic ones. Children 1 year of age and older may have a helminthic infestation. This provokes intoxication of the body, and hence skin manifestations. With treatment and regular care, peeling goes away.
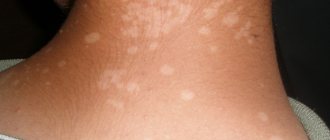
Capillary malformation - symptoms and treatment
Laser therapy is the main treatment method for capillary malformation. It is carried out only with selective lasers, since their waves act exclusively on blood hemoglobin [2][3][4][10].
Laser radiation affects the upper layer of capillaries, which causes sharp heating of red blood cells. As a result, the capillary either ruptures or sharply narrows.
Laser therapy can be started at any age, but optimally from the 1st month of life. If treatment is carried out under anesthesia, laser treatment is performed on average three times a year, but no more than four. It is believed that for successful socialization in society it is necessary to achieve the maximum result of treatment before starting school.
Laser treatment has its complications : temporary (reversible) and permanent (irreversible). All of them arise due to the thermal effect of laser radiation on tissue.
Swelling, redness and bruising are temporary complications. They indicate the effectiveness of the procedure and usually disappear 7-10 days after treatment.
Irreversible changes occur when the skin is overexposed to radiation. The resulting burn can lead to the appearance of a scar. These complications can be avoided by choosing a competent specialist and the right laser.
Another hardware treatment method is IPL - intensive pulselight, i.e. intense pulsed light . Unlike laser, IPL represents broadband light. Essentially, this is a powerful lamp, to cut off unnecessary ranges of which special filters are used. This technology is often used in cosmetology to treat skin diseases, including the treatment of capillary malformation.
Before the advent of laser technology, the main method of treating port-wine stains was surgical removal of the altered skin with plastic correction of the resulting defect. Hours of traumatic surgery were performed, often leaving disfiguring scars that caused more discomfort than the spot itself.
Sclerosation - administration of a drug (sclerosant) through an injection - is used in the treatment of combined malformations, for example capillary-venous. This method is not used in the treatment of simple port-wine stains due to the lack of a cavity into which the drug must be injected.
The use of beta-blockers in the form of systemic (propranolol, atenolol) or local therapy (timolol, arutimol) in the treatment of capillary malformation is ineffective, since they do not act on capillary angiodysplasia.
Among other things, experimental work is currently being carried out on the use of the drug sirolimus as systemic and local therapy, but this method has not yet received widespread use.
Signs of low hemoglobin in a child
Pathological conditions of the body can be temporary or chronic. This is an indicator of low hemoglobin in the blood. This is one of the factors that disrupts the normal functioning of the skin. In the first days of life, hemoglobin is at the level of 180-240 g/l, and by the end of the first week it drops to 200 g/l. The norm for children over 1 year of age is 120-160 g/l. If your child's skin is peeling, it means his hemoglobin level may be low. Pay attention to the following signs: lethargy and drowsiness, moodiness, weakness, decreased appetite. In school-age children with low hemoglobin, disruptions in learning and memory are observed. A characteristic symptom is pale skin color.
When to see a doctor
A dermatologist will be able to help you deal with the symptoms and complaints of young patients after diagnosis at an appointment. He will determine why the child’s skin is peeling on different parts of the body. Leading specialists with extensive experience in dermatology and pediatrics work at JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) in the center of Moscow. Various peelings are not always the cause of pathological conditions. Seek advice when your child develops severe itching and the location of dry patches begins to increase and change shape. In advanced cases, the skin may peel off (peele).
Diagnosis of skin conditions
At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) you can conduct a comprehensive examination of the health status of children. When a child’s skin on his body peels, a dermatologist conducts an examination and asks about the time of onset of symptoms and their nature. Of the main diagnostic methods, ultrasound may be needed to identify the relationship of pathologies with the condition of internal organs and laboratory tests:
- blood test (biochemical, general, antibodies and antigens);
- analysis of scrapings from the peeling area (microscopy);
- histological and cytological studies;
- flora culture to determine sensitivity.
Possible diseases: symptoms
Peeling is not always such a harmless phenomenon. The reasons for its appearance may be not only living conditions, hygiene procedures with detergents and the influence of temperatures. Congenital, autoimmune, chronic diseases are causes of concern for parents.
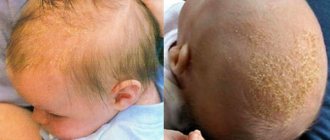
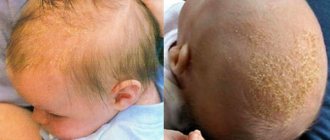
Seborrheic and atopic dermatitis
You should definitely seek advice if you have a history of seborrheic and atopic dermatitis. In the first case, the phenomenon in the form of dense brown-yellow crusts on the head is typical for all newborns, but they can also appear in preschool children. This type of seborrheic dermatitis usually resolves as the enzyme system strengthens with age. If we are talking about its other signs, when flaky spots on the child’s skin appear on the cheeks, forearms, and chest (red in color and irregular shape), the diagnostic tactics are different. There may be disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which will be investigated. Atopic dermatitis is a more complex disease. If you notice that your child’s skin is too dry, he scratches it a lot under the knees, on the neck and on the bend of the elbow joints, you need control of a dermatologist. Without treatment, atopic dermatitis can spread throughout the body as we age.
