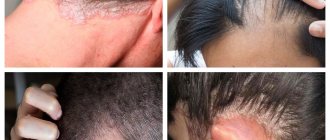
Main reasons
Despite the existence of the term “sun allergy,” sunlight itself is not an allergen. On the contrary, sunlight in safe quantities has a beneficial effect on the human body - it improves mood, promotes the absorption of vitamin D, and stimulates the immune system. Only when the ultraviolet component of sunlight interacts with any substance located on or in the skin do compounds with antigenic properties appear. It is these compounds, not the sun's rays, that cause sun allergy symptoms. Doctors call this disease “photodermatitis.”
Typically, photodermatitis can occur during periods when a person is exposed to significant sun exposure by spending a lot of time outdoors, that is, in the spring and summer. But this disease can also be provoked in winter: after all, some begin preparing for the beach season in advance by visiting a solarium, while others go to the south or to tropical countries for additional sun during the cold season. Therefore, sun allergy has become a year-round disease for many.
Sources
- Bolotnaya L.A. Photodermatoses // Dermatovenereology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology. —2009. — No. 1-2 (12). — pp. 188-197.
- Princely N. And there are spots from the sun // Asthma and allergies. - 2010. - No. 2. - P. 6-7.
- Macharadze D.Sh., Tsintsadze N.N. Solar urticaria and other photodermatoses // Medical advice. - 2011. - 5-6. — P. 30-34.
- Osipova V.V. Photodermatoses: photoallergic reactions // Asthma and allergy. - 2014. - No. 2. - P. 3-5.
- Polymorphic photodermatosis. Clinical recommendations. - M., 2015. - 15 p.
- Sidorovich O.I., Tsyvkina E.A. Photodermatoses: prevention and treatment // Medical advice. - 2022. - No. 18. - P. 132-134.
- Fedotov V.P. Photodermatoses (clinical lecture) // Dermatovenerology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology. - 2015. - No. 3-4. — pp. 143-157.
- Yarovaya N.F. Photodermatoses // Attending physician. - 2009. - No. 6. - P. 61-66.
Why do sun allergy symptoms occur?
The appearance of photodermatitis is promoted by internal and external causes.
Internal causes include chronic diseases of the liver and adrenal glands, some metabolic disorders, and malfunctions of the immune system. It should also be noted that people with fair skin and children are prone to photodermatitis.
External causes are the effects on the body of substances that can be divided into three large groups:
- Furocoumarins are special substances secreted by plants such as hogweed, parsnip, ash, parsley, dill, St. John's wort, and can cause allergies. Bergamot, lavender, musk, and sandalwood oils also have an allergenic effect.
- Components of cosmetics - eosin, para-aminobenzoic acid, retinoids, boric and salicylic acids, phenol, mercury compounds.
- Medicines - sulfonamides, barbiturates, aminazine, some antibiotics (doxycycline, tetracycline), some cardiovascular drugs (amiodarone, Trazicor), cytostatics, oral contraceptives, some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, ketoprofen, naproxen, meloxicam, diclofenac, lornoxicam) , both in the form of tablets and in the form of ointments, creams and gels.
Cosmetic peeling, permanent make-up or tattoos, even temporary ones, can also trigger photodermatitis.
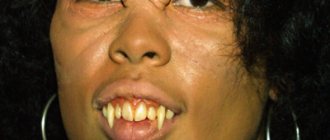
Solar cheilitis
There are several varieties of this disease with their own characteristics. In particular, eczematous cheilitis resembles classic eczema and appears on the lower lip in the form of blisters against a background of reddened and swollen skin. Over time, the bubbles merge into a single spot, open, and erosions form in their place. At the same time, the skin peels, cracks, and becomes covered with crusts after bursting blisters. The disease can be noticed by thickened, protruding lips7.
Another type is xerotic cheilitis, it develops slowly and lasts a long time. Dry, thin gray scales form along the edges of the lips. They disappear and new ones quickly appear in their place. With a long course, the formation of abrasions and wounds is possible.
Important!
Solar cheilitis is often observed in those who are exposed to UV radiation for a long time and often. This can cause malignancy.
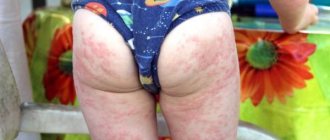
Symptoms of sun allergy: manifestation options
Within a day or a little later after exposure to the sun, soreness and itching of the skin begin to bother you. Then areas of redness and a rash appear on the skin in the form of spots, nodules, plates, blisters, sometimes merging into plaques. There is often a deterioration in the general condition. Most often, the rash occurs on the face, less often on the body and limbs. Rashes on the face may be accompanied by conjunctivitis, cracks in the corners of the mouth (cheilitis). After the acute symptoms subside, peeling of the skin is observed. With repeated sun exposure, the disease may worsen again.
It is important to distinguish photodermatitis from an ordinary sunburn. It is also accompanied by pain and redness of the skin, and in severe forms blisters may occur. But the rash and severe itching characteristic of photodermatitis do not bother you with a sunburn.
Solar prurigo
It is seasonal: it appears in the spring, when the sun's rays gain strength, and can last almost the entire summer, weakening towards its end. However, exacerbations are possible even on winter days if they are sunny. The disease can begin at any age, starting from 16 years7.
