Lip cancer is a severe, progressive oncological disease during which a malignant tumor forms on the upper or lower lip from epithelial cells located in the red border area. As the tumor grows, it penetrates other anatomical structures, causing the patient to have difficulty eating. Often the course of the disease is complicated by infectious inflammation. In the absence of timely medical care, tumor tissue begins to disintegrate over time, and the patient’s face becomes disfigured. Metastases spread most often through the lymphatic system.
Kinds
According to localization they distinguish:
- cancer of the lower lip, accounting for about 95-98% of all cases;
- Cancer of the upper lip, which occurs in no more than 2-5% of patients, but has a more aggressive and rapid course, affects mainly women.
According to histological classification, lip cancer is a squamous cell tumor, represented by two types:
- keratinizing – the most common, accounting for up to 95% of cases, which is characterized by a slow course with moderate germination into other tissues and slight metastasis;
- non-keratinizing - rarer and significantly more malignant, quickly growing into nearby tissues (usually into the anatomical structures of the jaw), forming ulcers and metastasizing relatively early through the lymph and blood flow. Metastases usually affect the lymph nodes under the jaw, in the chin and jugular vein, as well as lung tissue.
In addition, there are four clinical forms of the tumor: ulcerative, ulcerative-infiltrative, papillary and warty. The first two have a more malignant course.
Symptoms
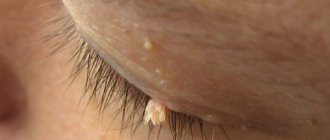
Many patients mistake the first signs of lip cancer for a rash characteristic of an exacerbation of herpes: a small seal forms on the lip, in which a slight itching is felt. At the same time or even a little earlier, the lymph nodes of the chin enlarge. As the tumor develops, the following appear:
- small painless ulcers, covered with a crust, with a bleeding, tuberous base;
- cracks and crusts along the red border of the lip;
- a compaction that grows in size over time and becomes crusty;
- pain in affected soft tissues;
- increased secretion of saliva;
- difficulty eating, deterioration of diction.
If left untreated, the tumor penetrates the tissues of the jaw and begins to destroy them. Simultaneously with the local symptoms of lip cancer, manifestations common to all types of cancer develop: general weakness, decreased performance, decreased appetite, unmotivated weight loss.
Etiology of childhood papillomas
You can become infected with the papilloma virus through several mechanisms, but for children, spread most often occurs during personal tactile contact with a carrier, for example during play, or when using common objects, which is especially typical for places where children gather in large numbers (kindergarten, playground), where Toddlers often exchange toys or have common objects. Another route of infection is transmission of the virus from mother to child perinatally and during childbirth. Passing through the birth canal, the baby can come into contact with papillomas or condylomas of the mother’s internal organs, which is considered a key factor in infection.
As already mentioned, any papilloma is a visual manifestation of the presence of a virus in the body. However, not all HPV carriers experience pathological proliferation of epidermal tissue or mucous membranes. If a person's immune system is sufficiently stable, skin growths may not appear for a long time. The following factors and conditions of the child’s body can provoke tissue proliferation:
- Weakening of the immune system due to vitamin deficiency or illness;
- Traumatic violations of the integrity of the skin: abrasions, scratches, wounds, etc.;
- Poor nutrition;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Hormonal changes during puberty.
It should be remembered that, according to statistics, nine out of ten people on the planet are carriers of the papilloma virus, which means you should not panic if you notice a small skin growth on a child, which is popularly called a wart.
Causes and risk factors
The main cause of lip cancer is a malignant modification of cells located at the border of the transition of the skin epithelium to the mucous membrane. As a result, cells begin to actively divide, which leads to tumor growth and displacement of healthy tissue. What becomes the trigger for the reformatting of the original healthy cell into a cancerous one has not yet been established, but the factors that increase the likelihood of developing pathology are well known:
- prolonged exposure to the open air, due to which the lips are constantly chapped and cracked;
- diseases of the digestive tract, metabolic disorders;
- habit of biting lips;
- unbalanced diet, chronic vitamin deficiency;
- regular consumption of strong drinks that burn the mucous membrane of the lips;
- smoking and microburns of the lips caused by it, the habit of chewing tobacco;
- irritation due to poorly fitting dentures or broken edges of a tooth;
- poor oral hygiene.
