Everyone has at least once encountered the appearance of a wen on the body. They can come in different sizes and form on any part of the body. There are cases when wen and lumps spread throughout the body. What is the reason for this phenomenon?
Rice. 1. Fats and bumps all over the body can be a sign of hereditary lipomatosis
Symptoms, signs, diagnosis of lipoma
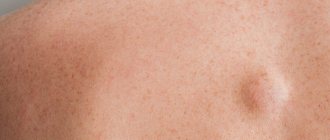
Before you remove a wen, you need to make sure that it is exactly that. The shape of the wen formed under the skin is round or oval. It is mobile and soft to the touch; as a rule, no pain is felt when pressing on it.
Fatty deposits located under the skin of the face, neck, back, arms and other parts of the body usually do not cause any symptoms. A lipoma formed on internal organs causes the following symptoms:
- When a lipoma appears in the esophagus, coughing, nausea, and a feeling that there is a foreign body in the throat may occur;
- Chest pain may be the cause of lipoma formation in the mammary gland;
- Symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and vomiting may occur with a lipoma in the brain.
A lipoma is diagnosed visually during a clinical examination; if this is not enough, using ultrasound, x-rays, and computed tomography.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma
- a benign tumor that most often appears on the head and neck in girls. As a rule, vascular formation is detected in newborns.
The reasons for the formation are not clear. Presumably, this is a viral infection carried by a pregnant woman.
Symptoms of pathology
- Superficial formations are red or purple in color and have clear edges. When pressed, the formation turns pale.
- Cavernous hemangiomas are located under the skin in the form of blood-filled nodules.
- Combined hemangiomas are a combination of superficial and subcutaneous.
- Mixed formations consist of different tissues.
- Hemangiomas of the perineum and genital organs are prone to ulceration.
How is the diagnosis done?
- The problem is diagnosed by a surgeon using an external examination and laboratory data.
- Using ultrasound, the depth and location are determined, the speed of blood flow and the volume of the tumor are measured.
- For large tumors, angiography is used.
Hemangioma in adults is a rare phenomenon. Most often, localization occurs on the neck and face, less often - on the arm, on the finger, on the hand, in the anus, on the external genitalia. It does not degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Treatment
The disease is often treated by surgeons. Hemangioma should be treated immediately after detection:
- For deep-lying formations, surgical excision is used;
- For large areas, radiation therapy is used, acting in small fractions;
- Cauterization (diathermoelectrocoagulation) is used for point formations.
- For small complex formations, sclerosing treatment is used - alcohol injections.
- Treatment of combined hemangiomas requires the sequential use of cryogenic and injection therapy.
- Hormonal treatment is indicated for children.
- All simple small hemangiomas must be cauterized with liquid nitrogen.
- Over a large area, the use of hormonal and radiation exposure is indicated.
- For cavernous and combined lesions, surgical, cryogenic and sclerosing methods are effective.
- For formations in the parotid region, complex treatment using angiography and embolization is used.
The disease is often treated by surgeons.
If left untreated in young children, the formation may resolve over time. If the formation increases or complications arise, then it is not recommended to delay. Vascular tumors on the face should be removed early, as the risk of complications is too great.
Treatment of wen
Despite the fact that a wen under the skin usually does not cause any inconvenience, many people are interested in how to remove a lipoma . First of all, you should consult a doctor, especially in cases where inflammation of the wen has occurred. Those who are wondering how to squeeze out a wen should know that you should never do this yourself.
Removing wen at home can not only provoke infection into the wound, but also leave unsightly atrophic scars. However, in addition to the medical procedures that a doctor can offer, there are also traditional medicine and pharmaceutical preparations that will help cope with this problem.
Surgical removal of lipoma
It would be more correct to call this procedure “traditional”, because any removal of tumors is a surgical procedure. Before the procedure, you will need to undergo an examination, the results of which will be needed by the surgeon. Most often, it will be enough to take a general blood and urine test and do fluorography. Depending on the general health of the patient, additional examinations may be required: blood sugar test, electrocardiogram, etc. - as prescribed by a specialist.
