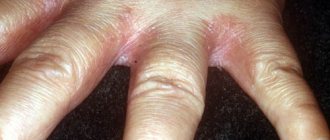
Causes of roughness on the face and head
On the skin of children's faces, more often on the cheeks, rashes and roughness are caused by allergens of household origin, that is, food products. The reason for this manifestation is the products consumed by the nursing mother or those introduced into complementary foods. The baby’s digestive tract is not yet able to cope with the latter, for example:
- Whole cow's milk.
- Chicken eggs.
- Citrus fruits and nuts.
A rash appears in the form of red or pink spots that are flaky and very itchy. Redness behind the ears of newborns may appear due to the frequent flow of formula or breast milk into this area, the excess of which is not eliminated by parents in a timely manner.
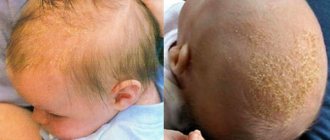
A dry spot on the fontanelle or forehead is observed in almost all newborns. If parents do not take measures to combat this, after some time the dry scales will spread throughout the head and will not allow the hair follicle to develop. You can eliminate roughness on your head with the help of special baby oils and a soft brush; with their help, you need to remove dry scales every day and very carefully to prevent them from spreading.
The pediatrician will give a more detailed recommendation for eliminating rough skin on the face and head after examining the baby, and will also recommend a nutritious diet after allergies.
Rough and dry skin on a baby's belly most often occurs due to the following reasons.
Walks in the open air
If peeling appears on the skin, walks are not canceled. They must be daily. You should not keep a newborn with dry skin in direct sunlight for a long time.
Children with skin problems are protected from direct sunlight
If it's hot outside, use UV creams for protection. At any age, children benefit from regular air baths, as well as short light massages.
You should not keep a newborn with dry skin in direct sunlight for a long time.
Features of children's skin
A baby's skin is significantly different from the skin of its parents. She is more vulnerable, gentle. Sweat glands are not sufficiently developed in the first year of life, and therefore the baby has to transfer excess heat through pulmonary breathing. If at the same time the baby has to breathe too dry air, or he lives in a room where, thanks to the efforts of his mother and grandmother, it is hot all the time, then the load on the immature sweat glands increases and the skin deteriorates.
The stratum corneum (the uppermost layer) of children's skin is well supplied with blood, so any scratches on a baby heal faster than on an adult. However, the stratum corneum, which is thin and loosely connected to other skin layers, creates favorable conditions for irritation and injury.
Initially, dry skin in babies practically never occurs due to the saturation of lipids - an innate feature of all toddlers. But these fats perfectly dissolve most of the chemicals that are contained in washing powder, soap, and urine, and therefore inflammation of the skin in children is common. Dry skin can also become due to health problems.
The most common cause of dryness, in which the skin becomes somewhat rough to the touch, is contact dermatitis, says Evgeny Komarovsky.
Features and functions of baby skin
Newborns have very thin, easily vulnerable skin, which loses heat very quickly. It also has an insufficient pH level up to a certain point, which causes various microbial diseases.
In addition, infants have a very low concentration of melanin, a pigment that protects against ultraviolet rays.
The thickness of children's skin becomes close to adult parameters only by the age of 7 years.
The epidermis is the most important part of the human body and performs the following functions:
- Protective. In newborns, this quality is poorly expressed, so their skin is often inflamed and damaged.
- Respiratory. The skin absorbs oxygen and evacuates carbon dioxide. The intensity of skin respiration in infants is much stronger than in adults.
- Sensitive. Receptors that perceive irritation are localized in the skin. In infants, the most sensitive parts of the body are the hands, face and soles of the feet.
- Thermoregulatory. The epidermis gives off heat and evaporates sweat. In babies, thermoregulation is imperfect, so they quickly overheat and become hypothermic.
- Immune. The skin contains cells that carry out many immune responses.
The epidermis is the place of formation of biologically active substances, enzymes and vitamins. This is why it is so important to keep your skin healthy.
Dry skin in a newborn is a natural phenomenon caused by a change in microclimate.
Diathesis (exudative and allergic) in a child
In newborns and infants, flaky areas of skin on the face, tummy, butt, back, arms and legs often appear due to diathesis. Contrary to popular misconception, this phenomenon does not apply to diseases. This is nothing less than a constitutional anomaly. In pediatrics, this term refers to the hereditary predisposition of the body to the appearance of certain pathological reactions or diseases. The table shows the characteristics of the types of this phenomenon.
Bathing helps keep your baby clean and also promotes better blood circulation.
