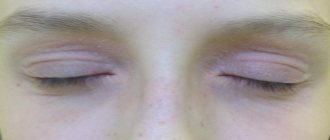
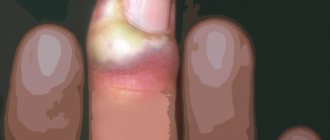
Causes of the symptom
Keep in mind! Redness of the skin around the eyes in an adult or child can be caused by numerous reasons:
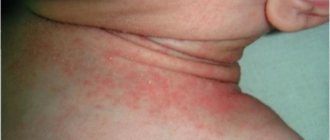
- Allergy. Redness may be accompanied by skin rashes and spread throughout the face. The disorder always affects the areas of both eyes.
- Blepharitis. This is an inflammation of the edge of the eyelid with characteristic redness of the skin, mainly in the area of the lower or upper eyelid. It may not extend to the corners of the eyes.
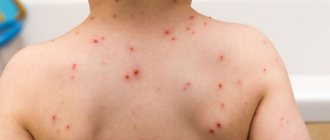
- Eczema. The disease is a chronic or acute skin rash of an inflammatory nature. In such cases, not only the skin, but also the whites of the eyes may turn red.
- Rosacea of the eye. With this disease of the blood vessels of the skin, extensive redness of the periocular area occurs. In this case, accompanying symptoms may appear in the form of pain, photophobia, sensations of the presence of a foreign body in the eyes and uncontrolled lacrimation.
- Lyme disease. A bacterial dermatological lesion leading to rashes and redness around the eyes. Additionally, the patient experiences a feeling of itching and burning. In a complicated form, fever, headaches and dysfunction of the nervous system may develop.
It is worth noting! In addition to these pathological causes, which require drug treatment, redness around the eyes can also occur under the influence of less serious factors.
For example, a symptom may indicate lack of sleep, intolerance to some cosmetics, or injury .
A separate symptom can be considered redness, accompanied by peeling of the skin.
In addition to the fact that this can be observed with allergies, such a sign
may indicate demodicosis - damage to the eyelash follicles by the skin mite demodex.
In this case, this is not the main symptom, and redness with peeling mainly affects the edge of the upper and/or lower eyelid
The spread of redness to the entire periocular space is a consequence of irritation in patients with thin and delicate skin, while the mite itself cannot live on areas of the skin without hair.
Know! In rare cases, peeling and redness are an indirect sign of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: pathological disorders of intestinal absorption, constipation, dysbiosis, gastritis.
But it is possible to accurately establish the connection between these problems and redness only after examination by a specialist.
Pathogenic causes
This group includes pathologies caused by weak immunity, allergies, bacterial or viral infections, and parasites.
Allergic reaction
The body's reaction to allergens that irritate the mucous membrane. It most often occurs in the spring, when plants begin to bloom and a huge amount of allergens enter the air. Because of them, the eyes begin to dry out and itch from the inside. Certain foods can cause a reaction: milk, eggs, chocolate, citrus fruits, pomegranates or strawberries.
Taking certain medications can also lead to allergy symptoms. These include antibiotics, vitamin complexes and preparations containing iodine. In women, allergies can be caused by incorrectly selected cosmetics.
Diagnosis of allergies is carried out using a series of laboratory tests that can pinpoint the cause of the discomfort. After this, the doctor selects antihistamines.
To prevent itching, you can wash your eyes with special drops several times a day. This reduces contact of the mucous membrane with allergens.
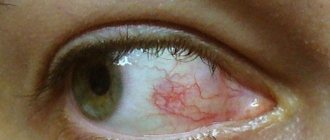
Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the mucous membrane, which is based on an allergy or infection. The infectious form is usually caused by viruses or bacteria, very rarely by a fungus. The disease can be transmitted from person to person through contact.
With conjunctivitis, itching is the first sign that requires you to consult a doctor to select treatment. During therapy, local antiviral or antibacterial drugs are used in the form of eye drops or ointments.