The operation itself on a small tumor is performed under local anesthesia. The surgical field is injected with anesthetic, disinfected, an incision is made through which the tumor is removed along with the capsule, and sutures are placed. The whole procedure takes no more than 15 minutes. The contents of the capsule are sent for histological examination, which is necessary to exclude a malignant process.[box#2]
If the operation is performed on open areas of the body - face, neck, arms - the surgeon may apply a cosmetic suture with an absorbable thread. In this case, there is no need to remove the stitches. Regular sutures are removed after 10-12 days, by which time the histology result is usually ready. If you are not prone to keloid scars, the scar will appear as a small light stripe that will become invisible over time.
How to remove wen using traditional methods
If it is not possible to visit a doctor’s office, you can try to remove the lipoma yourself. But this applies only to those formations that have appeared recently. If the lipoma is old, it needs to be treated only surgically.
Baked onion
Onions are considered one of the most effective means for removing wen. Do the procedure at least 2 times a day.
- Take one medium onion and bake in the oven.
- Grind the cooled onion using a meat grinder.
- Grate baby soap, add to onion and mix thoroughly.
- Apply the resulting mass as a compress to the wen.
Sour cream with honey
Before the procedure, you need to take a hot bath to steam the wen. Then the components of the prepared remedy for wen will better penetrate the adipose tissue of the tumor. Carry out the procedure every other day.
- Mix equal amounts of sour cream, honey and sea salt.
- Apply the resulting mixture to the problem area.
- After 20 minutes, rinse with warm water.
Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma
- a benign formation over the bone in the form of a smooth protrusion of cartilage tissue up to 12 cm in size with bone marrow contents. Osteochondromas can be multiple or single.
The reasons for the appearance of such formations are not fully understood. The risk of developing osteochondromas is believed to increase:
- Intrauterine anomalies of skeletal formation;
- Hereditary factors;
- Irradiation.
Osteochondroma of the bone occurs:
- In the area of the joints, eventually spreading to the middle of the bone;
- Localization occurs on the ribs, femur, vertebrae, tibia, foot and scapula;
- Less commonly, the hands, heel bone and humerus are affected.
The bones of the skull are not affected. There is no pain or mobility. The tumor has clear boundaries. If the tumor is small, it does not bother you; pain may occur when the blood vessels are compressed.
How is the diagnosis done?
- After an external examination, the patient is sent for an x-ray, which will show the formation and its connection to the bone.
- MRI or CT is used if the situation is unclear.
- Morphological analysis may be performed.
Treatment
The only method used is surgery - removal of the formation with its base and stem. The removal process is necessary if:
- Education is increasing;
- Has large sizes;
- Accompanied by pain;
- Causes skeletal deformation.
In other cases, the patient is observed and monitored using x-rays.
Forecast
The disease has a favorable prognosis - its growth stops with the end of the formation of the skeleton. Degeneration into a malignant state ranges from 1 to 10% (more often with multiple formations).
Recovery after surgery is quick. Patients are prescribed physical therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment of lipomas with pharmaceutical products
Those who prefer to use pharmaceutical drugs should purchase Vishnevsky ointment. This product should be applied to an adhesive plaster and attached to the affected area, after 2 days the plaster should be replaced with a new one.
You can also use hydrogen peroxide. This drug should be regularly lubricated. After a few days, the skin on the affected area will burst and the contents of the wen will leak out.
lipoma treatment
Laser lipoma removal
Unfortunately, laser removal of tumors has its own contraindications. This method is not used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, diabetes, the presence of infectious skin disorders in the area of intended exposure, or immunodeficiency states. Deep-lying, large or branched neoplasms, as well as those whose structure includes vessels and nerves, are not removed using a laser.
In general, the operation is similar to the previous methods. The surgical field is anesthetized, the skin over the tumor is cut with a laser beam, and small vessels are cauterized at the same time. Then the capsule with its contents is removed using a clamp and cut off with a laser. At the end, the wound is sutured and a sterile bandage is applied. The entire procedure takes 15-40 minutes, and during the rehabilitation period you only need to follow the rules of asepsis to avoid inflammation of the wound.
How a doctor can help you remove a wen
It is highly advisable that lipoma removal be performed by an experienced specialist. After a thorough examination, a dermatologist may prescribe the following procedures to remove wen:
- Mechanical cleaning. This method is considered the simplest. The procedure is carried out by piercing the wen with a needle, after which all its contents are removed. Sometimes the procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
- Removal of lipoma with laser . Laser therapy is considered the most progressive method for removing fatty tissue. The procedure is very quick and does not leave scars. In addition, the possibility of the wen reappearing in the same place is excluded.
