General practitioner (family doctor)
Gutorova
Natalia Konstantinovna
22 years of experience
Doctor
Make an appointment
Chicken pox, or, as they say, varicella, is an acute viral disease that occurs mainly at a young age and affects the skin. The pathogen belongs to a type of herpes virus and, after penetration into the body, remains in it for life. So, after the disease passes, it remains in the nerve cells.
Symptoms of the disease
The appearance of the first symptoms of chickenpox occurs after the incubation period. On average, it lasts from 7 to 21 days after the pathogen enters the human body.
In most cases, the initial manifestation of the disease is a high fever, which persists for 3-7 days and can be accompanied by body aches, headache, insomnia, restless sleep, and loss of appetite.
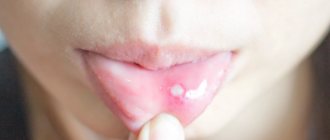
This is followed by the main symptom of chickenpox - a rash that appears on the torso and head (up to the scalp) and spreads to the limbs. Rashes can be found in the most unexpected areas, for example, in the vaginal area, on the mucous membrane of the mouth and the cornea of the eyes.
The diameter of one such formation is 1-4 mm. At first they look like bubbles surrounded by reddened tissue, inside which clear liquid accumulates. Then the bubbles become drier and form crusts instead.
At this stage, most people with chickenpox suffer from unbearable itching. However, scratching the papules is strictly prohibited: otherwise, they will leave marks in the form of scars.
In some cases, patients may experience enlarged lymph nodes, either selectively or all at once, among the symptoms of chickenpox.
Are you experiencing symptoms of chickenpox?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Chickenpox in adults
02.08.2015
It is a well-known fact: it is better to get over “childhood” diseases in childhood, ideally in preschool age. Chickenpox in adults is one of the most striking examples of this. If you didn't get chickenpox as a child and haven't been vaccinated against varicella-zoster virus, your introduction to chickenpox can be one of your biggest challenges.
Why is chickenpox dangerous in adults?
We immediately need to make a clarification: for so-called “childhood” diseases, the concept of “adult” begins already in adolescence. If the disease overtook you after 12 years, the likelihood of moderate or even severe chickenpox with a bunch of side effects is higher, the older you are. People over 50 years of age suffer the most from chickenpox if they are sick with it for the first time. However, fortunately, the chances that an adult will not have time to become infected with the varicella-zoster virus before such an advanced age are almost zero.
Where and how can an adult become infected with chickenpox?
Paradox: an adult is many times more likely to encounter the chickenpox virus than children. The same applies to teenagers who begin to move around outside the home a lot. The varicella-zoster virus is extremely volatile, easily travels through the air, and is transmitted by airborne droplets. And a sick person is contagious even before the first symptoms appear (about 48 hours before them). That is, no contact with the patient is needed. You can simply ride in the same elevator, in the same subway car, you can walk past a virus carrier, or sit in his place at a table in a cafe. The only thing that saves us is the instability of the virus that has entered the air. But you don’t really have to count on this if you haven’t had chickenpox yet.
Just as one cannot rely on nonspecific immunity. If someone tells you that a good immune system can save you from chickenpox, don’t believe it. The only way to become immune to the varicella-zoster virus is to become infected with the virus, either through illness or vaccination. And this immunity lasts as long as this virus is present in the body. Therefore, when an adult who claims that he did not have chickenpox as a child does not get chickenpox, there are only two options. Either in childhood he had asymptomatic chickenpox, or for some reason this disease was not recorded in his children's medical record. Alas, there are still parents who manage not to remember what their children were sick with in childhood.
Be careful: you can also get chickenpox from someone who has herpes zoster (shingles), because this disease is also caused by the varicella-zoster virus, being essentially a “reincarnation” of the virus in the body of a person who once had chickenpox.
Chickenpox in adults has its own seasonality - these are the winter and spring periods.
How does chickenpox occur in adults?
In adolescents and adults, chickenpox almost always occurs in a complicated form.
From the moment of infection to the first symptoms of chickenpox in an adult, a minimum of 7 and a maximum of 23 days pass. The disease begins with a sharp rise in temperature to 39-40 degrees, which can last for several days, being difficult to control. This is due to the characteristics of the immune response to the virus in adults.