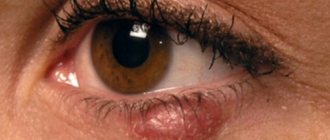
Blepharitis
Inflammation of the eyelids caused by anemia, diseases of the digestive system, diabetes, infection and other pathologies. As blepharitis develops, the refractive function of the eyes deteriorates, causing concomitant pathologies, such as farsightedness, to appear. The patient has a desire to scratch his eyelids, swelling forms.
The disease is accompanied by the formation of small scales or ulcers along the edges of the eyelids. Treatment of blepharitis takes a long time and, in addition to getting rid of the symptoms, includes eliminating the causes of its development.
Demodicosis
Damage to the skin by the parasitic demodex mite. The activity of the parasite leads to itching from the inside, pain and itching of the eye. The main method of treatment involves the use of gels or ointments that reduce the activity of the parasite.
Dry eye syndrome
Causes dryness and swelling of the mucous membrane, itching. The patient feels as if sand has gotten under his eyelids, which is why he begins to rub his eyes frequently, aggravating the condition. The syndrome is caused by a lack of tear production.
Dry eye syndrome is usually experienced by older people; it occurs in them 65-70% more often than in younger patients. Recently, the problem has been encountered among office workers who spend a lot of time in front of a monitor screen in an office with dry air. The syndrome is also caused by chemical or thermal burns and adenoviruses.
Barley
Purulent inflammation of the sebaceous gland of the eyelid or eyelash follicle. Develops against a background of reduced immunity, severe hypothermia, and frequent stress.
The infection penetrates the gland or hair follicle, after which pus formation and inflammation begin. First, a small itchy dot appears on the edge of the eyelid, painful when touched. Gradually, the tissues around it swell, redness appears, and the head of an abscess forms. After opening it, pus and dead tissue are released.
To treat stye and reduce itching, the doctor selects antibacterial ointments and drops and prescribes therapy to strengthen the immune system.
Methods of treatment and elimination
Redness can be eliminated in different ways depending on the cause - from cosmetic camouflage to complex antibacterial treatment.
If the issue is an allergy (seasonal or to a specific substance), the allergen or a group of them is first identified.
Note! After exclusion or maximum limitation of allergens, the patient is prescribed a course of antihistamines.
These can be tablets (loratadine) or eye drops (okumetil, allergodil, cromohexal).
If bacterial ophthalmological or dermatological pathologies manifest themselves in this way , appropriate therapy is required .
For conjunctivitis, drops of ciprofloxacin, sodium sulfacyl, chloramphenicol, and albucid can be prescribed.
If the causative agent is a virus , actipol, ophthalmoferon or their analogues are used. In difficult cases, it is possible to combine several groups of drugs and add steroid, immunomodulatory and antihistamine drugs.
Blepharitis is treated not only with antibacterial drops , but also by applying ointments containing an antibiotic (tetracycline, gentamicin ointments).
Another ophthalmological disease that affects the outer part of the eyelid is stye.
This disease in most cases does not require special separate treatment.
Non-pathogenic causes
These are reasons that are caused by third-party factors, for example, environmental features or incorrect actions of the patient.
Swimming in reservoirs
This is a common cause of infection by viruses, bacteria and mites. Their activity causes itching in the corners of the eyes, under or on the eyelids. Most often, diseases develop in the summer months, when microscopic algae begin to actively multiply in the water. If they come into contact with the eyes, they cause a number of unpleasant symptoms.
The reaction can also begin when swimming in a pool. Chlorinated water negatively affects the condition of the mucous membranes, causing itching.
Ultraviolet burns
Strong ultraviolet radiation can provoke pain and itching. You can encounter it when visiting a solarium without protective glasses, when watching the sun. A retinal burn can be caused by an electric welding process that uses a powerful light beam.
Blocked tear duct
Burning and itching in the eyes often occurs when the tear ducts are blocked by burning particles or fine dust.