Dry skin on feet
As already mentioned, roughness and dry skin can appear in various parts of the body. Very often such lesions occur on the skin of the legs. Most often, rough skin on a child’s legs is observed in the summer, when high temperatures and wind dry the legs, it cracks and hurts due to loss of moisture. During this period, it is recommended to wear sandals or other shoes that allow your feet to have maximum air access.
- For better security, it is advisable for the child to wear socks - this will protect the feet and prevent dirt and dust from getting on them, especially if there are already cracks and wounds.
- Before putting your child to bed, it is imperative that you carefully care for his feet. Use baby soap for washing. After this procedure is completed, the feet should be wiped dry, and then a special fortified cream should be applied to soften the skin. It should be rubbed in, carefully massaging the area to be rubbed. This will eliminate roughness of the skin of the legs and reduce its sensitivity, as well as avoid complications.
- With all the well-known prickly heat, the appearance of diaper rash, as well as diaper dermatitis, parents also need to show care and concern. After all, they tend to spread quickly and even in some cases lead to the formation of a pustular rash. There may be no consequences if the child is shown to a doctor in a timely manner and treatment is started.
During this period, it is recommended to wear sandals or other shoes that allow your feet to have maximum air access.
Prevention of dry and flaky skin in children
Everyone is familiar with the well-known truth that it is always easier to prevent a disease than to undergo long and expensive treatment later.
Dry skin and the appearance of flaky spots are no exception, and you need to think about preventive measures in advance.
Use only high-quality mixtures from well-known manufacturers.
Prevention measures
To avoid dry skin, offer your child something to drink often. Make sure there are enough vitamins in his diet. Moisturize your baby's skin after bathing. In your care, use only hypoallergenic products tested by dermatologists.
The creams should include moisturizing and soothing components: panthenol, niacinamide, oils (shea, olive, wheat germ), zinc oxide, vitamins A, B, E, F, plant extracts (chamomile, calendula, string).
Exposure to cold and dry indoor air contributes to excessive dryness of the skin.
Worm infestation
The appearance of dry patches on parts of a child’s body sometimes indicates the presence of parasites in the child’s body. This reason is detected extremely rarely; experts generally associate changes in the condition of the skin with the above factors. Doctors consider dry skin as a reaction to toxins. With this diagnosis, the child will be prescribed antiparasitic treatment.
Treatment of dry skin in children.
Causes of dry skin in newborns
Among the medical problems of dry skin in children, perhaps the first place is occupied by atopic dermatitis. The disease is based on a genetic defect in barrier function, resulting in increased loss of moisture. The disease begins at an early age and is characterized by dryness, itching, and during periods of exacerbation - the appearance of inflammatory foci. If an exacerbation must be eliminated with medications, then in the period between exacerbations, the care recommended by the doctor must be carried out daily. Typically this is the use of emollients.
LIPIKAR BAUME AP+M
Lipid-restoring balm for face and body
Relieves dry skin in children. Instantly soothes atopic skin, reduces itching and irritation, and increases the intervals between outbreaks of excessive dryness.
581 rub. more details
Ichthyosis is another cause of dry skin in newborns. This is a congenital disease, which is accompanied by a violation of keratinization of the upper layer of the epidermis. As a result, fish-like scales can form on the body, hence the name of the disease. This is not a very common disease, it can occur in different ways, from mild manifestations to severe conditions requiring constant therapy.
Diseases of the endocrine system (underfunction of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus), helminthic infestation, some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, deficiency of certain vitamins A and PP are also reasons why a child has dry skin. Regular monitoring of the baby, periodic examinations by a pediatrician, and timely treatment, if required, will allow these causes to be suspected and eliminated in a timely manner.
If a child has dry skin on his body, there are other reasons. In the first month of a baby’s life, physiological dryness of the skin may develop. In utero, the child is in an aquatic environment, and after birth it moves into an air environment, and it takes time for the baby to adapt. The main cause of this condition is the insufficient functioning of the sweat glands, which begin to activate after birth. Physiological dry skin can manifest itself in the form of peeling all over the newborn’s body. Gradually, over the course of a month, this physiological condition disappears. After water procedures, it is enough to moisturize the baby’s skin with a light cream or special milk. For example:
LIPIKAR LAIT
Unscented milk for dry to very dry skin
Nourishes and restores the lipid barrier of the skin. Suitable for small children and babies.
992 rub. more details
But if the skin of a one-year-old baby is excessively dry, this is a reason to consult a doctor to get recommendations for care to avoid the development of complications.
Any inflammatory process, be it a cold or a more severe condition, accompanied by a rise in temperature contributes to the loss of moisture from the body. Dyspeptic symptoms, insufficient drinking, frequent diarrhea or poisoning of the child are accompanied by loss of fluid, and, as a result, dehydration develops. One of the manifestations of this condition will be very dry skin in a child, which can be corrected by moisturizing the face and body with baby light cream or milk.