Why do wen form on the body?
Multiple wen and lumps throughout the body indicate some kind of disorder in the body. It is difficult to say exactly why they form. There are some factors that can become provocateurs:
- weakened immunity;
- poor nutrition, which contains a lot of fats, carbohydrates, and few vitamins and proteins;
- injuries;
- metabolic disorders, especially carbohydrate and fat;
- hormonal health problems;
- smoking;
- hereditary predisposition;
- regular compression of the same areas of the body.
In people over 40 years of age, the risk of developing wen increases.
Rice. 2. Wen on the body can hurt
Prevention of lipoma
After lipoma removal, the following preventive measures must be observed:
- reduce the consumption of fatty meats and high-fat dairy products;
- introduce vegetable oil and fish into the daily menu;
- refuse late dinners;
- move as much as possible.
You need to follow these recommendations not only if a lipoma has already appeared, but also if there is a hereditary predisposition. Doctors say that the risk group for the formation of wen includes middle-aged and elderly people.
Mesenchymoma
Mesenchymoma
– a malignant formation related to sarcoma. Angiosarcoma and liposarcoma can be found in its composition.
The exact causes of the occurrence have not been clarified. Perhaps this is the effect of carcinogens on the fetus. Risk factors are:
- Vibration, hypothermia and ionizing radiation;
- Chemical exposure – toxic substances, drugs;
- Bacterial and viral infections.
The location is predominantly the chest and abdominal cavity, mediastinum and retroperitoneal space. The formation is manifested by pain, cough, heartburn, shortness of breath and a feeling of fullness.
Diagnosis is carried out using radiography, ultrasound, MRI, biopsy and endoscopic examination. Treatment is carried out surgically. Auxiliary methods are radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
How are atheromas and lipomas treated?
Atheromas are treated surgically; the type of operation will depend on the size of the formation. Small sebaceous cysts can be removed with a laser. Most often, atheromas are large in size and are removed with a scalpel. The “bump” on the skin is surrounded by two incisions, then the cyst is peeled out and removed along with a small piece of skin. Stitches are placed on the wound.
Atheroma cannot be cured by “sucking out” the contents with a needle and syringe. It is imperative to remove the walls of the stretched sebaceous gland - if they remain, they will begin to produce sebum again, and the cyst will grow again.
If atheroma suppurates, surgical treatment is performed, and the doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics. Lipomas do not need to be treated. The operation is performed if:
- education is large and growing rapidly;
- the lipoma is in an inconvenient place and is constantly in the way;
- bothered by soreness;
- The patient himself insists on removing the lipoma.
Wen is removed in the classic way, using a scalpel. Relapses are possible, but extremely rare. Typically, atheromas and lipomas are removed on an outpatient basis; hospitalization is not necessary. Anesthesia is also not needed - local anesthesia is sufficient. The operation lasts on average 15–20 minutes.
Make an appointment by phone +7 (495) 120-08-07.
Intraosseous lipoma
Intraosseous lipoma is a rare benign tumor, accounting for about 0.1-2.5% of all bone tumors. It is the most common lipogenic bone tumor {6}.
Epidemiology
They can be present in an extremely wide age range (from 5 to 85 years), although the peak age of detection usually falls in the 4th–5th decade of life. There is a slight predisposition in males {6}.
Clinical picture
Pain is the main symptom in most cases, but more than 30% of bone lipomas are an incidental finding during examinations performed for other reasons {1}.
Distribution, localization
Although intraosseous lipomas can be found anywhere within the skeleton, most cases occur in the lower extremity. When located in long bones, they are usually localized in the metaphysis {1,7}:
- Lower limb: 71% Calcaneus: 32% (considered the most common lesion in the calcaneus)
- Femur: 20% (especially intertrochanteric region)
- Tibia: 13%
- Fibula: 6%
Pathology
Intraosseous lipomas are located almost exclusively in the medullary cavity, usually in long bones. They consist of mature adipocytes without admixture of hematopoietic tissue or bone trabeculae {7}.
Diagnostics
Radiography
The radiographic appearance of intraosseous lipomas has a broad differential diagnosis, including numerous benign bone lesions. The typical presentation is a benign osteolytic bone lesion with well-defined margins.