There is an easy way to deal with blockage: just pinch the dots at the inner corners of your eyes for a few seconds. Usually after this, tears begin to flow, clearing the tear ducts. If this does not happen, you should consult a doctor.
Which doctor treats itching?
Pathology is the responsibility of an ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist). He conducts an initial examination and makes a preliminary diagnosis. The patient may need help from doctors of other specialties, such as an allergist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and others. In this case, treatment will be prescribed not only to get rid of the symptoms, but also to eliminate the underlying disease.
Prevention
Since redness of the skin around the eyes is most often the result of irritation of the visual organs , this should be avoided.
It is necessary to ensure that in the room in which a person stays during the day is not too dry (this problem usually occurs in offices or apartments with working air conditioners).
If there is a need to spend several hours in a row at the computer, you need to take a short break once an hour, which is advisable to use for eye gymnastics.
Remember! If possible, your diet should include foods containing B vitamins (beans, grains, fruits, vegetables, dairy products).
This element restores eye tissue and generally has a positive effect on the functioning of the visual organs.
You need to sleep at least 6-7 hours a day . During this time, the eyes have time to rest from the fatigue accumulated during the day, and the tear membrane is restored.
Where can I get appropriate advice?
You can find out the characteristics of various medical centers in Moscow and not only choose a competent specialist to visit, but also make an appointment with an ophthalmologist at home, using the information content of our Directory for private clinics “Your Doctor”, which additionally allows you to theoretically familiarize yourself with the pathological disorders of interest.
Publication date: 2018-02-07
Burning in the eye and lacrimation: what is it and how to treat it?
If your eyes are burning, you need to contact a specialist for help. After an external examination, he can conduct a biomicroscopy and determine how thick and hyperemic the edges of the eyelids are, tests for tear production and dysfunction of the meibomian glands in order to diagnose dry eye syndrome, and measure intraocular pressure. Based on the results obtained, a diagnosis is made, and in addition to dry eye syndrome, disorders can be caused by barley, conjunctivitis, allergies, and glaucoma.
As for treatment, it is selected individually and depends on the complexity of the problem and diagnosis. Non-drug treatment includes warm compresses and self-massage of the eyelids to cleanse the surface of the eyelids, to relieve the inflammatory process and toxic-allergic reaction.
The prescription of drug therapy by a specialist depends on the clinical manifestations and extent of the pathological process:
- eye drops for burning and lacrimation and various medications for oral administration (for allergies, dry eye syndrome, fatigue, infections);
- antimicrobials, antihistamines, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics.
It is recommended to avoid contact with various substances on the mucous membrane, rubbing the face with dirty hands, stress, overwork, and violations of personal hygiene rules. In no case should you postpone visiting a specialist if a burning sensation in the eye is accompanied by other symptoms, namely increased sensitivity to light, discharge, decreased visual acuity, double vision, pain. Any abnormal manifestations that do not go away for several days indicate serious illness. And early diagnosis simplifies treatment.
What treatment may be needed?
Since redness and burning around the eyes are only symptoms and not a diagnosis, you should consult a dermatologist to find out the diagnosis and begin treating the patient. Sometimes tests are taken for this (for example, for demodicosis).
How is burning around the eyes treated if it is associated with infectious diseases? Treatment usually involves instilling antiviral or antimicrobial drops that fight the pathogen. But in these cases, it is not the dermatologist who should make his appointments, but the ophthalmologist.
Itching around the eyes and burning associated with an allergic reaction to cosmetics usually goes away on its own if you wash off the offending product and do not reapply it.
But if it is a food allergy or one of the symptoms of hay fever, then you should take some anti-allergenic medication. However, it rarely happens that due to a food allergy or reaction to plant pollen, only the eyes and the area around them suffer - usually there is also a runny nose, lacrimation, itching and redness of the wings of the nose, etc.
