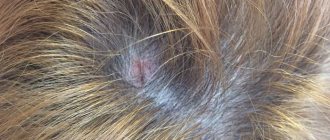
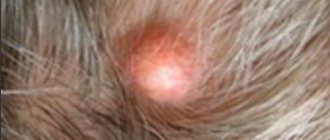
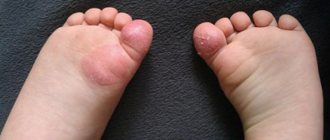
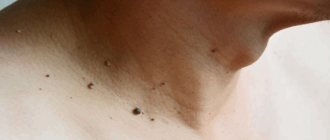
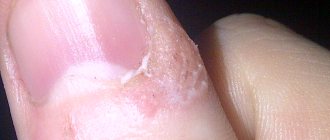
Diagnosis of papillomas on the hands
Visually determining whether we have a papilloma is quite difficult.
So, in children, similar symptoms can occur when infected with molluscum contagiosum.
In adults – when affected by certain types of helminths.
At any age, a similar picture can be caused by skin tuberculosis and some other dermatological diseases.
Therefore, in some cases a thorough examination is required.
The very first stage is dermatoscopy.
If this method was not enough to formulate an accurate conclusion, a biopsy and histological examination of tissue from the suspicious area is performed.
If HPV infection is beyond doubt, then PCR testing of affected skin cells may be indicated.
It will allow you to tell exactly what type of papilloma virus is causing the problem.
Accordingly, develop optimal tactics to combat the infection.
Indications for treatment of papillomas on the hands
Medical indications for the treatment of papillomas on the hands can be interpreted quite freely.
Doctors will recommend getting rid of them in the following cases:
- Identification of pathogens with a high oncogenic risk - types 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 45, 56, 59, 66 and 68
- Localization in which a person’s functionality decreases and has a negative impact on the quality of life (example - palm)
- Many small papillomas on both arms of the child, as they can become a source of infection for other children
- Localization in which manifestations of HPV are constantly injured
In addition to such purely medical indications, there are also cosmetic ones.
After all, few people will like an unsightly and unsightly growth on the hands or open parts of the forearms and shoulders.
Of course, more women come forward with requests to remove papillomas on their hands for cosmetic purposes.
However, men also take care of their appearance.
As for children, decisions are most often made by parents.
How is the human papillomavirus transmitted: what is the danger?
Everyone should know how the human papillomavirus is transmitted. This is the only way to protect yourself from dangerous diseases. Often, papillomas are not given much importance. Many people believe that if a growth appears on the body, it will disappear on its own. This mistake haunts humanity, and the consequences may be undesirable.
Papilloma tissue tends to grow, which leads to the spread of papillomavirus throughout the body. Sometimes its individual strains can cause cancer.
What is human papillomavirus
This virus is a chronic infectious manifestation of various diseases that can appear in a person at any age. In medical practice, this virus comes in two types: one that does not carry a high risk of dangerous diseases, and a virus with a high risk.
The papilloma virus multiplies on the skin and its mucous membranes. As a result, the following growths form on the skin:
- warts;
- condylomas;
- papillomas in the mouth and larynx;
- papillomas on internal organs.
Many cases have been recorded in which papillomas become the cause of cervical cancer in women, as well as cancer of the male genital organs. To avoid such consequences, it is necessary to know about the routes of transmission of the disease.
How does the virus enter the human body?
The infection spreads through the mucous membrane or skin of a person. If there are no acute diseases, then papilloma does not manifest itself in any way, and growths do not form on the surface of the skin.
If growths of different colors have formed on the skin, then this indicates a precancerous condition, when the human skin, and the entire body, suffers a malignant disease, or the immune system is significantly reduced.
The “favorite” place for bacteria to penetrate are cuts, scratches and other skin lesions through which the virus can penetrate. The likelihood of infection increases if:
- A person has colds or other reasons for which immunity is greatly reduced.
- Dysbacteriosis of the intestines or female genital organs is observed. In this case, the beneficial microflora dies and is replaced by harmful microorganisms, in this case, papillomavirus infection.
- Presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Relapse of chronic diseases.
- Stress and depression, which reduce a person’s defense against viruses.
