December 07, 2020
Chickenpox is an infectious disease caused by the Varicella-Zoster virus (the third group of the herpes family). This disease is treated in children by a pediatrician, in adults by a therapist; the infection is characterized by a profuse itchy rash on the skin and surface of the mucous membranes.
Chickenpox is an infectious disease caused by the Varicella-Zoster virus (the third group of the herpes family). This disease is treated in children by a pediatrician, in adults by a general practitioner; the infection is characterized by a profuse itchy rash on the skin and surface of the mucous membranes. The incubation period for chickenpox can range from 10 days to 3 weeks. Chickenpox is highly contagious and the virus is transmitted through direct contact with a carrier.
Children often get sick in entire groups (groups in kindergarten or classes at school). When the virus first enters the human body, it provokes chickenpox, most often this occurs at the age of 3-6 years. Having chickenpox forms a stable immune response of the body to repeated infection; after 6 years of age, 70% of children already have stable immunity to this disease.
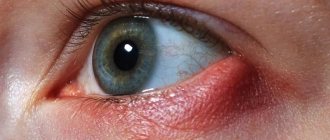
Once infected, the virus remains latent in nerve cells and can regenerate, causing a secondary infection called herpes zoster, also called “shingles.” It usually occurs in adults aged >50 years or in frail and immunocompromised individuals. Accompanied by a painful rash that can lead to permanent nerve damage.
The causative agent of chickenpox
The main causative agent of chickenpox is the varicella zoster virus, which belongs to the general family of herpes viruses type 3.
Infection with the pathology occurs through the air through close interaction with a sick person.
The pathogen itself is very weak in the external environment, and if it does not penetrate the body, it dies instantly after 10 minutes.
If the virus infects the mucous membranes, the infection develops quickly. The pathogen spreads throughout the bloodstream, causing the appearance of characteristic clinical symptoms.
Chickenpox vaccine for adults
For specific prevention, a live vaccine is used. In case of contact with an adult with chickenpox, the vaccine is administered within 72 hours. If a person has contraindications to vaccination, he is given immunoglobulin - normal human or specific zoster.
Contraindications to vaccination
- severe allergic reactions in general and to chicken eggs in particular (administration of the vaccine in the presence of an allergy leads to the development of anaphylactic shock, which can be fatal);
- allergy to aminoglycoside antibiotics - streptomycin, amikacin, gentamicin;
- a sharp decrease in immunity (in people with severely decreased immunity, vaccination causes the development of chickenpox);
- probable or confirmed pregnancy.
Preventive vaccination of adults can be carried out at any age. Two vaccinations should be given 6-10 weeks apart. Vaccination is not included in the National Vaccination Calendar. It is done only in case of contact with a patient or at the request of the person himself at his expense.
Vaccination is easily tolerated; side effects include a short-term increase in temperature. The duration of protection after vaccination is 10-15 years. After vaccination, a person is not contagious unless single blisters appear on the skin.
It is recommended to prevent contact between a vaccinated person and a person who has not had chickenpox for three days.
Vaccination during pregnancy and after it
If pregnancy is planned, the vaccination must be done no later than three months before its onset. Vaccinations are contraindicated during pregnancy.
Breastfeeding is NOT a contraindication to chickenpox vaccination. Thus, a nursing mother can be vaccinated.
Chickenpox symptoms
It is quite difficult to detect viral pathology at the initial stage. Because it has similarities with ARVI and influenza. Subsequently, after infection, characteristic signs of chickenpox appear, which help differentiate the disease from other conditions. Therefore, any doctor, taking into account the overall clinical picture, can accurately make a diagnosis.
As a rule, the main symptoms of chickenpox in adults and children are:
- Intoxication syndrome - this includes headache, high temperature, body aches, enlarged lymph nodes, chills, sore throat and sore throat.
- Weakness and malaise.
- Poor appetite.
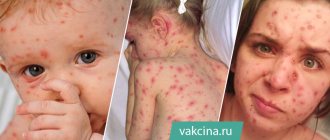
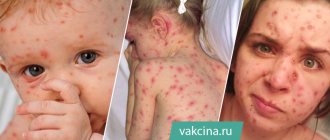
- Skin rashes. Red sores (vesicles) appear all over the body and are filled with serous contents.
- Severe itching.
The very first sign of chickenpox is considered to be an increase in temperature, which occurs 1-2 days before the dermatological rash. It is accompanied by other striking signs of intoxication, usually lasting about 5 days. Chickenpox without fever and catarrhal symptoms is quite rare.
The rash affects all parts of the body, including mucous surfaces and hair. First, spots appear, then medium-sized bubbles with a clear liquid form in their place. After some time, the formations on the skin become cloudy and dry out, becoming covered with a thin crust.