Among patients with lip cancer, rural residents who constantly work outdoors predominate. Men get sick two to three times more often than women; the main age group at risk is people over 60 years of age.
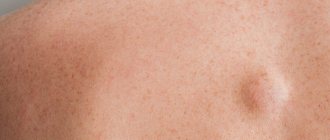
Are bumps on the lips dangerous?
The danger of bumps on the lips depends on the cause of their occurrence. Small blisters that appear after eating hot food or an insect bite will not harm the body.
Complications can result from:
- retention cyst caused by trauma;
- inflammation due to infections;
- herpes and papilloma on the lip.
Important!
New growths that appear due to smoking or drinking alcohol are also dangerous. If you don't change your lifestyle and give up bad habits, they can develop into lip cancer. A lump on the lip is a neoplasm caused by injury or disease. To prevent the pathology from developing into cancer and causing further complications, consult a specialist.
Stages
There are four stages of lip cancer.
- The size of the neoplasm is small and does not exceed 2 centimeters; the malignant tissue is concentrated within the lip. Lymph nodes are not affected, there are no metastases.
- The pathological tissue increases in size up to 4 centimeters, but the lymph nodes are not affected and there are no metastases.
- The tumor exceeds 4 centimeters in diameter and affects one or two regional lymph nodes.
- Malignant tissue spreads to the jaw bones, tongue, maxillary sinus, or penetrates the masticatory muscles and pterygoid process, reaches the carotid artery and grows into the base of the skull.
Diagnostics
External signs of lip cancer, as a rule, are not enough to accurately determine the diagnosis, so the oncologist prescribes a series of laboratory and instrumental tests for the patient.
- A smear or scraping from the surface of the ulcer to perform a cytological analysis of cells and determine the type of cancer.
- Tissue biopsy followed by histological examination of the removed sample to confirm malignant changes.
- Ultrasound of the neck to identify affected lymph nodes.
- X-ray of the lower jaw, chest to identify metastases or ensure their absence.
- CT scan of the facial skeleton to detect metastases in them.
Attention!
You can receive free medical care at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the program of State guarantees of compulsory medical insurance (Compulsory health insurance) and high-tech medical care.
To find out more, please call +7, or you can read more details here...
Treatment
After diagnostic confirmation of lip cancer, treatment must begin immediately, since the sooner it is carried out, the less traumatic and more organ-preserving the methods used will be.
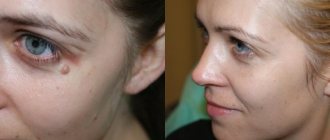
- Surgery. At the first and second stages, in the absence of metastases, surgery, as a rule, serves as the main method of treatment. The affected tissue is removed, and reconstructive lip surgery is performed at the same time. Patients in the third and fourth stages can be operated on depending on the local spread of the tumor and the expected volume of tissue to be removed. At the same time, the affected lymph nodes in the neck must be removed. If the tumor has spread to vital organs, surgical treatment is not performed.
- Radiation therapy. As an independent method, irradiation is used for small tumor sizes and few metastases; chemotherapy can be used to enhance the effect. After surgery, radiation exposure is necessary to avoid relapse of the disease and destroy residual cancerous foci.
- Chemotherapy. For inoperable cancer and distant metastases, chemotherapy is prescribed to inhibit the growth of malignant tissue and prolong the patient's life. Courses are prescribed, depending on the patient’s condition and the characteristics of the tumor, simultaneously or alternately with radiation.