Most often, people suffering from nicotine addiction, as well as women taking birth control pills, get sick.
How the virus spreads
If a person has no symptoms, this does not mean the papilloma virus is absent. The initial stage, when there are no growths yet, can be diagnosed using the latest equipment. In medicine, there are several ways through which dangerous microorganisms are transmitted.
Both men and women can become infected with the dangerous virus. The following transmission methods are distinguished:
Sexually
This is the most common way to become infected. Just one sexual encounter, and the papillomavirus can be transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person.
Many people are interested in the question of whether papillomavirus is transmitted from woman to man. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in men, however, a large number of women can become carriers of the disease. In this case, the location of the bacteria becomes the genitals or the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, where genital warts appear. In this case, there is a 100% risk of infection.
Predisposing factors for the disease are:
- early onset of sexual activity;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- condylomas or warts that the sexual partner has.
Reproducing in the mouth, in the absence of qualified treatment, there is a high probability of developing throat cancer. To avoid such consequences, you must use a condom.
If the localization of the virus is human skin, then a condom will not help. Papilloma is transmitted from direct contact with human skin on which condylomas and warts are located.
By everyday means
In this case, infection occurs in the following ways:
- Sharing the same towel, soap and other personal hygiene products with a person who has condylomas on their hands. Pathology occurs if there are injuries and abrasions on the body.
- Using the same toothbrush or utensils leads to infection through the patient’s saliva.
- The clothes of an infected person can also become a hotbed for the development of the virus and be transmitted to a healthy person.
- Self-infection through shaving, hair removal and other methods. The disease develops if a wart, which previously did not pose any danger, is damaged with a razor or other object. If damaged, this growth provokes the development of neoplasms, which can pose a significant danger to human health.
Infection in public places through contact with infected people
Medical practice has recorded cases where the virus was transmitted through blood transfusions, operations to remove condylomas, when doctors accidentally spread the source of infection throughout the body, and poor sterilization of manicure instruments in salons.
Mother-to-child transmission of the virus
Human papilloma is not a hereditary disease, however, the risk of transmission from mother to child still exists. When carrying a child, the risk of transmitting the virus is minimal, but still, if the placenta is damaged or other changes occur, papilloma can spread to the unborn baby.
The virus will reach him through the placenta, since the fetus has not yet formed bronchi and alveoli. In this case, the child develops respiratory papillomatosis. If after the birth of the baby he experiences breathing problems, then an examination is carried out, after which medication or surgery may be prescribed. The latter option is used much more often, as it has a greater chance of cure.
Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo all the necessary tests to eliminate the risk of developing papilloma.
There is a very high probability that the child will become infected with the virus when passing through the birth canal. The consequence is the appearance of genital warts in the child’s mouth and larynx, which leads to various disorders of the respiratory system and decreased immunity.
If papillomas were detected in the woman’s genitals before giving birth, the birth is carried out artificially to reduce the risk of infection of the child.
Another way to infect a child from the mother is through breastfeeding. In this case, the child develops respiratory papillomatosis, which must be treated immediately.
Features of the virus in men and women
In women, the virus enters through the cervix, rectum or oral cavity. If there is a frequent change of sexual partners, the risk of infection increases to its maximum. The consequences of the disease can be infertility, cancer and many other ailments.
The papillomavirus in men most often manifests itself on the scrotum, head of the genital organ, anus or oral cavity. In men, the disease can occur without symptoms; only after severe stress or decreased immunity can the development of papillomavirus occur.
A dangerous aspect of HPV in men is the development of cancer of the male genital organs or anus.
In order to prevent the virus from entering the human body, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene, as well as lead a healthy lifestyle and be faithful to one sexual partner.
Methods for destruction of papillomas
Effective and relapse-free removal of single or multiple papillomas on the hands can only be guaranteed by contacting a qualified dermatologist.
The doctor takes into account diagnostic data, age, gender of the patient and selects the optimal method.
The choice is quite wide:
- local cytotoxic drugs
- cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen
- radio wave excision
- laser ablation
- plasma coagulation
- traditional surgery using a scalpel
Each of the listed methods has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Ointments and creams for local treatment of papillomas on the hands are based on preparations of celandine juice or acids.
They are available and easy to use, but sometimes their use causes burns and scars.