About what will help with allergic redness >>
Eye inflammation
Often inflammation of the eyelid is accompanied by discomfort. This disease is called blepharitis and is treated with specific medications. Many people, when discomfort appears in their eyes, begin to take some measures themselves - this is correct. But if the unpleasant sensations do not disappear 3-4 days after the procedures, an accumulation of purulent contents appears on the eyelashes after sleep, then you should seek qualified medical help. Only a doctor can determine how to treat red eyes during inflammatory processes, which drugs will be most effective and how long to continue therapy.
If you do not seek qualified help in a timely manner, complications may develop. For example, the pathological process will spread and inflammation of the eye shell may develop, or blepharitis will become chronic, which will provoke deterioration of vision.
Any discomfort in the eyes is a sign of problems, so you need to take even minor disturbances or minor deterioration in well-being seriously. Eye drops for inflammation and redness should only be selected by a specialist, because self-medication can lead to the development of an allergic reaction and a deterioration in the condition of the visual organs. And all known folk remedies should be used only as an auxiliary therapy and after consultation with an ophthalmologist.
Information on in what cases inflammation of the cornea of a child develops and what drugs are used for treatment can be obtained on the pages of our website.
Related articles: Symptoms of conjunctivitis in children Causes of spots before the eyes
Dry and red eyes
The cause of this condition can be the entry of a foreign body into the eye - it immediately becomes red, tears flow from it, but at the same time the mucous membrane is dry, and “scratching” of the eyeball is felt. In this case, you can help with a handkerchief or a cotton swab - you need to carefully try to remove the foreign body from the eye. But if you cannot quickly remove the foreign body from the eye, you need to consult an ophthalmologist.
Dry eyes can be associated with excessive strain, a condition often diagnosed in people whose work involves computers. In this case, the person will complain of a slight burning sensation and pressure in the eyes, itching will appear, and after rubbing with the hands, redness will appear. There are eye drops for dryness and fatigue - they are sold in pharmacies and are recommended for use by people whose work activities involve eyestrain.
If your eyes are tired, accompanied by dryness and redness, you can also use folk remedies - apply ice cubes to your eyes for 5-10 minutes, make a tea compress for 7 minutes, rinse your eyes with rose water.
Why does itching in the eye area occur?
Physiological reasons
The short-term appearance of the symptom is due to irritation of the eyelids, conjunctiva and lacrimal glands. The provoking factors are:
- Cosmetical tools.
The symptom is observed when using inappropriate, low-quality or expired mascara, eye shadow, pencils, creams, makeup removers, etc. - Irritants.
The cause is fine particles in the air: dust, smoke, washing powders, various chemical suspensions. When swimming in a pool, chlorine dissolved in the water gets on your skin and mucous membranes. Severe symptoms are observed when the lacrimal ducts are blocked by dust or fumes. - Ultraviolet.
Irritation, itching and burning occur with prolonged exposure to the sun. A similar, but more pronounced picture is revealed when one refuses to use safety glasses in a solarium. - Overwork.
Unpleasant sensations occur after prolonged work on the computer, reading text that is too small, or the need to strain your eyes when manipulating small objects, especially in low light conditions. - Correction problems.
The symptom is detected when glasses are chosen incorrectly, the rules of use are violated, or there is increased sensitivity to contact lenses.
Conjunctival lesions
Conjunctivitis is a large group of inflammatory diseases of the conjunctiva of various etiologies. Common symptoms include burning, itching, a gritty sensation in the eyes, photophobia, watery eyes, swelling and redness. In clinical practice, bacterial and viral variants of the disease are more common. Possible fungal and chlamydial infections. Non-infectious inflammatory processes occur with chemical or mechanical irritation, visual impairment, vitamin deficiencies, and metabolic disorders.
In most cases, both eyes are affected. In the acute form of the disease, the manifestations are pronounced. Pain, pain, conjunctival hyperemia, swelling of the eyelid area, and copious discharge are noted. Possible disturbances in general condition. In the chronic form of the disease, discomfort, mild itching, and increased fatigue of the visual apparatus prevail.
