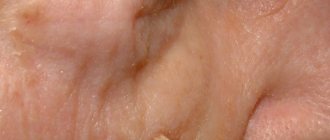
Symptoms of melanoma are a set of indicators according to which ordinary moles on the body, which everyone has, are beginning to degenerate or have already degenerated into a malignant tumor. The appearance of melanoma depends on its type and stage; superficial spreading, acral lentiginous, nodular melanomas and lentigo are known.
More than 20% of melanomas belong to the superficial spreading variety. However, patients rarely live more than 5 years. However, with timely and high-quality treatment, life expectancy can be significantly increased, and for this it is important to know what melanoma itself looks like in order to recognize it in time.
Forms and complications of nevi
There are melanocytic (containing pigment cells - melanocytes) and non-melanocytic nevi (formed by cells other than melanocytes), which include epidermal nevus, nevus of the sebaceous glands, Becker's nevus and some other benign formations, vascular nevi of the skin.
Melanocytic nevi
There are acquired and congenital melanocytic nevi.
Acquired melanocytic nevi (AMN) are benign skin tumors. As a rule, they do not have a tendency to undergo malignant transformation. Special forms of acquired melanocytic nevi include Spitz nevus, Reed's nevus, spotted nevus (spilus), halonevus (Setton), and blue nevus (Jadassohn-Tiche) lying in the deep layers of the skin.
Atypical (dysplastic) nevi (AN) are classified into a separate group. Unlike common acquired melanocytic nevi, atypical melanocytic nevi may have some clinical characteristics of melanoma, such as asymmetry, ill-defined borders, multiple colors, or a size greater than 6 mm. Their main difference from a malignant tumor is stability, absence of changes over time and similar characteristics in one person. Atypical melanocytic nevi have a relatively increased risk of malignant transformation and require careful monitoring.
Congenital melanocytic nevi occur as a developmental defect (hemartoma) and are usually present at birth. Large congenital melanocytic nevi are also associated with an increased (but still low) risk of malignant transformation. Very rarely, they can be associated with a pathological accumulation of melanocytes in the central nervous system (neurocutaneous melanosis). Congenital melanocytic nevi with the expected size in an adult (over the course of life they will increase in proportion to the child’s growth) also require increased attention and medical supervision.
Nevi of Ota and Ito also have a melanocytic structure, but they are not based on excessive cell division, but on their accumulation in the deep layers of the skin.
How to distinguish normal moles from pathological ones
To summarize the above, we highlight the characteristic distinguishing features of benign and malignant moles:
- A benign mole has a regular shape, while a nevus is prone to degeneration into a malignant tumor, usually with an uneven relief shape.
- A safe mole has a uniform color, but one prone to “bad” degeneration can be of different color shades.
- “Bad” moles are usually not congenital, they are acquired.
- “Bad” nevi are usually larger than harmless ones.
- “Bad” moles can rapidly increase in size, and never decrease or disappear on their own; safe moles, on the contrary, can disappear or decrease in size.
- A “bad” mole can cause discomfort and pain, and it can also cause itching.
- A “bad” mole can mutate, acquire new elements and change shape and color.
Knowing the distinctive features of various types of moles, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from a serious problem. By detecting such a problem in a timely manner, you will be able to eliminate it as quickly and efficiently as possible.
Symptoms of nevi
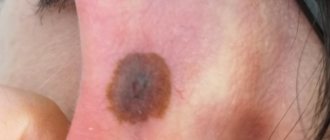
Nevi look like spots or nodules on the skin. Some of them are barely noticeable, others have a rich brown (melanocytic or pigmented) or red (vascular nevi) color.
As a rule, nevi do not cause any discomfort and are not felt.
Nevi can change their appearance and increase throughout life. It is important to correctly assess these changes; such manifestations can not only be a variant of the norm, but also serve as one of the signs of malignant skin formations.
