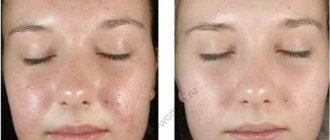
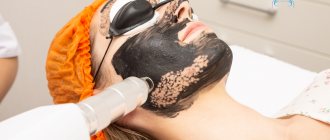
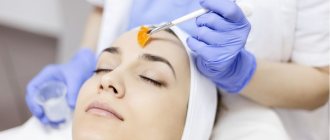
Chemical peeling is iatrogenic damage to certain layers of the epidermis and/or dermis.
In response to damage, a huge amount of pro-inflammatory mediators, growth factors, and biologically active substances are released, which leads to the activation of protective regenerative mechanisms, an increase in the metabolic and mitotic activity of basal keratinocytes and fibroblasts. The expected effects of the chemical peeling procedure are improvement of the appearance of the skin: color, smoothing of the skin profile, improvement of micro- and macrorelief, activation of reparative processes, increased synthesis of epidermal lipids and extracellular structures of the dermal matrix. The effect depends more on the depth of skin damage and less on the chemical preparation. The stimulating effect of chemical peeling is indirect. This is the skin's reaction to inflammation that develops as a result of skin damage.
Classification
- Superficial peeling (within the stratum corneum) minimal inflammatory reaction, m/painful, the safest. AHA, aβ-complexes, phytic, Jaisner, 1-15% TCA.
- Median (within the Malpighian layer). Medium peeling is accompanied by necrosis of the Malpighian layer, with the development of a pronounced inflammatory reaction (hyperemia, edema) and severe peeling; the rehabilitation period is 7-14 days. Allows you to change (smooth) micro- and macrorelief. Recommended for the correction of superficial wrinkles, enlarged pores, post-acne, and stretch marks. 15-25% TCA, combined TCA + enzyme (papain), Blue peel, Krulig peeling, phenol.
- Deep (with damage to the papillary dermis)
The only type of peeling that allows you to correct wrinkles, a high risk of scarring, rehabilitation up to 1.5 years. 25-50% TCA, phenol up to 40% - the “gold standard” of peeling. The most effective, the most toxic. It has a selective cytotoxic effect on melanocytes - recommended for the correction of hyperpigmentation.
Causes of peeling
Exfoliation (this is another name for deep cleansing of the skin) is impossible without exfoliating dead epidermal cells. But sometimes the peeling occurs too intensely. Causes of peeling:
- Intensity of cleansing.
Peeling can be deep, medium or superficial. In the first two cases, the epidermis is especially severely injured. Therefore, the consequences are also more noticeable: redness, peeling, swelling. - Composition of the peeling product
. Lactic and malic acids are considered gentle. They do not cause intense peeling. And the use of trichloroacetic acid is more traumatic. - Individual characteristics.
Patients with drier, more sensitive skin suffer from severe flaking after a peeling session.
Superficial chemical peeling AHA
When talking about superficial chemical peeling, we primarily mean peeling with AHA, or fruit acids.
The first mention of cutaneous use of AHA dates back to 1974. Van Scotch and Yu, studying the effect of various drugs for ichthyosis, found that glycolic acid is able to control the processes of keratinization of the epidermis, weakening the adhesion between corneocytes. Subsequently, the therapeutic effectiveness of ANA was established for all forms of hyperkeratosis.
The AHA group includes: glycolic, lactic, apple, tartaric, lemon
Low pilling fabrics
There are a certain number of materials that are not subject to a process called pilling. These include natural fabrics: cotton, linen, wool, silk and some artificial ones. Let's look at them in more detail next.
Cotton fabrics
Cotton fabrics with low pilling properties include:
- Chintz;
- Denim;
- Batiste;
- Calico;
- Poplin;
- Veil;
- Kanifas:
- Percale;
- Teak;
- Pique.
Indications for use
Biological aging of the skin. Almost all types of peelings are used to correct signs of aging. The choice of one procedure or another is determined primarily by the severity of cosmetic defects. ANA peeling optimal age 23-30 years (prevention of aging), no correction of age-related changes. Number of procedures 4-6, ANA concentration 50-70% Additional components: antioxidants
Photoaging is changes in the skin under the influence of UV rays. 50-70% ANA, number of sessions 8. The most promising is the combination of ANA with antioxidants and whitening agents.
Pigmentation -
- dyschromia - 70% ANA, amount 8. Optimally αβ-complexes
- chloasma, hyperpigmentation - it is recommended to use AHA up to 50%, as inflammation can cause increased pigmentation. Pre-peel preparation is required to reduce the risk of increased hyperpigmentation, includes the use of phytic acid 3-10%, combined preparations of glycolic acid + kojic acid, ascorbic acid, glabridin, antioxidants that reduce inflammation are recommended, and the use of UV filters is mandatory. Number of sessions 8.
- Comedonal, papulopustular form of acne. Initially, the use of ANA for acne vulgaris was limited exclusively to the treatment of post-eruptive hyperpigmentation and scarring. This was the only method for correcting secondary skin changes in this disease, which is possible even against the background of unresolved inflammatory elements. Subsequent clinical observations showed that the use of this group of drugs significantly accelerated the relief of the inflammatory process and extended the time of remission
Consequences of the procedure
Some consequences are not worth fearing. The procedure itself is a chemical burn, after which the cover begins to recover on its own. The level of collagen and the number of elastin fibers increase. New cells replace dead layers. This manifests itself in redness, peeling, burning and swelling.