Angular conjunctivitis debuts with severe itching and burning, which are subsequently added by pain, as well as pain that intensifies when blinking. The lesion is always bilateral, manifestations increase in the evening. The secretion is foamy, then viscous. The deterioration in general condition is insignificant. The pathology is prone to recurrence.
Keratoconjunctivitis manifests suddenly; in chronic ophthalmological diseases it can develop gradually. Pain, stinging, photophobia and the sensation of a foreign object are combined with fog before the eyes and decreased visual acuity. Adenoviral lesions are characterized by small hemorrhages in the conjunctival area. With bacterial infections, a white-yellow infiltrate forms on the eye.
Itching in the eye area
Diseases of the eyelids
Typical symptoms of blepharitis include itching, redness and swelling of the eyelids, blurred vision, abnormal discharge, and increased sensitivity to wind, bright light and other irritants. Depending on the form of the disease, thickening of the edges of the eyelids, the formation of scales, and the formation of ulcers with subsequent scarring of the skin, loss, discoloration, or impaired growth of eyelashes are possible.
Dermatitis of the eyelids is a polyetiological disease. When infected with the herpes simplex virus, blisters form on the skin of the affected area along with a burning sensation, which crust over and disappear. There is a high probability of recurrence. Seborrheic dermatitis is a combination of itchy skin, eyelash loss, and peeling skin.
Purulent processes
The development of stye begins with itching. Then the affected area quickly becomes painful, swollen, and hyperemic. Possible weakness and general hyperthermia. After 2-3 days, a pustule forms in the center of the infiltrate. After opening the abscess, the symptoms gradually decrease. Meibomitis is characterized by the formation of a purulent focus on the inside of the eyelid. Swelling, redness, severe pain in the affected area, and a feeling of a foreign body in the eye are detected. In chronic cases, the eyelid is thickened, patients are bothered by burning and discomfort.
Non-inflammatory pathologies
People with epicanthus, along with a cosmetic defect, may experience a feeling of “sand,” a narrowing of the field of vision, and sometimes burning and itching. A chalazion is a round, dense formation in the thickness of the eyelid. In some patients, it is accompanied by lacrimation and unpleasant sensations when touched. With trichiasis, itching is a consequence of improper eyelash growth. Lacrimation, pain, photophobia, and hyperemia of the conjunctiva are noted.
Parasitic diseases
The symptom is considered one of the main manifestations of demodicosis, caused by microscopic mites. The edges of the eyelids are swollen and hyperemic. The eyelashes are surrounded by a “collar”. There may be a feeling of a foreign object, a feeling of tightening of the skin, and loss of eyelashes. Hyperkeratosis develops. Due to severe itching, patients scratch the eye area, the scratches become covered with crusts and become infected. Pathology is often detected in several people in a family.
Dirofilariasis is caused by small roundworms; infection occurs through the bite of a mosquito. Parasites live in the eyelids or conjunctiva. Initially, patients complain of severe itching, swelling, and lacrimation. The formation of a compaction is accompanied by redness of the affected area, blepharospasm, and progressive ptosis. There may be a sensation of movement in the eye or under the eyelid. The movements of the worms are accompanied by severe pain and burning.
Dry eye syndrome
Pathology develops with Sjögren's syndrome, endocrine ophthalmopathy, and kidney disease. It can be provoked by lagophthalmos, chronic conjunctivitis, other eye diseases, and ophthalmic surgical interventions. Significant factors in the development of dry eye syndrome are prolonged work at the computer, incorrect selection or violation of the rules for using contact lenses. Symptoms include stinging, burning, redness, and a gritty sensation. Intensifies in the evening.
Allergic conjunctivitis
Occur due to hypersensitivity to a specific antigen. Characterized by bilateral damage. Symptoms appear within a few minutes to a day or more from the moment of contact with the allergen. There is lacrimation, burning, redness and swelling of the conjunctiva. The itching is so severe that it forces patients to constantly rub the eye area, which leads to an increase in other symptoms. The following forms of allergic conjunctivitis are distinguished:
- Hay fever.