Signs of a mole degenerating into melanoma
Signs of degeneration of harmless birthmarks into malignant melanoma are such phenomena as itching, burning in the area of the mole, skin tension at the base of the nevus, bleeding of unaffected moles, tingling at the site of the birthmark, cracks in the mole and ulcerations from it.
To determine whether a person has signs of a mole degenerating into melanoma, experts have come up with a special system for assessing the condition of a mole, which is called the “melanoma chord”, where A is the asymmetry of the neoplasm, K is the unevenness of the edge of the birthmark, K is the bleeding of the mole, O is the uniformity color, P – large size of the neoplasm, D – dynamics of the condition of a mole of any nature.
By assessing the above indicators, you can conclude that the mole is unstable and promptly contact an oncologist for qualified help.
Stages of changes in nevi
Melanocytic nevi , both acquired and congenital, are characterized by staged changes throughout life. The classic path of development includes 3 stages, which differ in the depth of the formation:
- a simple nevus or borderline nevus is a superficial flat brown spot;
- a complex or combined nevus is located deeper and looks like a brown spot or raised formation on the skin;
- An intradermal nevus is a light-colored, raised formation located deep in the skin.
How does amelanotic melanoma manifest?
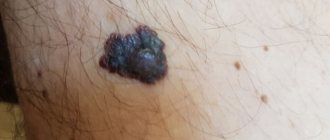
Pigmentless or achromatic melanoma is a rare, but no less dangerous disease. Its first signs can be considered the appearance of a small bump on the skin, which quickly begins to grow. Outwardly, such a formation may resemble a wart and does not attract much attention to itself, since its color completely matches the skin tone. As achromatic melanoma grows, it may become slightly pinkish or whitish in color with a rough surface and peeling epithelial scales. The skin at the site of the tumor becomes rougher. Sometimes the appearance of such melanoma resembles a scar without a clear edge. Pressing on the tumor does not cause any discomfort, which makes many patients not pay attention to it.
In shape, non-pigmented melanomas can be flat or dome-shaped. The second form is caused by the vertical proliferation of cells, which leads to a more voluminous size compared to a flat one. The main feature of such a tumor is its uneven growth with obvious asymmetry, uneven edges and compaction of the structure. However, with the nodular form of achromatic melanoma, the symmetry of the neoplasm and evenness of color are preserved.
When such melanoma grows enough, it begins to cause discomfort to a person, which is expressed in pain, itching, swelling, and redness of the tissues. The surface of the neoplasm may crack, bleed, and form ulcers. All this indicates the progression of melanoma to late, severe stages that are practically untreatable.
An alarming sign of a neoplasm is hair loss from its surface, which indicates malignancy of the pathology. It is also dangerous to detect enlarged regional lymph nodes.
Treatment of nevi
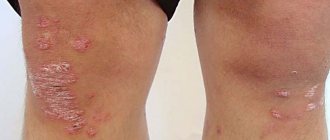
In most cases, no treatment is required, only observation is required, since nevi are benign formations. If a malignant nature is suspected and formations with a high risk of malignant transformation are identified, surgical excision is performed. It is possible to remove the nevus at the request of the patient for aesthetic reasons or because of discomfort (for example, when localized in areas of frequent trauma by clothing).
Features of the treatment method
Surgical excision of the nevus is optimal. This method allows for radical removal with a scalpel followed by suturing of the wound surface. In some cases, when nevi protrude above the surface of the skin, a radio knife, electric knife or laser knife can be used. In all cases of surgical treatment of melanocytic nevi, it is necessary to conduct a histological examination of the removed tissue.
Manifestations in the early stages
Content:
- Manifestations in the early stages
- How does amelanotic melanoma manifest?
- Signs of metastasis in the final stages
- Well-being when sick
- Signs of a mole degenerating into melanoma
- Appearance of melanoma and how to distinguish it from a mole
Melanomas can appear on any part of the body, but most often the tumors are located on the legs or back. Melanoma can also appear on the palms, mucous membranes of the mouth, vagina, rectum, and scalp. In aging skin, melanomas often manifest in the facial area.