CT / MRI
Based on CT attenuation or MRI signal characteristics, the differential diagnosis may be narrowed to fatty bone lesions. The fatty components of intraosseous lipomas may exhibit varying degrees of involution and necrosis. Based on these features, Milgram and co-authors {2} identified three categories:
- Stage 1 : Well-defined, viable lipomas with uniform fat content
- Stage 2 : Predominantly fatty lesions with central necrosis, calcification, or ossification
- Stage 3 : Heterogeneous fat-containing lesions with multiple necrosis, cystic transformation, mural sclerosis, and extensive calcification or ossification.
Stage 1
The lesions have a homogeneous, hyperintense signal typical of fat on T1- and T2-weighted images, which is completely suppressed on fat-suppressed sequences (STIR, FS). The trabecular pattern of cancellous bone is usually absent in the lesion.
Stage 2
In the structure of the formation, inclusions that are hypointense on T1-weighted images appear, having a hyperintense signal (granulation tissue / necrosis) or hypointense signal (calcifications or ossifications) on fat-suppressed sequences.
Stage 3
In addition to the telltale characteristics of stage 2 lesions, stage 3 lesions may contain fluid cavities and nonintense bony septa and may be surrounded by a thickened nonintense sclerotic rim. Although there are usually no signs of aggressive growth, expansive intraosseous lipomas can invade the cortex. This can be used to differentiate them from older bone infarcts, which may also develop cystic degeneration over time. In addition, in intraosseous lipomas, T2-hyperintense granulation tissue of central necrosis is surrounded by viable adipose tissue. In contrast, in bone infarcts, adipose tissue in the center is surrounded by granulation tissue at the periphery. In cases with significant secondary involution and necrosis, a biopsy may be required to confirm the diagnosis {3}.
Treatment and prognosis
Intraosseous lipomas that do not affect bone stability can be treated conservatively. If there is a threat of a pathological fracture, curettage and bone transplantation are performed. There are no relapses after surgical treatment. However, malignant transformations have been described sporadically {1}.
Differential diagnosis
- In the calcaneus: normal triangular radiolucency, unilocular bone cyst
- In the proximal part of the tibia: bone infarction
- In the proximal femur: liposclerosing myxofibrous tumor
Diagnosis and treatment of lipoma at the JSC Meditsina clinic in Moscow
The clinic of JSC "Medicine" in the Central Administrative District of Moscow is ready to offer professional assistance to patients with suspected single or multiple cases of lipoma development. The center’s specialists have high-quality equipment and extensive practical experience in using various methods of removing a tumor focus. Each patient is guaranteed attentive attention, referral to a full course of examinations and an individual approach to developing lipoma treatment tactics. Appointments are available on the clinic’s website and by calling the numbers provided.
Contraindications for surgery
Surgical removal of a lipoma, like any other surgical intervention, has a wide range of contraindications.
- Thus, surgical removal of wen is not performed on women in an “interesting” position, or during breastfeeding. Doctors recommend refusing surgery during “critical days.”
- Herpes, recent colds or infectious diseases are also reasons to undergo surgery.
- It is highly undesirable to perform surgical removal of a wen if the patient has been diagnosed with diabetes.
- Surgical removal is also fraught with complications due to secondary immunodeficiency - in other words, reduced body resistance.
What you need to know about cardiac lipoma
- A lipoma is a tumor of adipose tissue.
- The main causes of lipoma are differentiated fat cells
- Detected incidentally due to a heart murmur or abnormality on chest x-ray
- Around 60 cases of lipoma have been described worldwide.
- There is no age predisposition
- It is much less common than lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum.
- Large tumor mass (mass weighing up to 4.8 kg has been described)
- Lipoma often originates from the epicardium
- Spreads to the pericardial sac.
What to do if lipomas hurt?
In its normal state, a lipoma has a spherical appearance (a round tumor with clear boundaries up to 5-7 cm in diameter). The lipoma is enclosed in a capsule. In most cases, it has a nodular structure, does not hurt, does not itch, does not bother palpation and practically does not grow. If the lipoma has become painful and is growing rapidly, then this may indicate not only inflammation, but also possible malignancy of the tumor. The catalyst for the inflammatory process in a lipoma can be injury and infection that has entered the body. Sometimes the cause of pain in a lipoma can be compression of nerves and blood vessels by the tumor. Pain in a lipoma is a signal for the patient to urgently seek advice and help from a doctor.
Rice. 2. If the lipoma hurts, it needs to be removed