Dermatovenereologist (cosmetologist)
Baichorova
Marua Azretovna
21 years of experience
Dermatologist (cosmetologist)
Make an appointment
Sweating is a natural mechanism formed during the process of evolution. Its primary function is body thermoregulation. Almost all mammals have sweat glands. When the body heats up, they are activated and release a specific liquid that cools the body during evaporation. Sweating is also involved in the process of removing excess water, metabolic products, salts and other substances through the skin. That is, this is a natural process, but for some people it proceeds too rapidly, even for no apparent reason. The phenomenon is called hyperhidrosis.
Normal sweating
Hyperhidrosis is not a disease, but rather an individual characteristic of the body, which causes a lot of trouble in everyday life. Normally, increased sweating is a common reaction to the following factors:
- temperature increase;
- physical exercise;
- stress;
- hot and spicy food;
- hormonal changes associated with menopause, pregnancy, puberty.
In addition, it can be a side effect when taking certain medications.
With little physical activity, a person produces about 0.5 liters of sweat per day, but as temperature and load increase, this volume can increase to 10 liters. Sweat glands respond to signals sent by the brain in two ways:
- increase or decrease the amount of sweat;
- open for active release of moisture, or close.
Types of hyperhidrosis
There are primary and secondary hyperhidrosis. The first is a permanent property of a person; it begins to manifest itself in childhood or adolescence, while the work of the sweat glands deviates from the norm. They may open too quickly or not close at all, causing increased sweating even in a cool room. The reason for this phenomenon still remains unclear.
The second develops in certain diseases. Among them:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- tuberculosis;
- neurasthenia:
- syphilis;
- rheumatism;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- diabetes;
- a sharp decrease in blood glucose levels;
- oncology;
- hyperthyroidism.
Statistics say that about 5% of people in the world suffer from primary hyperhidrosis, which is equally common in men and women, and secondary – about 15%. It manifests itself locally, only in certain places where the largest number of sweat glands accumulate (under the arms, on the feet, head, face, palms, groin), or generalized. And although this condition does not pose a threat to health, excessive hydration can have unpleasant consequences:
- local swelling, redness and inflammation;
- body hypothermia;
- psychoemotional disorders.
Are you experiencing symptoms of hyperhidrosis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
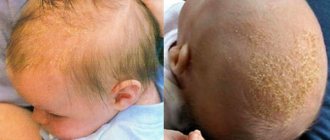
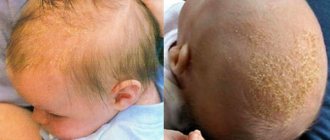
Exfoliative keratolysis – what is it?
Recurrent focal palmar desquamation is symmetrical peeling on the palms, fingers, and in some cases on the soles of the feet. Characteristic signs of the disease are severe dryness of the skin and the presence of air bubbles.
The condition is often mistaken for eczema, psoriasis or contact dermatitis, so it is important to undergo all examinations recommended by your doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Exfoliative keratolysis is a pathological desquamation of epithelial scales. This occurs as a result of mass death of keratocytes due to negative processes occurring in the child’s body and insufficient production of new cells. Unprotected fragments appear on the baby’s fingers; they are visible to the naked eye and cause discomfort to the baby.
Which doctor should I contact? Diagnostics
If you have hyperhidrosis, you should first consult a therapist, who can refer the person for further consultation to the following specialists:
- a dermatologist if there are signs of dermatosis and inflammation of the sweat glands;
- to a neurologist if autonomic disorders are suspected;
- an endocrinologist to rule out diabetes mellitus and thyroid dysfunction;
- cardiologist, for angina pectoris;
- an orthopedist, since sweating of the feet often accompanies flat feet;
- a psychotherapist if the problem is psychological in nature.
In order to determine the degree of hyperhidrosis and areas of increased sweating, the Minor test is used. Take a 2% iodine solution, apply it to the skin area under study, dry it and sprinkle with starch. If sweating exceeds the norm, the skin turns purple and sometimes black. These areas are then marked for subsequent treatment.
Child’s body – white spots, red spots, skin rashes
Possible diseases whose symptoms are white spots:
- Pityriasis versicolor Fungal disease of the epidermis. At the first stages it appears in the form of flaky spots of a pinkish color, and when exposed to sunlight, the spots become more noticeable and acquire a white color. Usually the location is the neck, chest, shoulders, back.
Among the reasons for the occurrence of such unaesthetic spots:
- increased sweating
- hormonal changes (typical for teenagers)
- failure to comply with hygiene rules
This disease is not dangerous. The main thing is to contact a dermatologist in time, who will prescribe the appropriate antifungal ointment.