Cryodestruction, although it requires certain tools (Dewar flasks for storing liquid nitrogen), is still inexpensive.
Suitable for combating numerous small papillomas and warts on the hands.
It copes poorly with large formations.
The reason is that the cold is removed from the deeper layers of the skin by a network of capillaries, and the tissues do not freeze.
Radio wave excision requires a special scalpel.
The advantage is that it is bloodless and allows complete removal of a large papilloma with a deep and wide root.
However, the procedure is painful.
Laser ablation is a fairly good method.
Its essence is that coherent light radiation of a certain wave is most absorbed by cells affected by papillomaviruses.
As a result, they coagulate, and minimal harm is caused to healthy skin.
Plasma coagulation is a relatively new but effective method of treating papillomas on the hands.
Its essence is that the formation is first cooled well, and then quickly heated to high temperatures and simply evaporated.
The procedure is almost completely painless.
But pathogens are released with the steam, which can cause the development of a process in the respiratory tract.
So additional protection is required - a mask, a HEPA filter.
The traditional scalpel is used in doubtful cases and when there is no access to other techniques.
Disadvantages are pain and bleeding (albeit minor).
Advantages: reliability and the ability to send removed tissue for histological examination.
All methods of destruction have one serious drawback: with an unskilled approach, scars may remain after the procedures.
Overgrowth of connective tissue on the palms and hands is a very unpleasant and difficult process to treat.
Recovery after surgery
It is important to maintain hygiene; do not wet the wound. If the wart was very large, then you should not put any physical strain on your hand to prevent bleeding. When the wound is on your leg, you can’t walk a lot or lift weights. It is important to allow the wound to heal faster. Minimal stress and the use of an antiseptic will help speed up the healing process.
It is important to remember that small papilloma can be easily removed; a small wound will heal in a week in any case. But large and large warts multiply greatly and leave behind deep wounds.
Adjuvant therapy in the treatment of papillomas
It is now becoming obvious that the effectiveness of destructive techniques should be supported by adequate drug support.
Therefore, injections or tablets for papillomas and warts on the hands are becoming commonplace.
The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Immunostimulants – Amiksin (tilorone)
- Antiviral – Cycloferon
- Interferons – Viferon
- Immunomodulators – Lykopid
Medicines begin to be taken several days before the removal procedure and continue for at least 5 days after destruction.
Specific names and doses are selected individually.
So, Viferon can be taken in tablet form or this drug can be injected directly into the papilloma.
Despite a lot of nuances, when used correctly, the therapeutic approach significantly reduces the likelihood of relapse and reappearance of the removed papilloma on the hand, palm or other areas of the skin.
Causes
The appearance of papilloma on the body occurs after contact with a carrier of the virus. Most often, people become infected from a handshake, contact on public transport, and from any salon procedures where the rules of hygiene and sanitization are not followed. Also, the cause of papilloma on the finger, a photo of the neoplasm is presented in the article, can be sexually transmitted infection, a kiss with a patient, or touch. The virus can penetrate through unprotected areas of the body (wounds, cracks, abrasions, etc.), and the infection can pass from the mother’s body to the child’s body during pregnancy.
Treatment of papillomas in children
When deciding what to do with a papilloma on a child’s arm, many different factors should be taken into account.
It wouldn’t hurt at all if the opinion of the smallest patient was also taken into account.
Children have very delicate and thin skin.
In their case, preference should be given to those methods that have the least side effects and trauma.
This may be laser therapy, plasma coagulation or cryodestruction.
Among chemical methods, preference should be given to an ointment such as Solcoderm.
Whether to use immunotherapy together with destructive methods is a rather difficult decision.
Since children have an immature immune system, unqualified intervention can greatly harm their health in the future.
Celandine
A fresh cut of grass is used, from which yellow juice flows. It is with this juice that you need to completely cover the papilloma. All papillomas must be lubricated at once, sparing no celandine. The juice, oxidizing in air, becomes orange, and later dark brown. It dries out the wart perfectly, but you need to lubricate it at least twice a day. You can use a vinegar tincture, for which it is important to dry the stems with flowers, then compact them tightly in a jar and fill them completely with vinegar. This tincture must be left in the dark for at least a week for it to gain its strength.