Only after the age of 6 years does a child’s skin become like that of an adult. And before this age, it is characterized by high permeability and therefore loses natural moisture much easier and faster. It is more vulnerable to injury, and through damage it can become infected, especially in infancy. Therefore, it is important to carefully monitor and care for her every day.
If your baby develops areas of irritation or dryness as a reaction to food, contact with a substance, or after being in the sun, we recommend that you consult a doctor. The causes and treatment are always different, and the wrong medications and creams can lead to serious skin lesions.
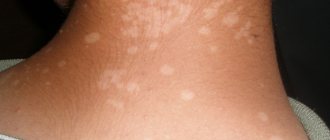
Hives
In appearance, this reaction is similar to traces of a nettle burn; the skin becomes rough, bumpy, swells, sometimes blisters appear (and sometimes the matter is limited to swelling). The rashes are itchy and may be painful to the touch. The skin and mucous membranes are affected, the rash can spread throughout the body, on the back and abdomen, or be located only in certain areas (for example, with increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, solar urticaria appears only on open areas of the body).
Hives can be triggered by food allergens (honey, citrus fruits), medications, insect bites, even cold and sun.
What distinguishes urticaria from skin diseases is the rapid appearance of many elements, while in skin diseases the rash begins with 1–2 elements and spreads over some time. Also, unlike skin diseases, rashes with hives last 1–2 hours, after which they disappear. The danger of this condition is that swelling of the mucous membrane can spread to the tissues of the larynx and impair breathing - this is called Quincke's edema. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
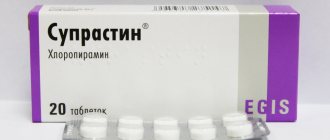
To treat urticaria, it is necessary to eliminate the allergen and take an antiallergic drug (loratadine, fexofenadine, cetrin). For food allergies, sorbents (Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel, Filtrum) are recommended; they will bind some of the allergens, preventing them from entering the blood. Fenistil can be used topically.
External factors that cause dry skin in a child
Dry skin in a one-year-old child may not only be due to medical problems. Improper or excessive care, too frequent bathing, poor nutrition, and climate affect the condition of the dermis. Using very hot water or very hard water when washing will dry out your skin. We recommend paying attention to special mild detergents, monitoring the water temperature when bathing (not higher than 37°C), choosing soft towels and using a moisturizing or nourishing cream after a bath.
Another external cause is dry air and overheating. Thermoregulation processes in babies are poorly developed and continue to develop after birth, so the baby cannot quickly and adequately respond to overheated air or excessive wrapping. This is also due to the fact that the sweat glands after birth do not function sufficiently and have underdeveloped ducts. First of all, the formation of sweat glands ends on the forehead and head, then on the chest and back. The formation of the sweating function occurs over 7 years.
It is recommended to use a humidifier at home, especially in winter when the heating is running (the recommended humidity in the room should be 40-70%) and preference for light clothing that does not allow overheating (sometimes the easiest way to determine may be to feel your back and neck under clothing - they should not being hot or wet, as well as red cheeks in a baby with normal, non-rough skin are signals of overheating).
Another feature is the incomplete formation of melanin in children, a pigment that protects the skin from UVA rays. Therefore, until the age of 6 months, the baby should avoid direct sunlight, and at an older age, do not forget about sun protection. Up to a year, a child can be in the open sun for no more than five minutes a day, and only with a special children's sunscreen. Ultraviolet light dries out the skin and also increases the risk of cancer.
Frost and cold air are another challenge. Under the influence of bad weather in autumn and winter, the development of redness, dryness, peeling and irritation of the skin is possible. What to do to avoid dryness? Use cold cream (or emollient) about 20-30 minutes before leaving the house to prevent chapping of your baby's face and hands.
If your child’s dry skin lasts for a long time, you should first contact your pediatrician to rule out various diseases. If you have a skin rash, you may need to consult a dermatologist. Following your doctor’s recommendations, as well as proper daily care, will help you cope with dryness.
Allergic diseases
Allergy is one of the main problems of our time: according to WHO, a third of the population of developed countries already suffers from one or another of its manifestations, and in the future the number of such patients will increase. Proponents of the hygienic theory of allergies believe: the problem is that we live in a too clean, almost sterile world, and the immune system, due to the lack of real “enemies,” attacks the proteins of its own body.
Allergic reactions and diseases associated with excessive allergic readiness of the body often manifest themselves on the skin.
Rules for caring for dry baby skin
Caring for a child’s skin during the day consists of several stages: washing the face, washing hands, washing intimate areas after each bowel movement, and bathing.