Subungual or acrolentiginous variety
In 3% of all diagnosed cases of melanoma, specialists identify cancer of the nail plates. This disease has its own specific symptoms, which include the appearance of a tumor on the finger, darkening of the nail or the appearance of a clear dark stripe on it, cracking of the nail plate over time with the release of sanguineous fluid or pus. It is important to know that nail melanoma most often occurs in the area of the thumb. As it grows, the tumor changes color to bluish-red or black and its shape to mushroom-shaped.
Cutaneous melanoma
The symptoms of cutaneous melanoma are determined by the naked eye, so you should always pay attention to your own health so as not to miss changes in the development of a mole and seek medical help in a timely manner. The main symptom of melanoma manifestation is the degeneration of a mole (nevus). This degeneration can be expressed in different forms, for example, the mole may begin to enlarge, its contour becomes jagged and asymmetrical, the pigmentation color darkens or acquires blue or reddish shades, itching occurs in the area of the formation, as well as swelling or wet discharge. Against the background of the above symptoms, regional lymph nodes may enlarge.
A mole can begin to degenerate after an injury, or for no apparent reason. Most often, hair falls out in the pigmentation zone, the skin begins to peel off and form crusts, and the skin pattern on the surface can no longer be read. It is also possible that melanoma satellites – skin rashes near the tumor site – may occur. The mole becomes very smooth and acquires a mirror-like surface.
Ocular variety
Melanoma of the eye is very common. Its peculiarity is the absence of symptoms in the first stages of pathology, which greatly complicates the course and treatment of the disease. The patient should be alerted to symptoms such as:
- sudden deterioration of vision;
- the appearance of photopsia or colored dots, sparks before the eyes;
- the occurrence of metamorphopsia or distorted perception of spatial and dimensional quantities;
- change in pigmentation in the iris;
- the appearance of “blind spots” in the field of vision;
- swelling in the eye area;
- retinal clouding.
Symptoms of ocular melanoma may occur even before the oncology is fully formed and do not allow an accurate diagnosis to be made. With different localization of this disease, hemorrhages in the eye area, secondary glaucoma, and retinal detachment may also occur.
How are nevi treated in the Rassvet blade?
The doctor will examine the patient's skin completely to eliminate the risk of missing melanoma or other skin cancer. Suspicious formations are further studied using a device that allows you to examine the skin with 10 times magnification - a dermatoscope. The patient's chart describes nevi that require observation. The doctor will suggest surgical removal of suspicious nevi, followed by histological examination of the removed material (sent to an expert laboratory). Removal of nevi for aesthetic reasons can be performed at the request of the patient.
Recommendations of a dermatologist for patients with nevi:
- avoid excessive ultraviolet irradiation of the skin (tanning, sunbathing, solariums, ultraviolet drying of manicure and pedicure coatings); when staying outdoors for a long time, use a broad-spectrum photoprotective cream with SPF 30 or higher, clothing that covers the skin, a hat and glasses with an ultraviolet filter;
- try not to injure nevi when shaving, combing, changing clothes;
- undergo an annual preventive examination of nevi with a doctor;
- independently examine nevi according to the ABCDE rule;
- if there are a large number of nevi (50-100 or more), especially in combination with the presence of risk factors (sunburn, visits to a solarium, melanoma and skin cancer previously identified or in close relatives, the presence of atypical nevi), undergo a digital skin mapping procedure.
Author:
Kuzmina Tatyana Sergeevna dermatologist, Ph.D.
Well-being when sick
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Typically, the early stages of melanoma do not cause the patient any inconvenience, discomfort, or pain. After stage 3, when metastases occur, pain begins to appear, and with the onset of stage 4, anemia, weakness, frequent cough, aching bones, exacerbation of chronic pathologies, enlarged lymph nodes, loss of appetite, headaches, nausea, vomiting, and convulsions are added to it. . Depending on the location of metastases, memory loss may occur, vision may deteriorate, and constant pain in the skeleton, right hypochondrium, and chest space may occur.