The complete disappearance of papules occurs 2-3 weeks after the onset of the pathological process. The most important thing is to not scratch the skin. Otherwise, infection may occur.
Contagiousness
The cause of the disease is the chickenpox virus, Varicella Zoster. It belongs to the group of herpes viruses and is also called the third type of herpes virus. It is very unstable in the environment and dies when exposed to sunlight. In drops of saliva it remains active for about 15 minutes. The chickenpox virus can spread over long distances, which is why it got its name.
The source of infection is a person with chickenpox. It becomes contagious from the last day of the incubation period - that is, even before symptoms appear. Infectivity ceases on the fifth day after the appearance of the last rash. The spread of infection occurs through airborne droplets - the virus is released with droplets of saliva when sneezing or coughing. In this case, it is not necessary to be in close contact with the patient - the virus can even pass into neighboring rooms through ventilation grilles.
Adults usually become infected with chickenpox when caring for a sick child or when being in the same room as a sick child. Only an adult who did not have chickenpox as a child can get sick. Repeated cases of chickenpox are casuistically rare. The exception is adults with weakened immune systems - cancer, HIV infection.
After chickenpox, the virus remains in the body for life. It is its presence that ensures the maintenance of specific immunity and prevents the occurrence of recurrent cases. Reactivation of the infection occurs against the background of hypothermia, stress, weakened immunity and manifests itself in the form of herpes zoster, which also occurs only once.
Prevalence
In 2022, the incidence in Russia was 570 cases per 100 thousand population. Of this amount, the incidence in adults is only 10%. Men and women get sick equally. Chickenpox is registered in all regions. Chickenpox has a clear seasonality - the peak incidence occurs in autumn and winter.
Kinds
Chickenpox occurs in several clinical forms:
- typical - with malaise and blistering rash (usually without pus);
- rudimentary - with a very scanty rash;
- hemorrhagic - the contents of the vesicles are bloody;
- generalized - with damage to internal organs.
Purulent blisters with chickenpox in adults appear in the event of a secondary infection. This is usually observed due to improper skin care and poor hygiene.
There are three degrees of severity of chickenpox:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
The severity is determined by the severity of symptoms of intoxication and the abundance of the rash.
Drug treatment of chickenpox
Local therapy plays a special role in the treatment of rashes. It helps improve the healing of skin surfaces, preventing the appearance of scars, cicatrices and secondary infection of pimples.
It is advisable to treat skin lesions with any antiseptic agents. These are brilliant green, Tsindol, Baneotsin, Fukortsin. This group of drugs eliminates re-infection of elements, promotes their rapid drying and epithelization.
The most modern medicine is Calamine. It is applied topically and has a complex antiallergic and antiseptic effect.
Also prescribed for the treatment of the infectious process:
- Antipyretic drugs. Reduces temperature and improves well-being.
- Antiviral agents. They are used to destroy the main infectious agent.
- Antihistamines. Suppresses severe itching and prevents other signs of allergies. Used for oral and external use.
- Painkillers. Fight headaches and throat discomfort. Used in tablet form.
When localizing papular elements in the oral cavity, it is recommended to use:
- Boric acid 1% as an antiseptic.
- Kamistad, Kalgel and other painkillers.
- Sea buckthorn oil or Solcoseryl to reduce irritation and accelerate epithelization.
Treatment tactics
Therapeutic measures for chickenpox occurring without fever are aimed at:
- elimination of manifestations of the disease;
- prevention of secondary bacterial infection.
Patients with mild disease do not require hospitalization. Treatment must be comprehensive.
| Medical direction | Recommendations |
| Mode | Bed rest in the absence of fever is not mandatory. |
| Nutrition | The patient's diet must be balanced and complete, with the obligatory inclusion of fermented milk and plant products. Dishes should be light and nutritious; spicy, salty, starchy and sweet foods should be avoided. Products should be boiled, baked or steamed. |
| Drinking regime | It is necessary, even with the erased form of the infection, to drink up to 1.5–2 liters of liquid per day; preference is given to still mineral water, green tea, fruit, preferably freshly prepared, non-acidic juices. |
| Drug treatment | For mild forms of the disease, drug treatment is usually limited to external therapy. Treatment of rash elements with disinfectants is carried out in order to prevent the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. Most often, a 1% alcohol solution of brilliant green or a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) is used for these purposes. To soften and heal the skin, you can use products with allantoin and dexapanthenol. To relieve skin itching, lotions are used (Calamine, etc.). |
| Aeration | It is necessary to regularly ventilate the room, ensuring a flow of fresh air. Disinfection is not carried out due to the instability of the virus; regular wet cleaning is sufficient. |
| Hygiene procedures | When chickenpox is erased, you can and should take a bath or shower. After water procedures, the skin should not be rubbed with a towel, but carefully blotted. Bed and underwear must be changed regularly. |
Compliance with these measures will prevent complications.
