Localization
The development of a dermoid cyst is possible in almost any organ or tissue, as doctors note. Most often the presence of cysts is found in:
- the ovarian area in women of reproductive age, which can seriously affect the ability of the fair sex to conceive;
- the lower eyelid area (mostly children are affected, but the pathological neoplasm can be easily removed with the help of surgeons);
- the coccyx area, where the size of the ovarian dermoid cyst rarely reaches large sizes, and the formation can go unnoticed for a long time;
- the area of the anus, where without symptoms of inflammation, pathology is generally detected only by digital rectal examination, etc.
The discovery of dermoid cysts in any organ or tissue makes this pathology quite common. Moreover, as doctors note, the presence of dermoid cysts can either not make itself felt for a long time or cause severe discomfort.
Symptoms
Detection of cysts - if they are on the surface - rarely poses serious difficulties for the doctor. Dermoid cysts are not very large in size and are usually painless even on palpation. Depending on the contents, the neoplasm can be either dense or soft.
If a dermoid cyst is found in one of the internal organs, it may not make itself felt for a long period of time. Symptoms appear mainly when the tumor reaches a certain size. For example, if there is an ovarian cyst, a woman will complain of:
- pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- more frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- the appearance of pain during sexual intercourse.
If inflammation of a cyst localized in the anal area develops, there will be pain during bowel movements and difficulty in taking a sitting position.
Symptoms that can characterize a dermoid cyst are very diverse. However, often due to the benign nature of the neoplasm, the pathology is an accidental finding.
How to get treatment:
- Make an appointment. By phone (89031830141), make an appointment from the website, by E-mail.
- Consultation. In person or remotely (E-mail, WhatsApp, Viber).
- Examination. Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. For proximal hypospadias or in combination with cryptorchidism - endocrinological examination.
- Hospitalization and collection of tests. Collection of necessary tests and preparation for surgery.
- Surgical treatment. Microsurgical reconstructive plastic surgery.
- Extract. Recommendations in the postoperative period.
LASER REMOVAL OF atheromas in “EL. EN."
Do you want to get great results?
Choose laser removal of atheromas with short rehabilitation and no scars. Our surgeon will recommend the optimal laser treatment method and perform the procedure. 1 Photocoagulation
The method is suitable for eliminating atheromas with a diameter of up to 5 mm. High-intensity laser radiation is directed (non-contact) to the neoplasm; as a result of the impact, the capsule and its contents are completely evaporated. After the procedure, a crust remains at the site of the atheroma; no stitches are required. After a certain time, the crust disappears, the resulting wound gradually heals, and the skin becomes even.
2
Excision
The method is most often practiced in situations where the diameter of epidermal cysts is up to 20 mm (but there are exceptions). The surgeon cuts the skin (with a laser knife or scalpel), stretches the cyst shell and evaporates the tissue around it with a laser - this is how the atheroma is separated from healthy structures. Then drainage is placed for several days.
3
Evaporation
It is practiced when the diameter of atheromas exceeds 20 mm. The surgeon opens the capsule, removes its contents, and then acts on the capsule with laser radiation - it evaporates. The operation is completed by installing drainage and suturing.
Our clinic also performs laser removal of ingrown toenails - the cost starts from 6,000 rubles. Sign up online or by phone.
Diagnostics
Before the procedure to remove a pathological tumor, the doctor will have to carry out a number of diagnostic measures in order to ensure that the diagnosis is correct, as well as to exclude more dangerous pathologies. After all, dermoid cysts can be confused with a number of other diseases.
Dermoid cyst on ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is a simple, painless and non-invasive way to obtain information about the characteristics of the cyst before surgery. It is possible to find out its size, growth characteristics, determine the stalk of the neoplasm and draw conclusions about its blood supply.
MRI
MRI for dermoid cysts is used if the neoplasm has a complex location or there is reason to believe that it is of a low-quality nature. MRI helps to better plan removal of the cyst capsule.
Blood test for tumor markers
If the ovaries are affected in women, it is recommended to donate blood for tumor markers. A cyst on the ovaries can degenerate into a malignant neoplasm, and in order to choose the right therapy, the doctor sends the patient for a blood test for tumor markers. Based on the results, a conclusion is drawn about how dangerous the formation on the ovary is, and whether there is a need for additional treatment.
Histology
Histology when the ovaries or other internal organs are involved in the process is performed in order to exclude malignancy of the neoplasm. The tissue obtained during removal is examined under a microscope to look for atypical cells.
Treatment
Small epidermal cysts, which do not cause the patient any physical or aesthetic concerns, doctors can simply observe their dynamics.
In other cases, the patient is sent for surgical treatment, which may include:
- laser coagulation (cyst desquamation);
- total removal of the epidermal cyst along with its capsule.
If it is not possible to completely resect the epidermal cyst, then the vast majority of patients experience a recurrence.
If the epidermal cyst is inflamed, the operation is postponed and the necessary anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. The abscess is opened and drained.
Indications for surgical treatment
It all depends on the location of the formation, its size, development dynamics, the patient’s age and condition, the effect on the functions of internal organs or their aesthetic value.
For example, if it is located under the skin of the face, on the neck or other open areas of the body, is large, grows, or manifests certain symptoms, then it should be removed after a full examination.
In case of a small formation, which does not manifest itself in any way and was an accidental finding of the examination, it is not always worth resorting to surgery - you should consult with a surgeon and evaluate all the pros and cons. Patients are often advised to see a doctor and undergo regular examinations. Only if the pathological formation begins to grow or change in some way should it be removed surgically.