- Vitiligo is a disease associated with abnormal pigmentation of the skin, resulting in distinct white heels that may peel. Most often, this disease is hereditary. In addition, the disease can develop after an infection, due to disturbances in the functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems, and in autoimmune diseases
Red spots appear on the body much more often and in most cases are not symptoms of serious diseases. However, the reasons for the appearance of redness may be:
- allergy
- stress
- insect bites
- infectious diseases (measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever, rubella)
Redness usually does not occur on its own without other symptoms. With the exception of cases when we are talking about temporary redness when a child cries, overheating, or nervous feelings. In other cases, red spots are accompanied by additional symptoms. Most often, this is a rash, itching, peeling, depending on the combination of which one can suspect the presence of a particular disease.
- Rashes in children , especially at an early age, are a common occurrence. For young children, redness combined with a rash may indicate the presence of heat rash, diaper rash or allergies.
- Miliaria and diaper rash are characterized by wet red spots in the folds of the skin, which arise due to excessive overheating of the child, poor hygiene
- If there is redness + rash + peeling, the vast majority are symptoms of an allergy, which the child may outgrow. In older children (after one year), rashes on the body can be the result of infectious diseases, each of which has its own symptoms and requires timely diagnosis by the attending physician
How to treat hyperhidrosis
If secondary hyperhidrosis is diagnosed, the underlying disease should be treated to eliminate it. In the case of primary, general tonic agents are often prescribed; it is also recommended to use disinfecting and skin-drying powders and strong antiperspirants. Sometimes treatment with a psychotherapist is also required. If the above methods do not produce results, more serious therapy is recommended.
Iontophoresis
This method has proven itself well for hyperhidrosis of the palms and feet. To do this, the hands and feet are immersed in warm water, through which a weak electrical discharge is passed. There are no painful sensations. To noticeably reduce sweating, two to four procedures of half an hour are enough.
Botox or Dysport
These drugs containing botulinum toxin are widely used in cosmetology to remove wrinkles on the face, due to their ability to block neuromuscular transmission. They have also proven effective in treating hyperhidrosis. They are injected into areas of increased sweating to block the nerve endings that activate the sweat glands. Usually several injections are required, but they last for a certain period (about six months), after which the course will have to be repeated.
Anticholinergic drugs
These drugs are widely used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and spastic paralysis. It turned out that they also help with hyperhidrosis by blocking nerve impulses sent to the sweat glands. A positive effect occurs two weeks after starting to take medications, but they should be taken with caution in case of hypertension, atherosclerosis, problems with the heart, liver and kidneys.
Endoscopic sympathectomy
When previous methods do not produce results, you can decide on surgery - endoscopic sympathectomy, in which the surgeon removes the nerves that conduct electrical signals to the sweat glands. This method can only be used for hyperhidrosis of the palms, armpits and face, and it also has many contraindications.
Hyperhidrosis in children
A child's sweat glands are activated from the 3-4th week of life, but they will become fully operational only by the age of 5-6 years. Due to incomplete formation, the body can react to various stimuli with a violation of thermoregulation. A fun game, prolonged crying, too dry air in the apartment, even evening breastfeeding can cause perspiration on the forehead. And that's okay. It is only important to ensure a comfortable ambient temperature:
- for newborns – 23-24 °C;
- for children 1–6 months – 20–22 °C;
- for children from 6 months to 1 year – 19-20 °C;
- for children over one year old – 17–19 °C.
The apartment should also maintain high air humidity, about 70%.
But sometimes parents may experience increased sweating in their child while sleeping in a rather cool room. There may be several reasons for this:
- Vitamin D deficiency and rickets. In this case, increased sweating is observed on the head, neck, palms, feet, and armpits. At the same time, sweat has a sour smell, it is sticky, and its secretion increases during sleep;
- heart failure. Hyperhidrosis in a child can be observed with congenital heart abnormalities, in addition to this, there is cyanosis of the skin, general lethargy and weakness, and slow weight gain;
- viral or bacterial infections;
- helminthic infestation;
- genetic diseases phenylketonuria and cystic fibrosis;
In adolescence, hormonal changes in the body begin, so nocturnal hyperhidrosis occurs quite often during this period. Over time, the work of the sweat glands normalizes.
A 5 year old child has peeling palms. Why does a child have peeling skin on his fingers: possible reasons
There are an innumerable number of reasons why a child’s skin peels off on his fingers, which means that only a doctor can reliably establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Possible reasons:
- Cold season. Have you noticed that in winter, the skin on your child’s fingers often peels off? The delicate skin of your hands is exposed to cold winds and sudden temperature changes. This leads to the epidermis losing moisture and cracking, thereby causing peeling of the skin. In addition, constant peeling due to the influence of low temperatures provokes the formation of painful wounds.
