Just like pimples and acne, papillomas spoil the appearance of the skin, but unlike inflammations, they do not go away on their own. They need to be removed. Find out how to get rid of papillomas on your face.
The appearance of any neoplasms on the face is an unpleasant thing. Moreover, they will not disappear on their own, and all cosmetics are powerless against them. You will have to look for a different approach to papillomas.
Causes of papillomas, their types and location
The cause of skin papillomas is the human papillomavirus (HPV). Science knows more than 150 types of HPV, they are divided into three groups:
- Non-oncogenic papillomaviruses - types 1, 2, 3, 5.
- Papillomaviruses of low oncogenic risk (6, 11, 42, 43, 44).
- Papillomaviruses of high oncogenic risk (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 51, etc.).
Viruses of the last two groups, with varying degrees of probability, can cause the development of malignant neoplasms.
Depending on the type of HPV, papillomas are divided into the following types: ordinary papillomas - also known as vulgar warts, filamentous growths, flat papillomas, genital papillomas - also known as condylomas, plantar warts, juvenile warts and papillomatosis.
The most common are vulgar, filiform and genital papillomas.
- Thread-like forms of papillomas are more common in people aged 40+ and are localized in areas with thin skin - on the chest, armpits, neck, etc.
- Vulgar warts most often “attack” the skin of the feet, palms, fingers and toes, but can appear on any other parts of the body. Often recur in conditions of decreased immunity.
- Condylomas appear only on the mucous membranes. They can affect the glans penis, foreskin, vagina, and labia minora.
- Plantar warts appear on the rough skin of the feet and on the balls of the toes.
- Papillomatosis is a generalized form of the disease, manifested by the formation of growths throughout the body.
What are papillomas
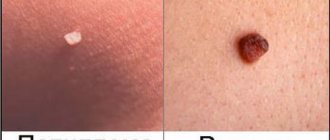
Papillomas are also benign formations. They come in a variety of shapes - leaf-shaped, spherical, filamentous or lobed, often resembling cauliflower in appearance. The growths have a soft, loose structure and are located on a thin stalk. Initially, their size is about 2 mm, but gradually they are able to grow up to 1-2 cm. The color of papillomas also varies from white to dark brown. The favorite location is areas of the body with thin and delicate skin, folds and mucous membranes, i.e. these are the neck, eyelids, nasolabial fold, armpits, area under the mammary glands, genitals, groin area, perianal fold, around the anus, in the rectum, urethra, bladder, etc. Quite rarely, papillomas can form in the oral cavity and on the vocal cords. The growth can be either single or multiple. Basically, there are 5-20 papillomas in one area. Their prevalence largely depends on the immune system and its ability to resist the virus. The main feature of this type of neoplasm is the increased threat of transition to a malignant form. This is especially true for papillomas that form on the mucous membranes of the female genital organs. If left untreated, they cause cancer.
How does HPV infection occur?
The mechanism of transmission of the virus is contact; the source of infection is the patient or the virus carrier. HPV can be released not only from growths on the skin, but also circulate in the blood, saliva and urine. In this case, infection can occur in 4 main ways:
- through contact and everyday life;
- sexually;
- during childbirth from mother to child (which may be the cause of laryngeal papillomatosis);
- during autoinoculation (self-infection or dispersion of the pathogen from existing foci during combing, shaving, or using a hard washcloth).
The risk of HPV infection usually depends on the state of the human body’s immune system, viral load and the presence of microtraumas and other inflammations on the skin and mucous membranes.
Even when infected with the HPV virus, papillomas do not always form on the skin and mucous membranes. The virus is localized in the basal layer of the epithelium and can remain inactive for a long time. Only under certain conditions (weakening of the immune system, stress, exposure to unfavorable environmental factors) do the processes of its replication start, which leads to cell proliferation and the appearance of tumors.
Indications for removal
The only way to treat already “formed” papillomas is to remove them. Indications for removal of tumors primarily include:
- Aesthetic problems. Papillomas are skin growths that are perceived as an aesthetic defect, especially when they are localized in open areas of the face and body.
- Papillomas can be constantly injured, cling to clothes, combs, etc. and due to this, quickly spread throughout the skin, soreness, inflammation, cracks and even bleeding may appear in the area of the tumors.
- Considering that some types of papillomaviruses have a high risk of oncogenicity, large papillomas (more than 6-10 mm) may be prone to degeneration, so timely removal of such tumors will prevent a serious illness in the patient.
Skin formations of non-viral origin
Fibroepithelial polyps are a common benign tumor, usually called “papilloma”.
Who it occurs in: middle-aged and elderly people, menopausal and postmenopausal women, pregnant women.
Half of the total population has at least one fibroepithelial polyp.
What they look like:
A 1 mm to 1 cm pedunculated nodule is usually skin-colored but may be yellowish or brown. Soft, mobile.
Can such “papillomas” cause cancer? No, they are not precancer. They are dangerous because when injured they can become inflamed and fester. Discomfort, cosmetic defect, but do not pose a serious threat to life.