The danger of melanoma lies precisely in the fact that the patient practically does not feel the most treatment-friendly stages, so he is in no hurry to seek help, and when metastases occur and the melanoma can no longer be cured, the patient begins to be bothered by all sorts of unpleasant symptoms, which have to be dealt with make significant efforts. In general, the state of health in patients with melanoma in late stages is negative, which further depresses already exhausted people faced with oncology.
Children's pigmented neoplasms
At the moment the baby is born, there are no pigment spots on his body. They actively appear on the skin of children by the age of four.
The types of moles in children and adults differ.
Children's nevi are divided as follows:
Borderline. Nodules rising above the skin with a clear silhouette of chocolate, dark and lilac colors. Painless on palpation. The dimensions of such a neoplasm range from several millimeters to five centimeters. There is no hair.
Intradermal, Various in size and color. Some species resemble blackberries, others grow on a stalk.
Complex. When viewed, they are dense, spherical or dome-shaped. Colors are dark shades of wine and chocolate, even black. Hairs grow in complex nevi. Requires monitoring by a dermatologist.
Congenital. The most common pigment formations among babies. They develop as a result of a failure in the process of converting the skin of the embryo into melanin.
To prevent an ordinary mole from causing trouble, you must follow some simple rules:
- sunbathe at the right time - before 10 am and after 6 pm
- use high-quality creams and lotions that protect from bright sun rays
- do not visit the solarium
- do not injure the mole with belts, straps, chains and bracelets
- visit a skin doctor
- if necessary, visit a medical institution specializing in the removal of skin tumors and perform surgery
What is a mole?
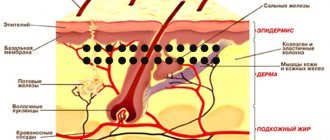
A mole is a skin growth filled with cells capable of forming the pigment melanin. These elementary units that produce melanin, located in the lower layer of the epidermis, are called melanocytes. The creation of melanin by melanocytes occurs under the influence of natural or artificial ultraviolet rays.
People have approximately the same number of melanocyte cells, but each person produces melanin individually. Based on the amount of suspended polymer compounds produced that color the fabric, humanity is conventionally divided into four classes.
Representatives of the first class have snow-white skin, light-colored eyes (blue or green) and red hair. Often their face is covered with freckles. Little melanin is produced, so the skin almost never tans.
Those belonging to the second class produce slightly more melanin than the previous group. They tan better, but at the same time sunburns form on the skin. Nature has endowed them with light-colored skin, blue, green or gray eyes and light brown hair.
The third class is represented by dark-skinned people with gray or almond eyes, coffee-colored or dark-brown hair. Due to the high amount of melanin produced, their skin quickly darkens in the sun, and damage to the skin during prolonged exposure to sunlight is extremely rare.
And the participants in the fourth grade are not sensitive to ultraviolet radiation, they are dark-skinned, brown-eyed, with dark hair.
Why do they appear?
Nevi are essentially benign skin formations.
Some people get scared when they see many moles on their body. What does this mean for a specialist? Only that the patient’s body is prone to accumulation (accumulation) of melanin in the surface layers of the epidermis.
The reasons for the appearance of numerous or single nevi are varied.:
1. External:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation, one of the most common factors in the formation of moles due to increased melanin levels during tanning;
- traumatic damage to the epidermis, systematic violations of the integrity of the skin contribute to the appearance of pathological changes in it;
- exposure to radiation, which rapidly changes normal skin cells;
- consumption of harmful products (GMOs, fast food, alcohol) and smoking, these habits negatively affect metabolic processes in the body.
2. Internal:
- endocrine disorders and diseases, any changes in hormonal levels can cause the appearance of skin pathologies, pigmentation, moles;
- hereditary predisposition, the presence of various nevi in the family.
The appearance of moles can be triggered by inflammatory and autoimmune skin diseases, toxic lesions, burns and frostbite, as well as the constant use of low-quality cosmetics and preparations for face and body care.