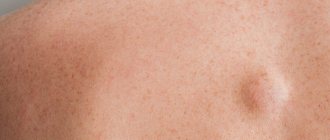
Manifestations of atheroma
Atheroma has characteristic manifestations in the form of a painless bulge, which is not fused with the surrounding tissues and does not differ in color. The diameter of the formation varies, it can reach 10 cm in diameter. The favorite localization of atheroma is skin areas rich in sebaceous glands (face, scalp, ears). Somewhat less frequently, sebaceous atheromas can form on the skin of the back and chest.
The addition of inflammation (it is provoked by the penetration of a bacterial infection) is characterized by redness of the atheroma and the appearance of pain. Further development of the infectious process causes the accumulation of pus in the cavity of the atheroma, which can come out through the fistula, or cause purulent melting of the surrounding healthy tissue.
Cyst removal methods
Removal of a dermoid cyst in most cases is not considered a complex procedure in surgical practice. Today, clinics use the laparoscopic method when it comes, for example, to ovarian cysts.
Laparoscopic surgery has become popular due to the fact that the intervention allows for a faster recovery and has a lower risk of complications.
However, if the pathological neoplasm is very large or localized in a hard-to-reach place, it is possible to remove the cyst through classical open surgery.
Women often worry that if the ovary is damaged, they will have to remove it entirely, but this is not always the case. If the surgeon can save the organ while ridding the patient of dermoid cysts, he will do so.
HOW IS ATHEROMA DIFFERENT FROM LIPOMA?
In appearance, any atheroma is in many ways reminiscent of a lipoma (“fat”), but these two neoplasms differ in structure. Lipoma is formed from adipose tissue. But atheroma is not a wen, it is a cyst of the sebaceous gland, which is characterized by very rapid growth.
How to differentiate an epidermal cyst from a wen without a visit to a dermatologist? Press your finger on the bump and then trace: if the bump moves to the side, the skin growth is most likely a lipoma. The bulge remains under the finger, in place, and does not move out - atheroma.
Another difference is the consistency of the contents. To the touch, the contents of the lipoma are softer and more plastic. If you use your fingers to change the shape, you can assume that a wen has formed. When the form persists, it is most likely an epidermal cyst.
In addition, a small dark spot is usually visible in the center of the atheroma - the same dilated duct of the gland. Naturally, the final diagnosis is made by the doctor, who also selects the optimal method for removing the tumor.
Carrying out the operation
It is often performed under general anesthesia, but if it is small and located subcutaneously, local anesthesia may also be used.
As a rule, a skin incision is made and, if necessary, the cavity is opened, access is provided and complete excision is performed. If possible, laparoscopy is performed; if this is not possible, then open intervention is performed.
Surgical removal of the formation can be performed on part of an organ or the entire organ. We are, of course, talking about paired organs. Removal of the ovary is recommended for significant size pathological formations and for postmenopausal women. Removing one kidney with a cyst is only advisable if it is not possible to save the organ. The liver and pancreas can only be resected to the extent that the remaining part of the organ can cope with its function.
That is why, when pathology is localized in the liver, pancreas or other unpaired organs, it is recommended to eliminate them at the earliest stages, including in children, since an increase in the size of the formations can lead to damage to most of the organ and the impossibility of performing radical surgery.
Consequences of surgery for dermoid cysts
Surgery to eliminate dermoid cysts, if they are detected at an early stage of development, rarely ends in any complications. Basically, within a couple of days after the intervention, the patient can return to his normal rhythm of life.
Difficulties may arise if the removal of the dermoid formation is delayed too much. Possible problems include:
- increased risk of cyst recurrence;
- high risk of hormonal disruptions if the formation is localized on a hormone-producing organ;
- degeneration of cysts into malignant neoplasms.
Treatment of complications of dermoid cyst
Complications may require both medication and emergency surgical intervention. For example, during suppuration, the use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs is indicated, and removal of the dermoid formation is possible only after the inflammatory process has subsided.
In case of necrosis of the formation, its emergency elimination is indicated, since this can lead to serious complications in the form of suppuration, intoxication, sepsis and even death.
Increased or suspected malignancy is also an indication for removal. In this case, there is no need for emergency surgery, but it should be performed as soon as possible after full preparation (additional examination, anesthetic preparation).
Today, refusal from surgical intervention is considered advisable only in cases where the neoplasm is minimal in size, does not manifest itself in any way, and the likelihood of complications is extremely low. In all other cases, it is better to remove the formation at least in order to prevent the development of complications.
Epidermal cyst - causes
The mechanism of development of the pathological process in which an epidermal sebaceous cyst is the blockage of the duct of the sebaceous gland, while its secretion accumulates. Over time, the volume of accumulated sebum increases, and horny masses, which are exfoliated cells of the epidermis, are added. There are several reasons for the development of such education:
- A metabolic disorder that leads to a thicker consistency of sebum with blockage of the gland ducts.
- Inflammatory processes of the skin (including acne or acne, as well as inflammation of the hair follicles) lead to swelling, which reduces the diameter of the excretory ducts of the glands.
- Traumatization of the skin, followed by scarring, while the connective tissue compresses the ducts of the sebaceous glands.
- Insufficient hygiene leads to blockage of the sebaceous glands with horny skin scales.
- Excessive enthusiasm for various cosmetic products or their improper use.
- Hormonal imbalance, in which the regulation of the process of sebum formation, as well as its release to the surface, is disrupted.
- Genetic predisposition.
Simultaneous exposure to several causes significantly increases the risk of developing such a voluminous skin formation.