- Vitamin deficiency. Often the cause of peeling skin is a banal lack of vitamins A and E. This phenomenon is more typical at the end of winter and beginning of spring, when the body has practically used up its reserves. You will see that the skin has become dull and has lost its elasticity. Longer healing of wounds is possible.
- Lack of moisture. Some people drink up to eight glasses of water a day, while others consider this complete nonsense. One way or another, a lack of water in the body can affect the integrity of the epidermis of the palms and fingers.
- Frequent contact with water. Water can not only moisturize the skin, but also harm it. This applies to people prone to dry skin. With prolonged contact with water, the skin begins to itch and peel.
- Chemical substances. In the life of every modern person there are many chemicals. In addition to benefits, unfortunately, they can also cause harm. Curious children may find a bottle of household chemicals, for example, and accidentally get their hands dirty. The baby's delicate skin may react with peeling.
- Allergy. Experts say that allergic reactions of this type are extremely rare, but they do occur. As a rule, the skin on the fingers peels off under the influence of a very strong allergen. To find out the cause of the allergy, it is enough to delve into the child’s history: to understand what new substances or foods the baby has encountered recently.
- Stress. Recently, doctors of various specialties have been paying attention to stressful situations: both positive and negative. In the modern rhythm of life, adults are often exposed to such factors, not to mention children.
- Helminthic infestations and intestinal diseases. The body does not fully receive all the necessary nutrients and, as a result, some children have peeling skin on their fingers.
- Infections. For example, scarlet fever, which develops with pharyngitis or tonsillitis and occurs due to group A streptococci. The child has peeling skin on the fingertips, especially on the pads. An elevated temperature also appears.
Folk remedies for hyperhidrosis
Before deciding on radical therapy, you should try traditional methods of combating hyperhidrosis. The most popular and effective is a decoction of oak bark. In addition to the fact that it helps normalize the functioning of the sweat glands, it also has a bactericidal effect. The decoction is prepared according to the instructions on the package. It should be used as a lotion on problem areas after taking a shower for 20 minutes. You can store it for several days in the refrigerator.
It is useful to wipe areas of excessive sweating with a cotton swab dipped in apple cider vinegar. It is recommended to do this as often as possible during the day, and a compress for 10 minutes before bed will not hurt. For hyperhidrosis in men and women, a contrast shower in the morning and evening is useful. A sharp change in temperature teaches the sweat glands not to react so violently to temperature changes.
Preventing peeling of fingers in a child
Parents just need to follow simple rules:
- do not abuse hygiene - do not teach to wash your hands too often using liquid or bar soap;
- strengthen the immune system from birth: take long walks in the fresh air, do not neglect sports activities, adhere to the principles of a healthy diet;
- protect your baby’s hands from temperature changes - wear gloves or mittens in winter, and lubricate the skin of your hands with moisturizing sunscreen in summer;
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner and be sure to consult a pediatrician.
It is important to monitor the baby’s health from the first days of life so that his well-being does not create reasons for concern!
Prevention
If you are prone to excessive sweating, it is recommended not to consume excessive amounts of alcohol, caffeine and nicotine, which stimulate the sweat glands. It is also recommended not to wear clothes made of synthetic fabrics, but to choose loose-fitting models that do not hug your figure.
If your feet sweat excessively, you should wear shoes and socks made from natural materials that absorb moisture well. However, they should always be worn under closed and sports shoes.
People suffering from hyperhidrosis have to shower more often than others and use stronger antiperspirants, which reduce the amount of sweat produced.
It is also recommended to pay attention to whether there are any side effects in the form of increased sweating from medications prescribed by doctors. Perhaps there is an alternative.
And most importantly: you need to learn to resist stress and control your emotions. Consultations with a psychotherapist, as well as various psychological practices, can help with this.
Rough spots on a child's body
- The appearance of rough patches of skin is a fairly common phenomenon among children in the first three years of life. If you find rough spots with a small reddish rash on your child’s body, most likely you are dealing with atopic dermatitis
- At the same time, in the morning while sleeping, the rash may be invisible and dry, rough skin can only be detected by touch. Spots may appear on different parts of the body, most often on the cheeks, arms or legs. During exacerbations, particularly in winter, the spots become irritated, red and raised
- Atopic dermatitis may be caused by a hereditary immune system that reacts to allergens in food and the environment, as well as a genetic predisposition to dry skin
- Atopic skin needs special care and hydration. In addition, an important role is played by the need to eliminate the allergen, follow a diet and carefully select cosmetics, clothing and everything that comes into contact with the child’s skin.
More information about atopic dermatitis can be found in the article Diet for atopic dermatitis in a child. Modern and traditional treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
Rough or dry skin can also be a consequence of dry air, chlorinated water, abuse of herbal decoctions when bathing, lack of moisture in the body, etc.