- Cryogenic method. Low-temperature destruction of tumor tissue is in some cases used in the initial stages to avoid surgery and chemoradiotherapy.
- Photodynamic method. Therapy for limited superficial oncological pathologies consists of the introduction of a photosensitizer and subsequent laser treatment.
Wart removal in the clinic
The clinic uses modern hardware techniques to excise growths:
- Laser therapy . The method allows you to quickly and without blood remove the growth. There is no discomfort during the procedure, as pain relief is performed. During one session, you can get rid of several tumors in a very short time. The method is suitable not only for adults, but also for children. The likelihood of relapse is minimized. Skin defects in the form of scars after laser use are very rare.
- Radio wave therapy . The technique is considered the safest. When excising a wart using a radio wave, there is no contact with the skin. It is not always possible to completely remove the growth. The procedure leaves no traces of impact.
- Electrocoagulation . The procedure requires anesthesia. Using an electrode to which a high-frequency electric current is applied, the wart is burned out, followed by cutting off the growth with a special metal loop. Scarring may appear after removal.
- Cryodestruction . Liquid nitrogen is used and the wart is treated until it turns white. As a result of exposure to low temperatures, the growth tissues die. There is no need for anesthesia for the manipulation. The disadvantage of the technique is the lack of control over the depth of nitrogen exposure. For this reason, frequent relapses occur.
- Surgical. Removal is done using a scalpel. The disadvantage of the procedure is the formation of a scar, so this technique is used only for certain indications (in case of malignancy of the process and large size of the wart).
Diagnosis and treatment of lip cancer in Moscow
If you find signs of lip cancer, contact the Meditsina clinic for a comprehensive examination and confirmation or refutation of suspicions. At your service:
- exclusive diagnostic equipment;
- own laboratory performing all types of analyses;
- oncologists of the highest category who will conduct treatment;
- a well-equipped inpatient department;
- medical service of international level.
Call us to find out the details you are interested in and schedule a consultation.
Questions and answers
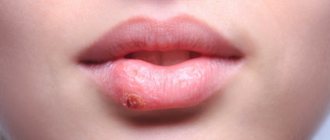
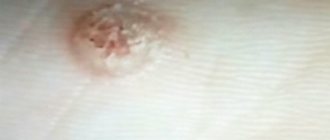
What does lip cancer look like?
In terms of external signs, lip cancer at the initial stage resembles a herpetic rash: a small swelling appears, which later turns into one or several ulcers covered with crusts. A thickened area with redness of the skin may form. Unlike a herpetic infection, ulcers do not heal after two to three weeks, but on the contrary, increase in size.
How to recognize lip cancer?
If a lump or swelling appears on one of your lips and does not go away within two to three weeks, you should definitely contact an oncologist to check for lip cancer. It is impossible to independently determine cancer by external signs; laboratory tests are required - histological and cytological examination of tumor tissue, biochemical blood tests, examinations using a tomograph and other types of medical equipment.
How long do people live with lip cancer?
A malignant tumor on the lip is one of the least aggressive oncological pathologies and is most often detected at an early stage. More than 90% of people who develop it live after diagnosis for more than 10 years, i.e. are completely cured of cancer.
Attention! You can cure this disease for free and receive medical care at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the State Guarantees program of Compulsory Medical Insurance (Compulsory Medical Insurance) and High-Tech Medical Care. To find out more, please call +7(495) 775-73-60, or on the VMP page for compulsory medical insurance
Attentive attitude to the health of the child is the most important task of responsible parents.
Moreover, often any pathological conditions, and especially neoplasms, cause fear and panic not so much in the smallest patient as in the caring mother. If you notice a papilloma on your child’s face or body, you should not perceive it as something terrible. Papillomas in children are a common phenomenon that is caused by one of the most common viral agents on the planet - the human papillomavirus (HPV). We will try to figure out how to rid the baby of an unpleasant tumor and whether it is possible to prevent infection.