It is permissible to bathe a baby every day, as it not only cleanses the skin, but also calms the child, strengthens him, awakens his appetite, improves tactile and emotional skills, and improves psychological contact with parents. One of the mistakes parents make is bathing their child for a long time in a bath with potassium permanganate. Such bathing dries out the skin and is not advisable to use. Contraindications for water procedures are high body temperature and the presence of purulent-inflammatory diseases or open wounds on the body.
Bathing water should be soft and, if necessary, filtered. The water temperature should also not be high; it is optimal if it is 34-37° C. In order not to damage the protective hydrolipidic layer of the baby’s skin, it is not recommended to use bathing products every day. Pay attention to special products for babies that have delicate formulas and have been tested by pediatricians and dermatologists.
LIPIKAR GEL LAVANT
Soothing shower gel with protective properties
Soothes the skin, thanks to the action of Niacinamide and the lipid-restoring properties of Shea Butter, helps restore the skin's protective barrier. Suitable for cleansing the skin of the face and body, does not irritate the eyes.
719 rub. more details
This gel can also be used to cleanse babies' heads and for daily intimate hygiene when changing diapers. Washing should be as gentle as possible; it is not recommended to use washcloths made of rough materials.
After bathing, dry the body and apply a moisturizer. The towel should not be hard, you should not rub the baby’s skin too much, it is better to gently blot away excess moisture. You can use a terry bathrobe. During the first 3-5 minutes after bathing, while the skin is still damp, it is advisable to apply a moisturizer. You can use Lipikar Lait milk . It has a rich formula based on cold cream - a classic combination of protective lipids, enriched with Shea butter (10%) to restore the lipid barrier. Suitable for very dry skin of children and adults. And niacinamide provides long-lasting comfort to even the driest, most delicate and sensitive skin.
Create a favorable microclimate in the room where the child is. The air should not be dry, the temperature should not be higher than 18-22°C. Monitor the humidity, ideally if it fluctuates in the range of 40-70%. To maintain humidity, you can purchase a humidifier. During the heating season, it is necessary to shield the batteries; you can cover them with a wet towel to evaporate moisture.
Choose clothes made of cotton fabric, it breathes well and absorbs excess sweat well. Give air baths while changing diapers. When walking, do not wrap your baby tightly to avoid sweating.
During the summer, avoid going out in the sun during the hottest hours, from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m., or when the ultraviolet index is above 4 (just check this indicator in the Weather app on your smartphone or almost any website to determine the weather forecast). Be sure to wear a Panama hat or a hat for your child to protect from the sun; on the beach, it is better for your child to wear a closed swimsuit or T-shirt. Do not neglect sunscreens; choose them according to the child’s age. Be sure to reapply the cream every few hours according to your child's skin type and sun exposure that day. When you return home, wash off any remaining sunscreen and apply moisturizing milk to your skin. For mild sunburn or redness of the skin, you can use:
CICAPLAST BAUME B5
Multi-regenerating and healing product for baby skin
Due to its rich, nourishing texture, it protects the skin and creates a barrier that prevents bacteria from reaching the surface. Panthenol in the composition promotes the healing of irritated skin.
654 rub. more details
When to consult a doctor
There are situations when a child needs immediate medical consultation. You need to make an appointment if dry, rough skin is accompanied by one of the following conditions:
- Bleeding from cracked skin.
- Severe itching that makes the child restless.
- Pus or yellow discoloration on dry, rough skin.
- Swelling of the skin.
- Dry, very rough skin is accompanied by fever.
- Dry skin causing colic outbreaks.
- These pathologies are treatable and it is important not to delay their elimination so that complications do not arise.
What to do to prevent your child's skin from drying out
Preventive measures against dry skin:
- regular care;
- drinking regularly;
- balanced diet with sufficient vitamins;
- use of special soft care products tested by pediatricians and dermatologists.
Baby bathing and care products are marked on the packaging: “suitable for the use/care of the skin of infants and children”, “suitable for children” or the like. Plus, as a rule, the production of children's products is subject to higher requirements for the safety of formulas and stricter selection of components included in the formula.
Folk remedies for dry epidermis in children
For physiological dryness and xerosis caused by non-pathological factors, you can use some traditional medicine recipes. Many medicinal plants have anti-inflammatory properties and also provide additional care for the baby’s skin. In this situation you can use:
- chamomile infusion;
- infusion of calendula, string, St. John's wort, eucalyptus, celandine;
- lotions with raw grated potatoes on places where there is increased dryness, accompanied by signs of atopy;
- moisturizing the epidermis with vegetable oils (olive, castor, sunflower, geranium oil, etc.).
Folk remedies are considered highly effective methods of combating dryness and inflammation of the skin. But since we are talking about a child, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician before using them.