Severe peeling of fingers
Localization of skin problem sites indicates different causes. Contact your dermatologist if your child of any age experiences peeling and itching between the toes—it could be scabies. The manifestation of such a symptom on the lateral surface of the fingers presumably signals a fungus. Silvery-white scales are characteristic of psoriasis or lichen. An urgent consultation is needed if a fever develops, which is typical for scarlet fever.
Manifestation of dry skin on the legs
If a child has peeling skin on his legs, the reason may lie in vitamin deficiency. In newborns, as they grow and receive sufficient feeding, the deficiency eliminates itself. If there is no improvement, the dermatologist prescribes vitamins in the right dosage according to age. The causes may also be gastrointestinal diseases, for example, dysbiosis. In case of peeling and itching in preschool and school age, children should be examined for the presence of fungal infections.
Rare disease - ichthyosis
This disease is rarely found in its classical manifestation, but about 30 varieties are known to medicine. At different stages of the disease, skin lesions appear from mild roughness, pityriasis-like peeling to severe forms. The epidermis resembles the scales of a fish. The main symptoms are: thick, keratinized areas of skin, severe itching and overheating of the body due to impaired sweating. The disease requires medical monitoring and daily correction of the skin condition with creams, ointments, gels, water treatments, etc.
Prevention and advice
The doctor determines why a child’s skin is peeling. At home, preventing this phenomenon is to use a humidifier. This is especially important during the heating season. Preventive measures also include the following:
- apply baby cream to the skin before walking in the cold season;
- exclude synthetic clothing from your wardrobe;
- select household chemicals from the children's segment (powders, rinses);
- do not wrap your child up too much at home or on the street;
- bathe babies and older children not in hot water (maximum 37);
- monitor your drinking regime (avoid dehydration);
- stick to a diet without foods that cause allergies;
- avoid vitamin deficiency.
“White” and “red” fever in children: what is it and why is it dangerous?
“White” fever is a very dangerous condition in which you urgently need to call a doctor. Anna Khoperskova, an infectious disease specialist at the Russian Railways Medicine children's clinic, spoke about the difference between “white” hyperthermia in children and the usual “red” one.
There are two conditions for fever: “white” and “red” fever.
“White” hyperthermia in children is the most dangerous. Therefore, if a child has pale, marbled skin, with a bluish tint to the nail beds and lips, the limbs are cold to the touch, the “white spot” symptom is positive when pressing on the skin, behavior is disrupted (the baby becomes indifferent, lethargic), delirium and convulsions are possible, immediately call a doctor, or better yet, an ambulance or emergency care,” the doctor recommends.
Under no circumstances should you give your child medications on your own, especially those containing acetylsalicylic acid and metamizole.
As for “red” hyperthermia, it is characterized by reddish skin - hot and moist to the touch, warm extremities, rapid pulse and breathing against a background of rising temperature. With “red” fever, the child’s behavior does not change.
“An increase in temperature or fever is a protective mechanism of the body, provided by nature as a reaction to exposure to pathogenic stimuli. During an illness, the essence of its occurrence is to increase natural protection by restructuring thermoregulation processes with the formation of higher body temperatures than in a healthy state,” explained Anna Khoperskova.
The causes of fever, in addition to a reaction to infection, can also be: overheating, metabolic or endocrine disorders, conditions after transfusion, allergic reactions, and the use of a number of drugs.
An infectious disease specialist at the Russian Railways Medicine children's clinic warned: playing games on the phone and watching TV should be avoided during treatment for “red” hyperthermia. Audio fairy tales and reading books can serve as a substitute. It is recommended to reduce the temperature using physical methods:
- undress the baby as much as possible;
- apply a cool, wet bandage to the forehead;
- regularly ventilate the room (without creating drafts);
- blow with a fan;
- wipe the body with water at room temperature;
- apply cold to the projection of large vessels (in the axillary and groin areas, on the side of the neck) and the liver area;
- to drink a lot of water.
It is recommended to take antipyretics at temperatures above 38.5 degrees. You don’t have to give medications to a child if he drinks a lot of fluids, is active, eats food as usual, has no toxicosis, and feels normal.
“It is necessary to give the child’s body the opportunity to develop that level of protective antibodies, which in the future, when encountering this infection, will help the child not get sick again or suffer from a mild form of the disease,” the doctor concluded.
Antipyretics must be given to those children who are at risk for developing complications due to high fever.
How to make an appointment with a dermatologist
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist at the pediatric department of JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) using the form on the main page of the site. It is necessary to enter feedback information in order to agree on a convenient time and date for a visit with the child.
If it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor can additionally refer you for examination to other specialized specialists: an allergist, an immunologist, etc. Contact reception number for questions and appointments with doctors. The clinic has a convenient location in the Central Administrative District near the Mayakovskaya metro station at the address: Moscow, 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10. Other stations are within walking distance: Belorusskaya, Chekhovskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya " Qualified doctors with extensive experience treat young patients with care and attention.
Take care of the health of your children together with JSC “Medicine” (clinic of academician Roitberg).