At this stage, an adult with chickenpox feels weakness, aching joints and muscle pain, headaches, nausea - all these are signs of general intoxication of the body. Against the background of high fever and intoxication, an adult with chickenpox may experience loss of consciousness. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance, since with such a course of chickenpox the patient should be observed in a hospital.
Important: under no circumstances use aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) or analgin (baralgin, metamizole sodium) as an antipyretic and analgesic for chickenpox. According to numerous scientific data, the use of these drugs for chickenpox (specifically for this disease, and not in general) often leads to liver complications.
Following the fever, a chickenpox rash appears. However, the temperature may remain high. Classic blisters usually appear first on the body, then cover the neck and face. The rash can spread to the mucous membranes of the mouth, pharynx, tongue, and even the mucous membranes of the genitals. In addition, the rash can affect the inner surfaces of the eyelids and spread to the cornea, which can lead to vision loss.
The main problem with rashes in adults is that they are not only more severe than in children, but they are almost always complicated by a bacterial infection. The blisters tend to turn into pustules - long-term non-healing pimples with purulent contents, after which so-called pockmarks - small indentations visible to the eye - can remain on the skin as a keepsake. The chickenpox rash itself lasts longer in adults than in children - up to 9 days. And its consequences often have to be cleaned up in the cosmetologist’s office.
In addition to a secondary bacterial infection, chickenpox in adults can lead to the following serious complications:
- viral pneumonia (this complication occurs especially often in adolescents and pregnant women).
- partial or complete loss of vision (when the rash spreads to the cornea of the eye, scars remain in place of the blisters)
- vulvitis in women and inflammation of the foreskin in men
- Optic neuritis (can also lead to vision loss).
- viral tracheitis, laryngitis (with a rash affecting the mucous membranes of the pharynx).
- acute stomatitis
- renal failure
- toxic liver damage
- encephalitis and meningitis (these complications occur when the chickenpox virus infects nerve cells and meninges.
As you can see, chickenpox in adults is no longer a harmless childhood disease. And it requires immediate treatment.
How is chickenpox treated in adults?
Children over 12 years of age and adults with chickenpox are prescribed specific antiviral treatment, and a special regimen is also prescribed. Most often, without waiting for the pustules to begin to appear, the doctor may recommend taking antibiotics.
To suppress viral activity the following may be prescribed:
1. Viricidal drugs directed specifically against herpes viruses:
- acyclovir = Zovirax = Virolex (from 2 years); also use acyclovir ointment for rashes and conjunctivitis (eye damage);
- valacyclovir (from 12 years old),
- famciclovir (from 17 years old), isoprinosine.
2. Immunomodulators: interferon, viferon. In severe cases of chickenpox, patients are given stronger immunomodulators (thymalin, thymogen, IRS-19) and cytokine drugs (roncoleukin).
3. Immunostimulants: cycloferon, anaferon
In severe cases of chickenpox, immunoglobulins are used intravenously. All of the above drugs should be used in age-specific dosages.
To alleviate the symptoms of the disease, the following are prescribed:
- Bed rest for 3-5 days (longer in complicated cases)
- Careful care of the skin and mucous membranes:
- treating the rash sites with antiseptic drugs to prevent secondary infection, which often accompanies chickenpox in adults (up to the formation of ulcers followed by scarring, leaving scars on the skin).
- treatment of the oral mucosa - rinsing with furatsilin and/or sodium sulfacyl
- for conjunctivitis, acyclovir ointment is used, and to prevent bacterial complications - albucid 20%, chloramphenicol ointment or tetracycline.
- antihistamines (suprastin, tavegil, etc.);
- antipyretics (ibuprofen, nurofen, or physical cooling methods - wrapping).
In addition, abundant alkaline drinking is indicated.
If a secondary bacterial infection cannot be avoided, antibiotics are used strictly as prescribed by the doctor , with 3rd generation cephalosporins being the drug of choice.
Important: if you have chickenpox or are recovering from it, beware of sunbathing during this period, as chickenpox rash can cause pigmentation disorders in the affected areas of the skin. It is best to hide chickenpox-affected areas of the body until complete healing, since even fresh chickenpox scars can become hyperpigmented.
Adults with pustular chickenpox are advised to avoid water treatments until the pimples begin to dry out.