In the affected areas, the skin turns pale (white dermographism), thickens, loses elasticity, and plaques form on the surface. The rashes are very itchy and crusts form due to scratching.
Pruritus often appears on the face and exposed parts of the arms. The rashes resemble small nodules in shape. At first they form in small quantities, then there are more and more of them, and they merge into single spots. The skin is dry. Over time, the skin may become covered with small pigment spots. If the disease is chronic and severe, atrophic scars may form. Additional symptoms are irritability and withdrawal7. Due to itching, a person suffers from insomnia.
Recommendations and treatment
At the first symptoms of a sun allergy, you should consult a doctor and strictly follow his instructions. The doctor’s very first recommendation for any allergy is to eliminate or reduce contact with the allergen.
- Avoid direct sunlight, stay in the shade, under an awning.
- Avoid visiting the solarium.
- Use UV protective products by applying them to your body 20 minutes before going outside.
- Don't forget about hats with brims or visors and clothing with long sleeves.
- After swimming in open water, blot your skin, but do not dry it. This will preserve the layer of sunscreen.
- Minimize the use of decorative cosmetics, creams, perfumes, etc.
- Carefully read the instructions for medications - medications should not contain substances that can cause photodermatitis. Talk to your healthcare provider ahead of time about options for changing medications for sun allergy symptoms.
- Avoid contact with plants containing furocoumarins.
- Increase your consumption of fresh vegetables, fruits and berries; they help restore damaged skin due to the presence of antioxidants and B vitamins.
How to eliminate sun allergy symptoms
To relieve allergy symptoms, your doctor may prescribe antihistamines (for example, Cetrin ® ). In the future, it is advisable to keep these medications on hand: unfortunately, an allergic reaction to the sun may recur.
To treat local skin manifestations, the doctor may recommend cold lotions, as well as external ointments or creams containing glucocorticosteroids.
If the cause of photodermatitis is internal, be sure to treat the disease that triggered the allergy to the sun.
Following these recommendations and following your doctor’s prescriptions will help you significantly reduce the appearance of sun allergy symptoms or completely get rid of the manifestations of photodermatitis.
Food photodermatitis
These are mainly pellagra and pellagroid - complex systemic diseases that affect the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, liver, vitamin and protein metabolism. Provoking factors are gastrointestinal diseases and alcoholism, which disrupt the absorption of proteins and vitamins. Their lack triggers a protective reaction in the body, which is expressed in increased photosensitivity. The pathology is chronic and worsens in spring/summer.
The main symptoms of food photodermatitis:
- dermatitis (rashes, itchy skin);
- diarrhea (loose stools);
- dementia (deterioration of memory and thinking abilities).
How to treat sun irritation with traditional medicine?
Grandma's recipes can be very effective, but you shouldn't rely solely on them. Combine them with the products prescribed by your doctor - in this case, you can quickly bring sun-damaged skin to normal condition:
- Potato. Grate 1-2 medium-sized tubers on a fine grater and apply the resulting pulp to the affected area.
- Aloe. Cut a suitable-sized leaf from an indoor aloe flower and rinse it under running water. Cut lengthwise and wipe the damaged area of skin. You can also make aloe juice. To do this, peel the leaf and grind it in a blender/pass through a meat grinder. Dilute the resulting mass with clean water in a 1:1 ratio, soak a bandage or napkin in it and apply to the affected areas for 10-15 minutes.
- Cucumber. Wash the cucumber, cut off the skin and grate the vegetable. Squeeze the resulting mass through gauze and apply to damaged areas. It is recommended to keep the cucumber mixture on the skin for at least half an hour.
- Cabbage. Divide the head of cabbage into sheets. Apply the leaf to red, itchy areas.
Clinical researches
Based on the results of numerous clinical studies, La-Cri products, including cream for sensitive skin, are recommended by the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
The effectiveness, safety and tolerability of the products have been proven by a clinical study. The cream is also suitable for daily skin care of children with mild to moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
Sources:
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, Notabene, 2017.
- Reken Martin, Schaller Martin, Sattler Elke, Burgdorf Walter, Atlas of Dermatology, MEDpress-inform, 2022.
- Schneiderman Paul, Grossman Mark, Differential diagnosis in dermatology. Atlas, Binom, 2022.
Doctor, is this forever?
Treatment of sun allergies involves eliminating exposure to ultraviolet radiation. In the case of solar urticaria, antihistamines help, and there are special medications that thicken the skin and reduce its sensitivity to sunlight. Treatment in this case consists of gradually accustoming the skin to the sun while taking medication.
To relieve exacerbation of photodermatitis, local treatment is prescribed in the form of ointments, sometimes hormonal, and internal treatment: vitamins B, E, C, nicotinic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antihistamines. Usually the course of treatment continues for several days or weeks. During this time, it is recommended to spend less time in the sun, wear a wide-brimmed hat, clothes with sleeves and sunglasses.
If sun allergy is left untreated, repeated episodes will lead to the development of photodermatosis. When you have managed to stop the allergy attack by carefully taking care of protecting your skin, eliminating provoking factors and strictly following the sunbathing regime, you have the opportunity to bask in the gentle rays. Sun allergies can be controlled and prevented, and children may even outgrow this disease.
medkrug.ru