Sometimes clients experience more serious reactions, which may require another visit to the dermatologist:
- Intense redness that becomes increasingly brighter and does not disappear within an acceptable recovery period.
- A watery rash indicates a violation of the procedure. Unpleasant consequences - spots, scars.
- Severe swelling, fever.
- Scars are a consequence of damage to drying crusts.
Such reactions occur if the remedy was chosen incorrectly, the specialist did not take into account contraindications or performed the session incorrectly. And also a negative reaction is sometimes provoked by the clients themselves if they do not follow the recommendations of their cosmetologist.
Medium chemical peels
TCA (15-25%) is a keratolytic, causing protein coagulation. Non-toxic substance.
When applied to the skin, TCA causes the formation of a frost effect. Depending on the depth of necrosis, the following types of frost effect are distinguished:
- Pink frost: “pointed” - throughout the entire depth of the stratum corneum; “clouds” - granular layer
- White (milky): translucent film - the border of the granular and spinous layer
- White deaf, compact: up to the basement membrane, dermal papillae
- Solid white with a yellowish/greenish tint: up to the reticular layer (there will be a scar in this place).
Contraindications
Absolute:
- Dermatoses in the acute stage (especially herpes infection)
- IV,V,VI skin phototype
- Tendency to form hypertrophic and keloid scars
- Rehabilitation period after other cosmetic procedures (Botox - 14 days, microimplants - 1 week, laser resurfacing, dermabrasion - no earlier than 1 year)
- Pregnancy, nursing (painful procedure)
- Mentally labile patients.
- Thin, sensitive skin with reduced regeneration
Relative: nevi, rosacea, hypertrichosis, spring-summer period
Expected skin reactions occurring immediately after a chemical peel (1-14 days):
- Edema. Most often, swelling and pastiness develop with deep peels. With superficial peeling, swelling is moderate or absent. It develops on the first day after the procedure, reaches a maximum on the 3rd day, and disappears by the 5th day. The severity of edema varies for each patient; it most often develops in people with thin and loose skin. It is extremely rare that after deep peels, significant swelling of the eyelids, neck and upper chest may develop. But there is never any swelling of the upper respiratory tract or any systemic damage after a chemical peel. There is no need to prescribe special therapy for the treatment of edema. Prophylactic administration of steroids does not prevent the development of edema. Although a number of authors recommend the use of glucocorticoids in a short course, both intravenously (during the procedure) and orally for 5 days, because this can significantly reduce swelling. As a rule, cold compresses are used more often to prevent swelling of the eyelids.
- Hyperemia. With superficial and medium peels, the erythema is moderate and disappears by 3-4 days. With deep peeling, erythema may persist for up to 1-2 months after the procedure. The most pronounced erythema occurs after laser resurfacing and dermabrasion. It appears immediately after the procedure. After 7-10 days, its intensity decreases, but it can persist for up to several months. This is due to the fact that during these procedures the dermis is “exposed”.
- Darkening of the skin. After a TCA peel, the epidermis often turns dark brown. After 3 days, separation and exfoliation of the destroyed layers of skin begins, which reaches a maximum by 5-6 days and completely stops by 7-14 days. As a result, the regenerated new skin has a pink color. Αβ-peeling
A combination of glycolic and salicylic acids. It is a superficial-medium peeling. Incoming salicylic acid (keratolytic) potentiates the penetration of glycolic acid.
The technique is similar to AHA peeling. Brighter erythema after 15-20 seconds, intense burning, possible frost effect. Exposure up to 1-2 minutes. Indications: thick, porous skin, post-acne.
How to avoid the formation of pellets?
On an industrial scale, to reduce the pillability of the material, the following measures are used:
- They produce profiled synthetic fibers that have a cross-section in the form of a rectangle, triangle, or asterisk. They reduce the likelihood of pill formation;
- The second way to reduce fabric pillability is to increase the length of the fibers;
- Pillability can be reduced by increasing twist or increasing fiber density;
- They also resort to special processing of fabric, for example, heat setting of fabric made from synthetic fibers.
Next, read how to deal with fabric pilling at home?
This can be achieved in the following ways:
- First, choose your fabric carefully, avoiding those that are most susceptible to this process;
- Secondly, take proper care of them;
- And finally, thirdly, eliminate such unpleasant and spoiling the appearance of products, pellets.
The pilling process proceeds systematically, so after eliminating the pills, be prepared for them to form again.
So, we have sorted out fabrics with high and low pilling, in order not to forget this information, catch a reminder that will not allow you to buy highly pilling fabric. To do this, you just need to carefully read the composition of the material of any textile product.
If you have already purchased a product made from pillable material and it is not possible to influence the structure of its fibers, remember that no special care will help you get rid of pills completely, but you can reduce their number if you follow the recommendations for washing, drying and ironing the product, indicated on the label.
Read on for ways to get rid of already formed pellets.
5 ways to eliminate pills (pellets) on fabric
- Woolen and drape items can be carefully shaved with a razor.
- Comb knitted items with a fine comb, being extremely careful to avoid puffs.
- The pellets, if a little, can be cut off with small nail scissors.
- The coat can be cleaned of pills using fine sandpaper, which should be used to rub the area where the pills formed.
- You can also get rid of pills using modern methods, which include the emergence of special machines for removing pills. With the help of which you can get rid of it very simply and as quickly as possible.
If you still have questions about ways to eliminate pilling, combat pellets, or you simply want to express your opinion, write your comments. And we wish you a flawless look, pill-free textiles and pill-free knitwear!