Chickenpox during pregnancy
If a woman who is not vaccinated or has not had chickenpox gets sick during pregnancy, the unborn child may develop congenital smallpox, which manifests itself as scars on the skin, low birth weight, and even delayed mental and physical development. But the risk that chickenpox during pregnancy will cause certain consequences depends on the stage of pregnancy at which the infection occurred. Chickenpox in late pregnancy is much more dangerous than chickenpox in early pregnancy.
Chickenpox in the early stages can lead to missed pregnancy and miscarriage, however, if the fetus survives, the risk of chickenpox complications will be very small (less than 1%).
Chickenpox in the 2nd trimester has consequences for the unborn child in about 2% of cases.
The greatest risk is for pregnant women to become infected in the 3rd trimester. If a pregnant woman becomes infected with chickenpox a few days before giving birth, then the risk of congenital chickenpox in the unborn child is 20-25%.
Source: Parents Happy parents
Other news
Epidemiologist Nikolai Briko: the situation with coronavirus in Russia is quite difficult
The coronavirus pandemic has forced doctors and scientists to reassess the situation with infectious diseases in Russia. In particular, in recent years, the country has seen an increase in the incidence of meningococcal infection, which indicates the importance of implementing measures to prevent it. Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Nikolai Briko spoke about which categories of citizens are most susceptible to meningococcal infection, the consequences of its combination with COVID-19, as well as the overall situation with coronavirus in the country.
Rospotrebnadzor warned about the danger of “chickenpox parties”
Some people believe that it is better to have chickenpox in childhood, because a child supposedly tolerates this disease more easily than an adult. Therefore, there are still parents who try to “plan” for the disease: they go to visit sick friends and organize “chickenpox parties,” Alexander Gorelov, deputy director for scientific work at the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor, noted in an interview with Sputnik radio.
In the Nizhny Novgorod region, 1.5 million people were vaccinated against influenza
In the Nizhny Novgorod region, flu vaccination is being completed, the press service of the regional government reported. The vaccination campaign covered less than half of the region’s population—1.5 million people, including 388 thousand children and adolescents.
In Bashkiria they talked about the benefits of vaccination against pneumococcus
Does the pneumococcal vaccination make it easier to cope with coronavirus in case of complications? Important information was presented at a briefing on the results of the activities of the healthcare sector in Bashkiria in 2022. As Industry Minister Maxim Zabelin said, indeed, vaccination against pneumococcus reduces the incidence of complications from Covid and the development of bacterial pneumonia.
Rostec began supplying Russian flu vaccines abroad
In 2022, FORT exported vaccines to the Republic of Belarus, Moldova, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan. In the overall structure of supplies, the largest volume (over 90%) fell on the quadrivalent vaccine Ultrix Quadri. In addition, foreign partners purchased the trivalent Ultrix vaccine.
Nacimbio launched an application about vaccinations
, which is managed by the Nacimbio holding of the Rostec State Corporation, launched the “Vaccinations - Personal Calendar” mobile application. It helps users create an individual vaccination schedule and reminds them about scheduled vaccinations. The Vaccinations app is available for free on Android and iOS mobile phones.
Covid-19 vaccines will be included in the preventive vaccination calendar
Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin instructed to include vaccines against the new coronavirus infection in the calendar of preventive vaccinations for epidemic indications, taking into account priority. Previously, COVID-19 vaccines were included in the VED. Mishustin noted that changes to the order of the Ministry of Health “On approval of the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations and the Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations for Epidemic Indications” must be made before December 17, 2020.
Vaccination against coronavirus has begun in Crimea
“Vaccination begins today in Crimea. First of all, high-risk medical workers who work with patients with a new coronavirus infection will be vaccinated. In the future, the daily number of vaccinated people will depend on the volume of vaccine received,” wrote the head of the republic, Sergei Aksenov, on his page on the VKontakte social network.
Cases of dangerous measles continue to be recorded in the Volgograd region
In the Volgograd region in 2022, measles was laboratory confirmed. This was reported by the regional department of Rospotrebnadzor. It is known that a dangerous disease manifests itself in those who have not been vaccinated. This year, 1 case of measles was confirmed in the region.
Scientists will combine the Oxford vaccine with Sputnik V
Scientists from the University of Oxford and the Russian Gamaleya Research Center for Epidemiology and Epidemiology will join forces to work on a vaccine for COVID-19. They agreed to conduct clinical trials of a combination of two drugs - the British vaccine and one of the two components of the Russian Sputnik V, the Russian Direct Investment Fund and the Swedish-British pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca reported.