There is a seasonal pattern. In a third of patients, symptoms appear in the spring, during the flowering period of alder, oak, and birch. At the beginning of summer, clinical manifestations are caused by contact with pollen of cultivated and wild cereals. In urban residents, symptoms are detected in late summer and early autumn, which is associated with the active growth of weeds in squares, parks and flower beds. - Spring.
Debuts at the age of 3-4 years. Subsequently, a chronic course is observed with relapses in the spring and early summer. The itching gradually increases, intensifies in the evening, and is accompanied by lacrimation and photophobia. Possible development of ptosis and blepharospasm. With the arrival of autumn, the symptoms disappear. Spontaneous recovery during puberty is typical. - Large capillary.
Caused by the use of contact lenses, irritation of the conjunctiva by postoperative sutures during keratoplasty or cataract extraction, calcium deposition in the cornea, other ophthalmological diseases and conditions associated with the treatment of pathological processes in the eye area. - Drug.
In 90% of cases it is provoked by the administration of topical drugs, in 10% of patients it occurs when using general agents. Most often observed when using antiviral and antibacterial ointments and drops, especially without a doctor’s prescription, taking into account contraindications and the mutual effect of several medications. - Chronic.
Accounts for almost a quarter of the total number of allergic eye diseases. Potentiated by cosmetics, perfumes, food products, fluff, animal hair, house dust and other allergens. Typically persistent with mild symptoms.
When the conjunctiva and nasal area are simultaneously affected, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis occurs. Depending on the nature of the allergen, the pathology can be seasonal or year-round. In the seasonal form, sneezing, lacrimation, profuse watery nasal discharge, itching in the nose and eyes, nasal congestion, and photophobia are observed. The persistent form is smoothed out, the symptoms are more constant. The discharge is mucous, thick, congestion worsens at night. Mild itching in the eye area.
Other allergic pathologies
Allergic keratitis is manifested by corneal syndrome (lacrimation, photophobia, blepharospasm), sensation of a foreign object. Burning, stinging, and constant pain are detected that prevent the opening of the eye. Allergic blepharitis, as a rule, manifests suddenly under the influence of various factors. Patients complain of persistent itching and swelling of the eyelids, pain, and photophobia. The skin around the eyelids darkens. Allergic dermatitis is characterized by redness, rash, and severe swelling. In severe cases, angioedema may develop.
Other reasons
Itching in the eye area is observed with Sjögren's disease. It is caused by a decrease in the amount of tear fluid, combined with “sand”, “scratching”, burning, redness of the eyelids, enlarged salivary glands, stomatitis, dry lips and oral cavity. The symptom is also characteristic of cystinosis; in the infantile form it is expressed moderately, in the juvenile and adult forms it is insignificant.
Ophthalmological examination
Can there be a sharp burning sensation in the eyes, profuse lacrimation when working at the computer?
Unpleasant sensations in the eyes often occur in people who are forced to work at a computer for a long time. This is to blame not only for the harmful radiation from the monitor, but also for the high load on the organ of vision, as well as a reduction in the frequency of blinking.
Normally, a person blinks from 10 to 20 or more times per minute. When working with digital information (at a computer, tablet, phone), the blinking frequency is reduced several times. Because of this, the precorneal film, which nourishes, moisturizes and protects the eyes from external influences, loses stability.
When the eyes no longer receive enough moisture, an unpleasant burning sensation in the eyes and watery eyes appears. Wearing contact optics can aggravate the situation. More tears are spent flowing around the contour and moistening the surface of the lens. If few of them are produced, a lot of unpleasant sensations appear. Increased tear production, which manifests itself as profuse lacrimation, does not help the situation.
If heating equipment or air conditioning is running in the room where a person is located, the burning sensation and dryness may also increase. Climate control dries the air, and dry air, in turn, promotes faster “weathering” of tears.