Sources
- Chicken pox: adults at risk. Excerpts from the state report “On the state of sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population of the Russian Federation.” Publishing house “Russian Doctor”, November, 2022.
- Chickenpox. Mayo Clinic.
- Chebalina, E. A., et al. “Chicken pox in pregnant women: risk, prevention, diagnosis, management tactics (clinical lecture).” Medical and social problems of the world 19, no. 4 (2014): 74-82.
- Yushchuk N.D. et al. “Chickenpox in adults” Attending physician #01/00 (2000).
- Scott Frothingham. Chickenpox in Adults. Healthline. 2018
- TASS News Agency, “Production of a domestic vaccine against herpes zoster will begin in 2027.”
- Rusakov, V. A., A. V. Chebykina, and V. A. Maidan. “Methods of medical control of chickenpox incidence.” Bulletin of the Russian Military Medical Academy S1 (2018): 170-172.
Are antiviral drugs needed for chickenpox?
Contrary to popular belief that with chickenpox you only need to lubricate the blisters with brilliant green, doctors recommend the use of antiviral drugs. They will reduce the severity of the disease, speed up recovery and reduce the severity of painful symptoms, primarily itching. The antiviral drug VIFERON® is used to treat herpes viral diseases, including chickenpox. It is the first drug in its class approved by the State Pharmaceutical Committee of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation for use in children, including newborns and premature babies, as well as pregnant women1. More about interferon
Alpha-2b interferon, which is part of the drug VIFERON, is created on the basis of modern technologies, has antiviral properties (blocks virus replication) and has a pronounced immunomodulatory effect, i.e. restores immunity.
VIFERON® Suppositories (suppositories) help suppress the activity of the varicella zoster virus (herpes virus type 3) and enhance the body’s own immune response to pathogenic microorganisms. Cocoa butter, which is part of the drug, contains phospholipids, which make it possible not to use synthetic toxic emulsifiers in production, but the presence of polyunsaturated fatty acids facilitates the administration and dissolution of the drug. The drug VIFERON® Suppositories can be used both by children from the first days of life and by adults, including pregnant women from the 14th week and nursing mothers. Recommended dose for adults in the treatment of herpes virus infection, including herpes zoster (HerpesZoster, herpes virus type 3): VIFERON® 1,000,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every day for 10 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued. According to the research of Professor V.N. Timchenko, which was published in the article “Modern aspects of antiviral therapy for chickenpox in children” in 2011 in the journal “Children’s Infections”, the use of the drug VIFERON for the treatment of children with mild and moderate forms of chickenpox contributes to:2
- reducing the duration of intoxication by 2.5 times;
- reducing the duration of fever by 3 times;
- prevention of secondary infection;
- reducing the duration of skin rash and itching by 3 times;
- a significant reduction in all stages of development of chickenpox elements;
- reducing the severity of the infectious process (90% – mild form).
In his study, Professor Timchenko V.N. used the drug VIFERON according to the following regimen: children under 7 years old - VIFERON 150,000 IU 2 times a day for 5 days, children over 7 years old received therapy with the drug VIFERON 500,000 IU 2 times a day for 5 days.
What antiviral medications can be taken for chickenpox during pregnancy?
Pregnant women from the second trimester of pregnancy (starting from the 14th week of gestation) for the treatment of herpes virus type 3 (Herpes Zoster, chickenpox and herpes zoster) are prescribed VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every day for 10 days , then 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every fourth day for 10 days. Then every 4 weeks until delivery - VIFERON® 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5 days. If necessary, it is indicated before delivery (from the 38th week of gestation) VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 10 days.
VIFERON® Gel and VIFERON® Ointment are used as local therapy for chickenpox.
Do I need to go to the doctor if I don’t have a fever?
When chickenpox has no fever and few rashes, patients are embarrassed to bother doctors. However, any sign of illness is a compelling reason to call the clinic or an ambulance. This is because asymptomatic forms of infection are also contagious. The patient should not visit the clinic, go to work or be in crowded places. It is important to rule out other diseases with a similar rash and obtain a release from work.
The doctor is called to the house. Diagnosis is made based on clinical signs. Based on the results of the examination and assessment of possible complications, the patient is prescribed a complex of treatment, and after recovery, a sick leave certificate is issued for an average of 10 days.
Prevention
Usually people get chickenpox in early childhood, since the pathogen is extremely easily transmitted from person to person. However, some people reach adulthood without having immunity to the Varicella Zoster virus.
To avoid getting sick, it is recommended to undergo a special vaccination, after which lifelong immunity will be developed, as if the patient had chickenpox. You can get vaccinated even if you had contact with a sick person and no more than 72 hours have passed since that contact.