Possible complications
As a rule, the disease goes away without serious consequences, especially if you do not scratch the papules. However, in rare cases, complications after chickenpox can still occur.
Among them:
- bacterial infection caused by streptococcus;
- viral pneumonia, which is more common in children of the first year of life and manifests itself in the form of high body temperature, excessive paleness of the skin, dry cough and severe shortness of breath even at rest;
- temporary disruption of the central nervous system;
- encephalitis;
- chickenpox meningitis.
To avoid such consequences, monitoring of the development of the disease and treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a physician - therapist, pediatrician or infectious disease specialist.
Treatment
Treatment of chickenpox in its standard course occurs at home after consulting a doctor. It is aimed at improving the general well-being of the patient: drugs whose active ingredient is paracetamol are used to reduce elevated body temperature.
In the vast majority of cases, patients suffer from unbearable itching of the skin. To alleviate the condition, special ointments and solutions are prescribed based on zinc and potassium permanganate, with the addition of tea tree oil. Antihistamines may be recommended. Often, a specialist will prescribe ointments whose action is aimed at destroying the viral pathogen.
In more serious cases (especially if there is concomitant shingles), the doctor will prescribe analgesics. In case of extremely reduced immunity, the patient is given immunoglobulins, and in case of intense intoxication of the body, detoxification solutions are administered.
Instructions for use PoxClean
The hydrogel is applied to the affected areas 3 times a day. Thanks to its cooling effect, itching decreases, the child stops scratching and picking off crusts. This means that the disease is tolerated more comfortably and there are no unsightly dimples and scars left after it. If three times a day is not enough, PoxClean can be applied more often (as needed to reduce itching). In this case, a reasonable “overdose” is not dangerous - this natural remedy does not contain toxic or aggressive substances (it is not for nothing that it is approved for use from 2 years).
PoxClean not only relieves itching - the unique patented biologically active antibacterial complex 2QR from Aloe Vera extract it contains protects the affected areas of the skin from infection, and also promotes rapid healing of wounds. PoxClean , which is important, also prevents further infection of damaged skin areas. Moreover, this happens naturally: the 2QR complex helps the skin’s natural immunity cope with harmful bacteria. PoxClean creates a kind of barrier on the skin that prevents their spread and penetration.
So, when using the cooling natural hydrogel PoxClean, the child, one might say, simply rests at home for two weeks, receiving immunity to chickenpox for the rest of his life. The itching subsides, no more clothes and sheets smeared with green, and the risk of peeling off crusts and the formation of unsightly scars is reduced.
Answers to common questions
Is there a way to prevent chickenpox?
The preventive measure – not to contact people who are sick – is not always effective. The fact is that infection can occur even before the first manifestations of the disease are detected in the patient. That is, he can communicate with friends without knowing that he is contagious.
It is possible to prevent the onset of the disease by vaccination with special live vaccines, which are based on a weakened chickenpox virus.
Which specialist should I contact for treatment?
Chickenpox in children is treated by a pediatrician or pediatric infectious disease specialist. If an adult gets sick, you should call a therapist or an adult infectious disease specialist immediately after detecting the first symptoms of chickenpox.
Is it possible to swim if you have chickenpox?
Due to the fact that the quality of tap water in most cities leaves much to be desired, in case of this disease you should take a shower (not a bath) using boiled or filtered water. Otherwise, there may be a risk of a bacterial infection joining the viral form, which, in turn, can cause serious complications. It is better to wash with warm water. It is strictly forbidden to use a washcloth, rub the skin or steam it.
Diagnostics
Typically, the diagnosis of chickenpox is made after examining the patient and determining the nature of the rash. In this case, the period that elapses from contact with an infected person until the appearance of rashes is of great importance. In addition, a scraping (smear) from the affected area, culture to detect the virus, and laboratory blood tests can be performed. Using special staining of the smear, you can determine the presence of giant multinucleated cells characteristic of this infection.
PCR analysis can detect even a small number of pathogens in the blood. Detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies may indicate ongoing infection with varicella-zoster virus. Antibodies of this class appear on the fourth day from the onset of the rash and sometimes persist for up to several months.
An increase in the level of leukocytes and ESR in a general blood test may also indicate an analysis. The level of hepatic protein ALT is most often significantly increased in patients with chickenpox. A chest x-ray is performed if a complication of chickenpox such as pneumonia is suspected.