Can be removed using minimally invasive (low-traumatic) methods.
Seborrheic keratosis
Who it occurs in: most often in men and women in middle and old age.
What it looks like: papules (tubercles) of pink, yellow-gray, brown, black color, often with a rough surface, of various shapes and sizes from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Can be located anywhere except the palms and soles. They look quite impressive, given the large size and multi-colored formations.
Can seborrheic keratosis develop into cancer? No.
Can be removed using minimally invasive methods.
Also included in the group of “papillomas” are various nevi (moles) - intradermal, warty and other formations that have an elevation above the surface and a “leg”. The issue of removal is decided by a specialist. For some nevi, only surgical excision is possible.
Methods for removing papillomas
In our medical center, before removing a tumor, a dermatologist examines it and, if necessary, performs dermatoscopy in order to differentiate the type of papilloma and select the optimal method of removal.
It is possible to get rid of papillomas in our clinic without surgery using the destruction of formations using a laser, radio knife and plasma. Removal of papillomas with a laser, especially removal of papillomas on the face, is not carried out so often due to the high traumatic nature of the method and the possibility of hypopigmentation and scarring. Preference is given to radio wave destruction, as well as diathermocoagulation. These methods are highly effective and low traumatic.
- The radio wave method is one of the most effective and least traumatic ways to remove almost all types of papillomas. It is performed on the Surgitron DF-120 device (Ellman International Inc, USA). Removal of the tumor occurs due to local evaporation of cells under the influence of heat generated in the tissues in response to the penetration of radio frequency waves. The cells evaporate and the tissues move apart as if cut with a scalpel. In addition, instant coagulation of blood vessels occurs in the treatment area, so there is no bleeding and no damage to surrounding healthy tissue. In this aspect, laser removal of papillomas is significantly inferior to the radio wave method.
- Diathermocoagulation using the Plasmaskin device (Ultramed, Russia) is a non-contact effect on the affected tissue with a plasma beam. The high temperature of the plasma (up to 2000-2500 C) is combined with the bactericidal effect of an air flow containing a high concentration of ozone and has a virus-destructive effect, destroying HPV DNA, which prevents its spread.
The use of radio wave energy on the SURGITRON DF-120 device (Ellman International, Inc., USA) is the method of choice for removing most forms of papillomas, regardless of their location (face/body), and here’s why:
- Radical - no relapses;
- Rapid epithelization - healing;
- Atraumatic - no complications, no marks or scars remain on the skin;
- Painless - anesthesia is required only in cases of large tumor sizes.
- Complete safety of procedures.
During the destruction of papillomas, anesthesia is usually used. Application anesthesia with the application of lidocaine cream can be used, or infiltration anesthesia, when the site of papilloma localization is injected with an anesthetic solution (Ultracaine). The choice of pain relief method is determined by the size and location of the papilloma.
If the patient has no contraindications, removal of papillomas in Moscow in our clinic can be carried out on the day of treatment, immediately after an appointment and examination by our specialist. In this case, no additional tests are required.
In order to prevent relapses after removing a large number of tumors, our experts recommend taking immunomodulatory drugs. Immunomodulatory therapy is selected individually.
Diagnostics
It is extremely important to correctly determine the type of tumor, taking into account oncogenicity and external similarity. Initially, the doctor conducts a clinical examination of the growth, if located on the genital organs - gynecological in women, proctological and urological in men. This is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. To establish a reliable clinical picture, it is recommended to conduct research at the cellular level using special diagnostic methods, namely:
- cytological examination of cell morphology - to identify DNA mutations;
- colposcopy - examination of the vulva, vagina and cervix using a special microscope - colposcope;
- biopsy - sampling of cells and tissues for the purpose of diagnosing the pathogen;
- histology - a type of biopsy - to determine a precancerous condition;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques - to identify all types of virus;
- Digene test. It is the most reliable and informative diagnostic method: it accurately determines the presence and type of HPV, the level of oncogenicity, and the degree of concentration of the pathogen in the body.
Most often, the diagnosis is made based on the results of using several methods, since individually each of them is erroneous to a certain extent.
Doctors to contact regarding this issue
Denezhkina Natalya Nikolaevna
Reshanova Lyudmila Mikhailovna
Varfolomeeva Oksana Igorevna
Chaplitsky Evgeniy Aleksandrovich, urologist-andrologist, specialist
What will happen to the skin after papillomas are removed?
The next day after the procedure, a brown crust forms at the site of the removed tumor. Healing takes from 2 to 7 days, it all depends on the size of the removed papilloma. After healing, the crust will come off on its own. The main thing at this time is not to wet or injure this area.
After the procedure, the doctor gives some simple recommendations for further skin care.
In our clinic, it is carried out using modern equipment by highly qualified doctors, which allows us to solve problems of papillomas removal quickly, efficiently and safely. We use disposable consumables, which guarantees maximum patient safety.